Using Active Directory user groups
Using Active Directory user groups (Privilege Elevation Rules only)
Use the Groups tab to add or remove an Active Directory user group from the security token of the target process. Removing a group decreases the privileges with which the process will run.
To add or remove an Active Directory user group using the Groups tab in the Create Rule Wizard:
- If the Administrators group (stored within the BUILTIN\Administrators Active Directory OU) does not appear on the list by default, click the
button to add it.
- Select this group of users, who have complete and unrestricted access to a local computer, instead of domain administrators.
- The
button will not be active if the group is already on the list.
- Use the
button to add or remove other groups. When the window opens:
- Use the Browse button to specify the group name.
- Select add or remove.
- To delete or modify a record within the Security Group list, select it and use the
or
button.
- You can only add security groups in Active Directory which have a group scope property of Built-in local to the security token of a process on a client computer if the client also has the same security identifier definition (SID) in its built-in security groups.
When removing a group from the security token, ensure that the user account under which the process is launched is a member of more than one primary group. Otherwise, the rule will not apply as intended.
Using validation logic
Available only in Privilege Manager Professional and Professional Evaluation editions.
By default, a rule will apply to all client computers to which the previously selected GPO is linked. For more granular targeting, you can use the Standard Rules and Validation Logic Rules sub-tabs of the Validation Logic tab in the Create Rule Wizard to target the rule based on the client’s operating system, their IP address, and/or a logged-in user.
Using standard rules
Within the Standard Rules sub-tab in the Create Rule Wizard, you can set a rule to apply only to clients with specified operating systems, servers, or workstations. By default, all operating systems are selected. If no options are selected, then the rule will apply to all supported operating systems.
To use the Standard Rules sub-tab in the Create Rule Wizard:
- Check the Server checkbox in the Class section to apply the rule to Windows Server 2008/2008 R2/2012/2012 R2.
- Check the Workstation checkbox in the Class section to apply the rule to Windows 7/8.1/10.
- In the Operating System section, check the checkboxes for your operating systems.
Using validation logic rules
The Validation Logic Rules sub-tab in the Create Rule Wizard allows you to set additional parameters to target the rule. You can define whether the rule will run on computers with a prefix in the name, a group or IP address range, or a user currently logged in. For example, you can target the rule to computers belonging to OUs that end with DEPARTMENT and are in subnet 192.168.0.X, except for the IP address 192.168.0.1.
|
|
Note: Client Deployment Settings can only be targeted to specific computers and not to user accounts or groups. |
Setting rule parameters
To set rule parameters using the Validation Logic Rules sub-tab in the Create Rule Wizard:
- Click Add to open the Add Validation Logic Rule window.
- Select the type of rule:
| Type of Rule | Action | ||
|---|---|---|---|

Computer Group |
Set a rule for one or several names, or partial names, of your Active Directory computer groups. Enter the NetBIOS name, for example: DERPA\DOMAIN CONTROLLERS | ||
|
User Group |
Set a rule for one or several names, or partial names, of your Active Directory user groups. The group membership value you enter will be compared against the groups that the user belongs to during the logon process and must match for the configuration to be processed. Enter the NetBIOS name, for example: DERPA\ADMINISTRATORS | ||

User Name |
Set a rule if specific users are logged into client computers. Enter the NetBIOS name, for example: DERPA\HELPDESK | ||

OU (Computer) |
Set a rule for names, or partial names, of computer-based OUs or the Computers container in your Active Directory. The OU value you enter will be compared against the OU the client computer belongs to during the logon process and must match for the configuration to be processed. Enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN), for example: DERPA.DERPADEV.LOCAL\DOMAIN CONTROLLERS
| ||

OU (User) |
Set a rule for names, or partial names, of the user-based OUs or the Users container in your Active Directory. The OU value you enter will be compared against the OU the user belongs to during the logon process and must match for the configuration to be processed. Enter the FQDN, for example: DERPA.DERPADEV.LOCAL\USER ACCOUNTS
| ||

