Using disk-based and memory buffering
The syslog-ng Open Source Edition application can store messages on the local hard disk if the destination (for example, the central log server) or the network connection to the destination becomes unavailable. The syslog-ng OSE application automatically sends the stored messages to the destination when the connection is reestablished. The disk buffer is used as a queue: when the connection to the destination is reestablished, syslog-ng OSE sends the messages to the destination in the order they were received.
|
|
NOTE:
Disk-based buffering can be used in conjunction with flow-control. For details on flow-control, see Managing incoming and outgoing messages with flow-control. |
Every such destination uses a separate disk buffer (similarly to the output buffers controlled by log-fifo-size()). The hard disk space is not pre-allocated, so ensure that there is always enough free space to store the disk buffers even when the disk buffers are full.
If syslog-ng OSE is restarted (using the /etc/init.d/syslog-ng restart command, or another appropriate command on your platform), it automatically saves any unsent messages from the disk buffer and the output queue. After the restart, syslog-ng OSE sends the saved messages to the destination. In other words, the disk buffer is persistent. The disk buffer is also resistant to syslog-ng OSE crashes.
The syslog-ng OSE application supports two types of disk buffering: reliable and normal. For details, see Enabling reliable disk-based buffering and Enabling normal disk-based buffering, respectively.
Message handling and normal disk-based buffering
When you use disk-based buffering, and the reliable() option is set to no, syslog-ng OSE handles outgoing messages the following way:
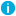
Figure 2: Handling outgoing messages in syslog-ng OSE
-
Output queue: Messages from the output queue are sent to the destination (for example, your central log server). The syslog-ng OSE application puts the outgoing messages directly into the output queue, unless the output queue is full. By default, the output queue can hold 64 messages (you can adjust it using the quot-size() option).
-
Disk buffer: If the output queue is full, disk-buffering is enabled, and reliable() is set to no, syslog-ng OSE puts the outgoing messages into the disk buffer of the destination. (The disk buffer is enabled if the disk-buffer() option is configured.)
-
Overflow queue: If the output queue is full and the disk buffer is disabled or full, syslog-ng OSE puts the outgoing messages into the overflow queue of the destination. (The overflow queue is identical to the output buffer used by other destinations.) The log-fifo-size() parameter specifies the number of messages stored in the overflow queue. For details on sizing the log-fifo-size() parameter, see also Managing incoming and outgoing messages with flow-control.
|
|
NOTE:
Using disk buffer can significantly decrease performance. |
Message handling and reliable disk-based buffering
When you use disk-based buffering, and the reliable() option is set to yes, syslog-ng OSE handles outgoing messages the following way.
The mem-buf-size() option determines when flow-control is triggered. All messages arriving to the log path that includes the destination using the disk-buffer are written into the disk-buffer, until the size of the disk-buffer reaches (disk-buf-size() minus mem-buf-size()). Above that size, messages are written into both the disk-buffer and the memory-buffer, indicating that flow-control needs to slow down the message source. These messages are not taken out from the control window (governed by log-iw-size()), causing the control window to fill up. If the control window is full, the flow-control completely stops reading incoming messages from the source. (As a result, mem-buf-size() must be at least as large as log-iw-size().)