Connection statistics
Figure 290: Basic Settings > Dashboard > Connection statistics
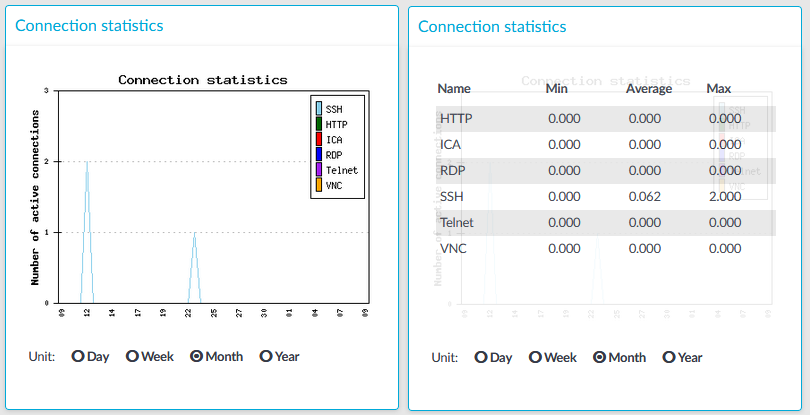
The Connection statistics module on the Dashboard is based on statistics of high-level proxy-service protocols (SSH, RDP, VNC, ICA, and so on). These numbers display all active high-level proxy-service protocols, but these numbers are counted by all service connections too, which are connected to some protocols. Because of this, these numbers can differ from the numbers displayed on the Active Connections page.
For example, if there are several active ICA connections in your system, it means that there are approximately the same number of CGP connections that are opened and counted in the Connection statistics module under the ICA label. If these CGP or ICA high-level proxy-service protocols are opening more than one TCP connections, these connections will be counted in the Network connetion module as different TCP connections, but these will count as only one connection on the Active Connections page.
Statistics
The connection types displayed can be the following:
-
RDP: The number of RDP connections.
-
SSH:The number of SSH connections.
-
HTTP: The number of HTTP connections.
-
ICA: The number of Citrix connections.
-
Telnet: The number of Telnet connections.
-
VNC: The number of VNC connections.
The Min, Average and Max values are displayed as a whole number if the value is constant for the statistics interval (the statistics are stored every 5 minutes). If minor changes occur in the actual values (for example, new connections are established), these changes can be displayed as fractions.
Memory
Figure 291: Basic Settings > Dashboard > Memory
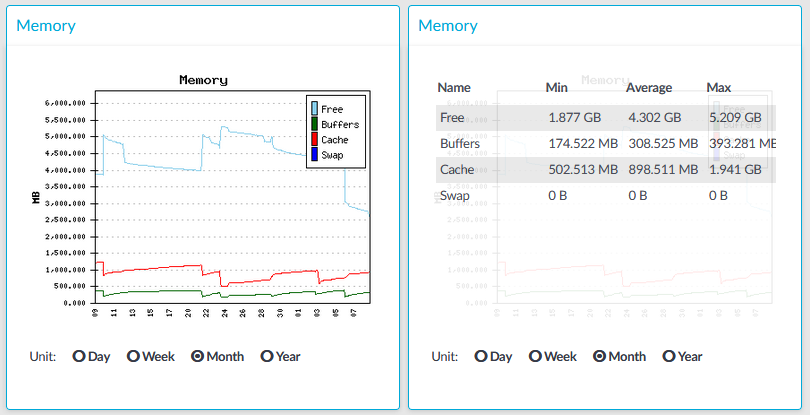
The Memory module on the Dashboard is based on data provided by the Linux kernel (/proc and /sys directories). The standard Munin plugins query this information from these locations and they are displayed on the GUI.
Statistics
The memory types displayed are the following:
-
Free: Free memory
-
Buffers: In-memory block I/O buffers.
-
Cache: Memory used for disk caching. This does not count as "used" memory, because it is freed when it is required.
-
Swap: Swap space usage (memory contents that have been temporarily moved to disk).This value might be high in case of lack of memory.
Disk
Figure 292: Basic Settings > Dashboard > Disk
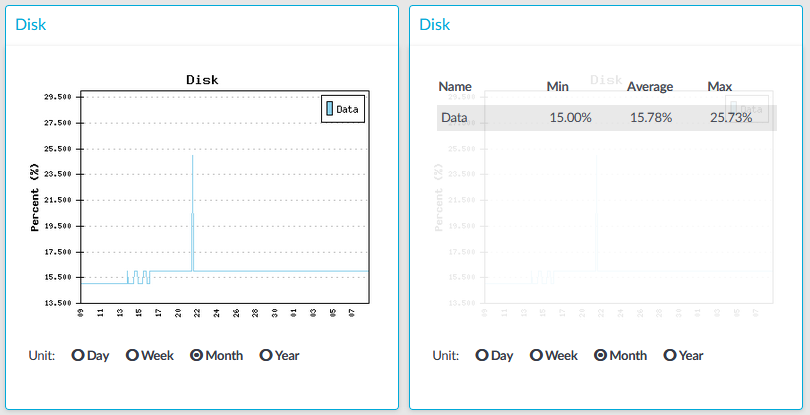
The Disk module on the Dashboard is based on the output of the df command.
Statistics
The information displayed is the following:
-
Data: The percent of disk that the core firmware uses.
CPU
Figure 293: Basic Settings > Dashboard > CPU
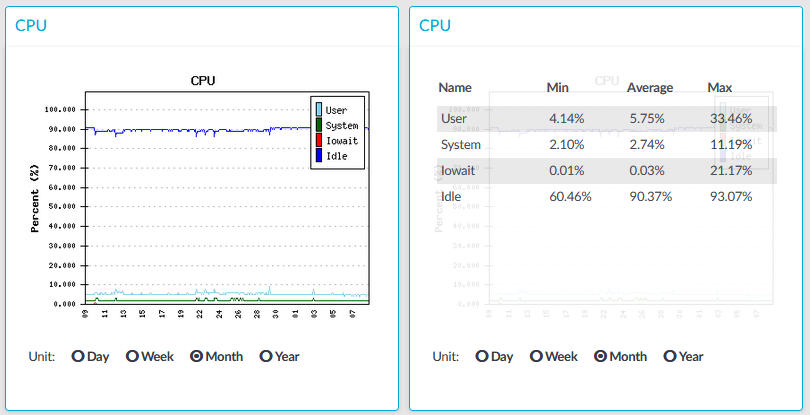
The CPU module on the Dashboard is based on data provided by the Linux kernel (/proc and /sys directories). The standard Munin plugins query this information from these locations and they are displayed on the GUI.
Statistics
The following details are displayed about CPU usage:
-
Idle: Idle time of the processors. If there are more than one processors, they all add up to x100%, for example in case of 2 processors it adds up to 200% maximum.
-
Iowait: Time spent receiving and handling hardware interrupts as a percentage of processor ticks. That is, waiting for IO.
-
System: Kernel CPU usage.
-
User: CPU usage of everything other than kernel.