Computer Name |
Set a rule for computers with names or partial names. Enter the FQDN, for example: DERPA.DERPADEV.LOCAL\PASERVER | ||

IP Address Range (v4/v6) |
Set a rule for IP addresses or ranges of computers. | ||

Registry Key Exists |
Set a rule based on the registry keys on client computers. | ||
|
File Exists |
Set a rule for files on the client computer or on the network. Specify a file that must exist on the client computer or on the network in order for the rule to run, for example: \\ComputerName\SharedFolder\Filename.exe DriveLetter:\Filename.exe
| ||

Date and Time Range |
Define when a rule should start and/or stop being enforced.
|
- Specify the rule's parameters in the dialog window that will display on the right:
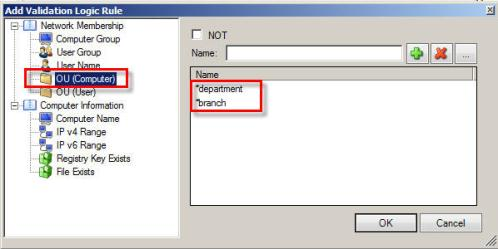
- Use the common asterisk (*) and question mark (?) wildcards in the validation value, as necessary.
- * : Stands for no or any number of any characters
- ? : Stands for a single character
- Check the NOT checkbox to exclude the items specified from the rule.
- For
Computer Group,
User Group,
User Name,
OU (Computer),
OU (User), and
Computer Name:
- Use the Name field to specify the rule's value manually (see example values in the table above), and then click the
button. Or,
- Use the
Browse button to select the items available on your network. You can filter the items by the first letters. Wildcards are not supported in the Filter field.
- The desired value will be added to the list. You may add as many rule values as necessary.
- Use the Name field to specify the rule's value manually (see example values in the table above), and then click the
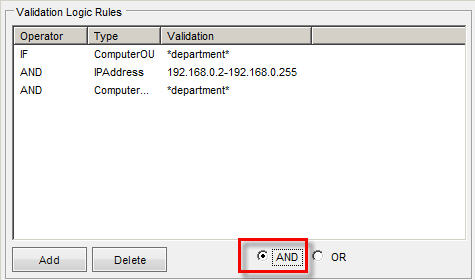
- Click OK when you are finished specifying the settings within the rule type. The record will display in the main Validation Logic Rules list.
- To add another validation logic rule, repeat the steps above.
- Add or combine validation logic rules with AND or OR Boolean logic. By default, rules will combine with OR Boolean logic. To make the rule use the AND operator, select AND at the bottom of the Validation Logic Rules window.
- To edit a rule setting:
- Within the Validation Logic Rules list, double-click a rule value or click the Edit button.
- Make changes in the dialog.
-
When finished specifying validation logic rules, click Next. If the Display Advanced Options checkbox has not been selected, complete the rule creation process.
Granting/denying privileges
Granting/denying privileges (Privilege Elevation Rules only)
On the Privileges tab in the Create Rule Wizard you can grant or deny privileges for a process, based on the standard Windows policies in the User Rights Assignment list (Local Security Settings\Local Policies).
To apply/deny privileges for processes (including child processes) using the Privileges tab in the Create Rule Wizard:
- Select the privilege and click Grant or Deny. To select multiple privileges, hold down the CTRL (or SHIFT) key while selecting the items.
- To discard your choices, select the privilege and click Not Set.
Differentiating security levels
Differentiating security levels (Privilege Elevation Rules only)
You can differentiate the security levels with which a process will run using the Integrity tab in the Create Rule Wizard. The integrity level is a feature of Windows operating systems beginning with Windows 7.
This parameter can be applied to clients running Windows Server 2008, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2012, and Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows 10.
By default, this setting will not apply and is set to the High integrity level.