Secure logging using TLS
The syslog-ng application can send and receive log messages securely over the network using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol using the network() and syslog() drivers.
|
|
NOTE:
This chapter describes how to use TLS encryption when using the standard syslog protocols, that is, the network() and syslog() drivers, for example, to forward log messages between two syslog-ng nodes, or to send log data to syslog-ng Store Box or another log server. Other destinations that support TLS-encryption are not discussed in this chapter (for example, http()). |
TLS uses certificates to authenticate and encrypt the communication, as illustrated on the following figure:
Figure 7: Certificate-based authentication
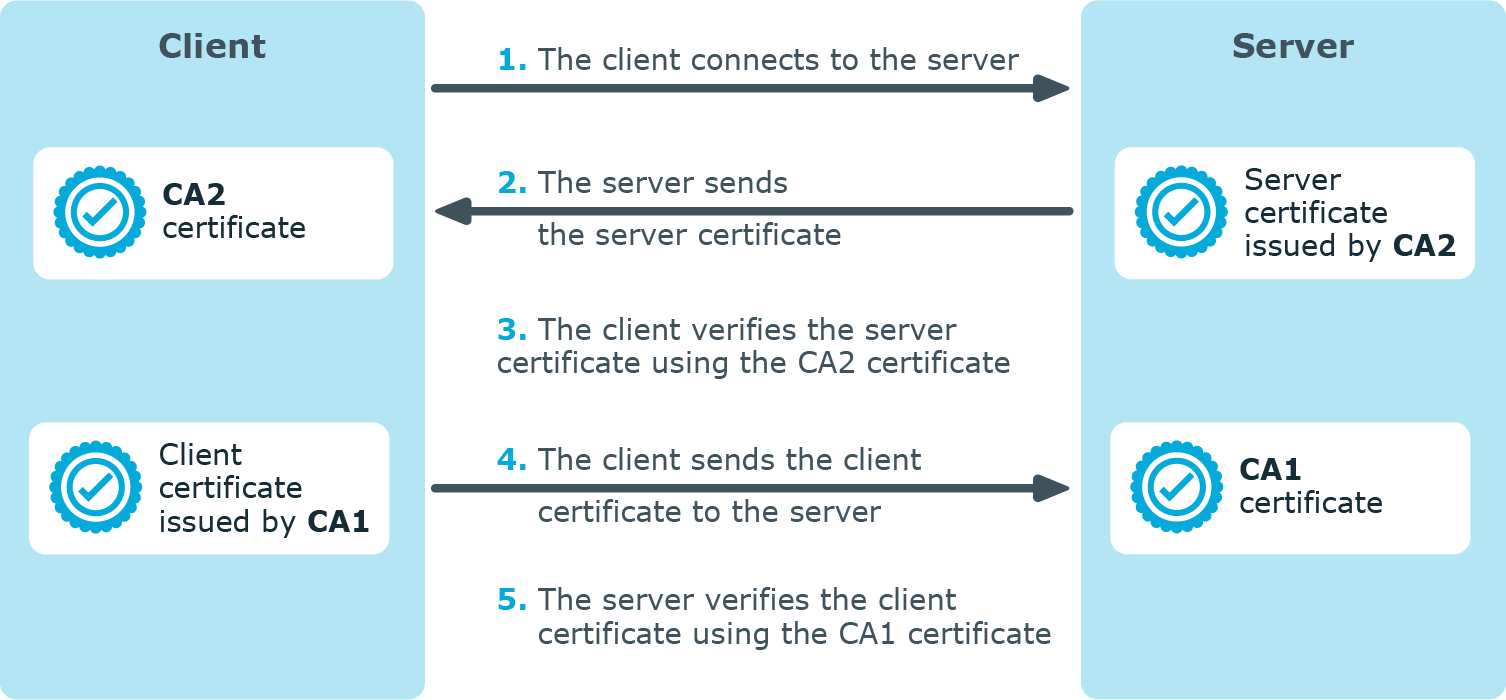
The client authenticates the server by requesting its certificate and public key. Optionally, the server can also request a certificate from the client, thus mutual authentication is also possible.
In order to use TLS encryption in syslog-ng, the following elements are required:
-
A certificate on the syslog-ng server that identifies the syslog-ng server.
-
The certificate of the Certificate Authority that issued the certificate of the syslog-ng server (or the self-signed certificate of the syslog-ng server) must be available on the syslog-ng client.
When using mutual authentication to verify the identity of the clients, the following elements are required:
-
A certificate must be available on the syslog-ng client. This certificate identifies the syslog-ng client.
-
The certificate of the Certificate Authority that issued the certificate of the syslog-ng client must be available on the syslog-ng server.
Mutual authentication ensures that the syslog-ng server accepts log messages only from authorized clients.
For more information about configuring TLS communication in syslog-ng, see Encrypting log messages with TLS.
For more information about TLS-related error messages, see Error messages.