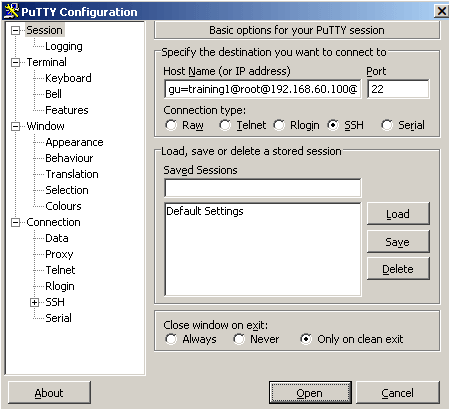
The following steps provide instructions for establishing SSH connections with servers that are listening on a non-standard port (the Inband destination selection > Targets > Port option is not 22), and the port number targeted by the clients is also a non-standard port (the To > Port option of the Connection Policy).
-
Enter the following command:
# ssh -p <scb_port> <username>@<server>:<port>@<scb>
...where <scb_port> is the port number of One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS), <username> is the username on the target server, <server:port> is the target server's hostname (or IP address), <port> is the target server's port number, and <scb> is the hostname (or IP address) of SPS.
If you do not specify the username or the address in nontransparent SSH and Telnet connections, One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) displays an interactive prompt where you can enter the username and the server address.
Example
Assuming the following values:
-
The username is training1
-
The target server is 192.168.60.100
-
The target server is listening on port 2121
-
The SPS server is scb
-
The SPS server is listening on port 4444
You can enter the following command:
# ssh -p 4444 training1@192.168.60.100:2121@scb
-
-
Alternative approach:
-
Enter only the hostname (or IP address, depending on your configuration) and port number of SPS with the following command:
# ssh -p <scb_port> <scb>
-
At the login prompt, provide the username on the target server, and the target server's hostname (or IP address) and port number using the <username>@<server>:<port> format.
-

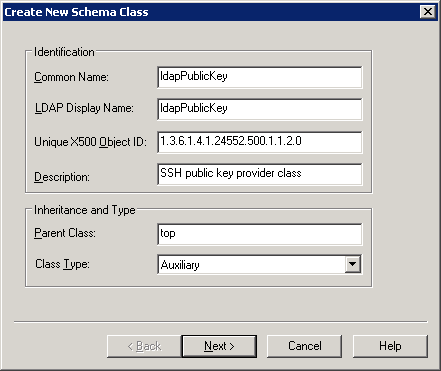
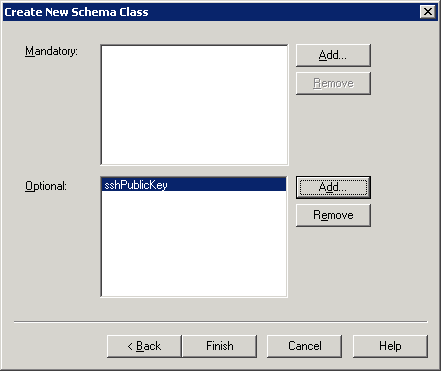
 to add a new user.
to add a new user.
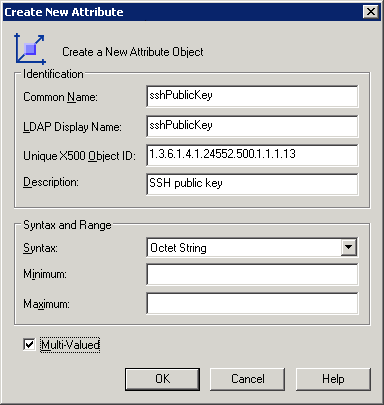
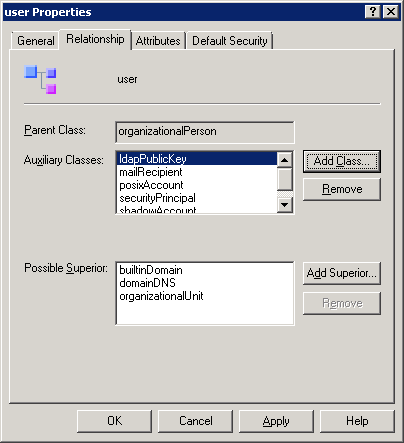
 to save the change.
to save the change.