Overriding Unix account information
You can override user account attributes on the local Unix host. This allows you to use the identity information from Active Directory but modify individual attributes on certain hosts as needed. User overrides are specified in the /etc/opt/quest/vas/user-override configuration file. Overrides are specified as follows:
DOMAIN\sAMAccountName:<Login Name>:<UID Number>:<Primary GID Number>:<Comment (GECOS)>:<Home Directory>:<Login Shell>
DOMAIN\sAMAccountName must refer to a valid Active Directory user account. You can omit any of the Unix account fields. If a field is not specified it will get the default value for that user. You can override every member of a group using the following syntax:
DOMAIN\sAMAccountName:::::<Home Directory>:<Login Shell>
DOMAIN\sAMAccountName must refer to a valid Active Directory group account. You can only specify the Home Directory and Login Shell attributes because all of the other attributes are user-specific. You can insert a special %s macro anywhere in the override entry to specify the user name. For example, refer to the /etc/opt/quest/vas/user-override.sample file. See also the Overriding Unix Account Information section in the vasd man page. See to Using manual pages (man pages) for information about accessing the vasd man page.
You can manage user overrides using Group Policy. For more information, see Account Override policies..
Managing Unix group accounts
You can Unix-enable Active Directory groups. A Unix-enabled group has a Group Name and a GID Number. These attributes cause an Active Directory group to appear as a standard Unix group. The group membership on Unix is the same as the Windows group membership, but any users that are not Unix-enabled are excluded from the group membership on the Unix host.
Nested group support
Safeguard Authentication Services supports the Active Directory nested group concept, where groups can be added as members of other groups such that users in the child group are members of the parent group as well.
Nested group information is provided in the Kerberos ticket. This information is cached when the user logs in. Any time a user performs a non-Kerberos login (such as when using SSH keys), nested group information is not available. In these situations, you can ensure that group memberships include nested groups by enabling the groups-for-user-update option in vas.conf.
See vas.conf man page for more details. This will produce more LDAP traffic, but group memberships will remain up-to-date. Unless this option is enabled, nested group memberships are only updated when a user logs in.
Managing Unix groups with MMC
You can access Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) from the Control Center. Navigate to the Tools | Safeguard Authentication Services Extensions for Active Directory Users and Computers.
After installing Safeguard Authentication Services on Windows, a Unix Account tab appears in the Active Directory group's Properties dialog.
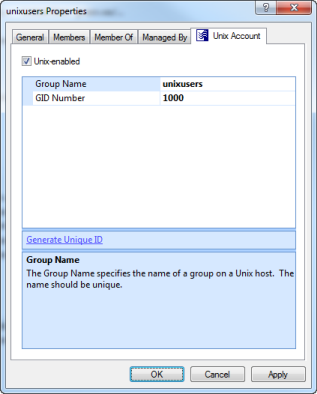
Note: If the Unix Account tab does not appear in the Group Properties dialog, review the installation steps outlined in the Safeguard Authentication Services Installation Guide to ensure that Safeguard Authentication Services was installed correctly or refer to the Unix Account tab is missing in ADUC for more information.
The Unix Account tab contains the following information:
- Unix-enabled: Check this box to Unix-enable the group. Unix-enabled groups appear as standard Unix groups on Unix hosts. Checking this box causes Safeguard Authentication Services to generate a default value for the GID number attribute. You can alter the way default values are generated from the Control Center.
- Group Name: This is the Unix name of the Windows group.
- GID Number: Use this field to set the numeric Unix Group ID (GID). This value identifies the group on the Unix host. This value must be unique in the forest.
- Generate Unique ID: Click this link to generate a unique GID Number. If the GID Number is already unique, the GID Number is not modified.

