You can use a formatting script to verify column values. Formatting scripts, as opposed to value templates, are only run when a value is assigned to the column.
To create a formatting script
-
In the Designer, select the One Identity Manager Schema category.
-
Select the table and start the Schema Editor with the Show table definition task.
-
Select the column and then the Column properties view.
-
Select the Value calculation tab and enter the formatting script for the column in the Formatting script input field.
Write the script in VB.Net syntax which allows all VB.Net script functions to be used.
-
Select the Database > Save to database and click Save.
IMPORTANT: Compile the database to bring the formatting script into effect.
TIP: Test compile using the Schema > Test compile menu item.
Example: Formatting scripts for email addresses
The value in the column Mail in the ADSAccount table should correspond to SMPT format. If this is not the case, an error message is sent. The formatting script for the ADSAccount.Mail column can be formulated as follows:
Dim str as String = Convert.ToString(Value)
If str.Length > 0 Then
If Not VID_IsSMTPAddress(str) Then
Throw New Exception("""" & str & """ is not a valid SMTP address.")
End If
End If
There may be dependencies between individual values, for example, by using value templates or customizers that require values to be placed in a specific sequence. In the case of One Identity Manager tools the correct placement sequence is enforced through blocking or releasing input fields. The correct place sequence must be ensured when importing data.
The following data sources are used in the given order to determine the placement sequence:
-
Customizer
The dependencies between columns and an object are stored in customizers.
-
Custom defined dependencies
To define custom dependencies between columns
-
In the Schema Editor, select a table column.
-
In the Column properties view on the Dependencies tab, define the predecessor of this column.
-
Column dependencies due to value templates
In this case, values resolved by a template (for example, Person.Firstname, Person.Lastname) are placed before values that are created by a template (for example, Person.CentralAccount).
If circular dependencies occur whilst determining the placement sequence, they are stopped at the point of lowest priority.
To only allow a specific value in a column, you can define a list with the permitted values. This list of permitted value is resolved once the column's display value has been formatted. For some columns of the One Identity Manager schema, already permitted values are supplied when the schema is installed.
NOTE: You can only enter or extend a list of permitted values for a column if the option Customizing permitted values list is not allowed is not set.
To create a list of permitted values
-
In the Designer, select the One Identity Manager Schema category.
-
Select the table and start the Schema Editor with the Show table definition task.
-
Select the column and then the Column properties view.
-
Select the Value settings tab and enable the Defined list of values option.
-
Click  and enter the following properties.
and enter the following properties.
-
Value: Value for the value list (technical name).
-
Display value: Name used to display the value. Translate the given text using the ... button.
-
Sort: Sort order of displaying the values in the list.
-
Select the Database > Save to database and click Save.
IMPORTANT: Compile the database to bring the list of permitted values into effect.
Example: Define permitted values
In the Spare field no. 01 input field for an identity, the values internal and external should be permitted. The list of permitted values is defined as followed:
1=internal 2=external
For an identity with the value 1, the display value internal is shown on the forms in the Manager.
Display columns with permitted values in the Manager
A special control element is used in the Manager to display columns for which a list of permitted values has been defined. The control element is displayed as a simple input field if no list is defined. If a list is defined the control element is shown as a drop-down.
Figure 10: Input field for list of defined values (with and without defined entries)
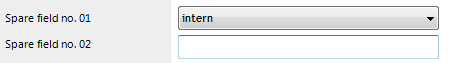
The control element is only available for columns on default predefined forms as well as custom columns (usually CustomProperty01-CustomProperty10).
Values in multi-values property (MVP) columns are delimited by char(7) or chr(7). Specify other requirements for each value of the MVP column.
To specify requirements for a MVP column
-
In the Designer, select One Identity Manager Schema.
-
Select the table and start the Schema Editor with the Show table definition task.
-
Select the column and then the Column properties view.
-
Select the Value settings tab and set the Multi-value column option.
-
In the Multi-value specification menu, configure the following settings.
-
Unique: Set this option if the value must be unique.
-
Case sensitive: Set this option if the case sensitivity should be taken into account when the value is tested.
-
Accent insensitive: Set this option if accent characters should not be taken into account when the value is tested.
-
Select the Database > Save to database and click Save.

 and enter the following properties.
and enter the following properties. . To delete a value, select the value and click
. To delete a value, select the value and click  . To delete all values, click
. To delete all values, click  .
.