Using departments to find approvers
Use the following procedure to determine the approver through a department given in the request.
Table 36: Approval procedures for determining approvers for a department
|
DP |
A department is entered in the request. The department is assigned a manager.
The manager of the given department is established as approver. |
|
DR |
A department is entered in the request. The department is assigned an application role in the Role approver menu.
All secondarily assigned identities of this application role are determined to be approvers.
Approvers are determined following the same method as described in Using approval roles to find approvers. |
|
DI |
A department is entered in the request. The department is assigned an application role in the Role approver (IT) menu.
All secondarily assigned identities of this application role are determined to be approvers.
Approvers are determined following the same method as described in Using approval roles to find approvers. |
Using requested roles to find approvers
If membership in or assignment to a hierarchical role is requested and the manager of the requested role is to be the approver, use the MS approval procedure. Then the manager and deputy of the requested department, cost center, business role or location are determined as the approvers. This approval procedure can only be used for assignment requests.
Waiting for further approval
NOTE: Only one approval step can be defined with the WC approval procedure per approval level.
Use the WC approval procedure within an approval process to ensure that a defined prerequisite is fulfilled before the request is approved. Therefore, the approval of a permissions group request should only take place if the corresponding user account exists. Deferred approval is useful when a request should be tested for rule conformity. If the user account does not exist when the requested permissions groups are tested, any rule violations that may occur due to the request will not be logged.
You can specify which prerequisites have to be fulfilled so that a request can be presented for approval by defining an appropriate condition. The condition is evaluated as a function call. The function must accept the request UID as a parameter (PersonWantsOrg.UID_PersonWantsOrg). It must define three return values as integer values. One of the following actions is carried out depending on the function’s return value.
Table 37: Return value for deferred approval
|
Return value > 0 |
The condition is fulfilled. Deferred approval has completed successfully. The next approval step (in case of success) is carried out. |
|
Return value = 0 |
The condition is not yet fulfilled. Approval is rolled back and is retested the next time DBQueue Processor runs. |
|
Return value < 0 |
The condition is not fulfilled. Deferred approval has failed. The next approval step (in case of failure) is carried out. |
To use an approval procedure
-
Create a database function which tests the condition for the request.
-
Create an approval step with the WC approval procedure. Enter the function call in Condition.
Syntax: dbo.<function name>
-
Specify an approval step in the case of success. Use an approval procedure with which One Identity Manager can determine the approvers.
-
Specify an approval step in the case of failure.
Example
To check whether the necessary user account exists when the permissions group is requested, you can use the TSB_FGIPWODecisionForGroup function that is supplied.
Table 38: Example of an approval step with deferred approval
|
Single step: |
Waiting Condition |
|
Approval procedures: |
WC - Waiting for further approval |
|
Condition: |
dbo.TSB_FGIPWODecisionForGroup |
|
Number of approvers: |
1 |
Table 39: Return value for deferred approval decisions in the TSB_FGIPWODecisionForGroup function
|
Return value > 0 |
The user account exists, thus fulfilling the condition. The delayed approval is decided positively. The request is passed onto the next approval step. Now an approval step must follow which can establish the approvers for the request. |
|
Return value = 0 |
The condition is not fulfilled. There is a request pending for a user account or the identity has an account definition with which a user account could be created. Approval is, therefore, deferred, and tested again on the next DBQueue Processor run. |
|
Return value < 0 |
The condition is not fulfilled. There is no request for a user account and the identity does not have an account definition with which a user account could be created. The delayed approval is decided negatively. The request is passed onto the next approval step. |
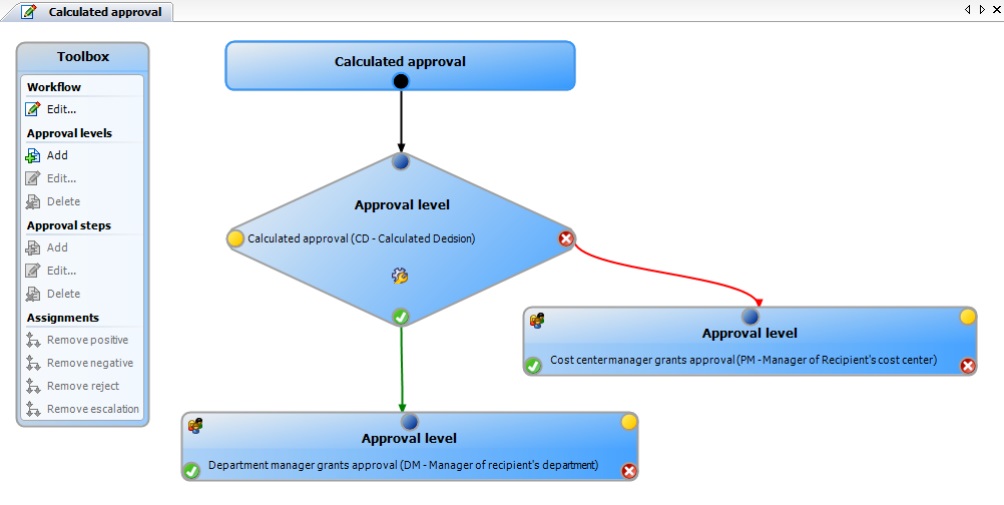
Calculated approval
NOTE: Only one approval step can be defined with the CD approval procedure per approval level.
It is possible to determine who should be presented with the request for approval on the basis of a defined condition. For example, if the price of the request is below a defined limit, then the department manager can grant approval. If this limit is exceeded, the request has to be presented to the cost center manager. In another case, requests from members of department XY can be granted immediate approval as long as the request does not exceed the defined price limit. If the limit is exceeded or if the employee belongs to another department, the approval has to be granted by the department manager.
To calculate an approval (CD approval procedure), enter a condition when you set up the approval step. If the condition returns a result, the approval step is approved through One Identity Manager. If the condition does not return a result, the approval step is denied by One Identity Manager. If there are no subsequent steps to be carried out, the request is finally granted or denied approval. The condition is defined as a valid where clause for database queries. You can enter the SQL query directly or with a wizard. The condition is always checked for the current request and requester.
Example for calculated approval
Requests with a price of under 1000 euros can be approved by the customer’s department manager. Requests over 1000 euros must be presented to the cost center manager.
Table 40: Approval step with calculated approval
|
Single step: |
Calculated approval |
|
Approval procedures: |
CD - Calculated approval |
|
Condition: |
EXISTS ( |
SELECT 1 FROM ( |
SELECT UID_ITShopOrg FROM ITShopOrg WHERE EXISTS ( |
SELECT 1 FROM ( |
SELECT UID_AccProduct FROM AccProduct |
WHERE round(PurchasePrice, 13) < round(1.000000E+003, 13) |
) as X |
WHERE X.UID_AccProduct = ITShopOrg.UID_AccProduct |
) ) as X |
WHERE X.UID_ITShopOrg = PersonWantsOrg.UID_Org) | |
|
Number of approvers: |
1 |
Figure 7: Approval workflow showing calculated approval