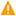
How syslog-ng OSE connects the MongoDB server
When syslog-ng OSE connects the MongoDB server during startup, it completes the following steps.
-
The syslog-ng OSE application connects the first address listed in the servers() option.
-
-
If the server is accessible and it is a master MongoDB server, syslog-ng OSE authenticates on the server (if needed), then starts sending the log messages to the server.
-
If the server is not accessible, or it is not a master server in a MongoDB replicaset and it does not send the address of the master server, syslog-ng OSE connects the next address listed in the servers() option.
-
If the server is not a master server in a MongoDB replicaset, but it sends the address of the master server, syslog-ng OSE connects the received address.
-
-
When syslog-ng OSE connects the master MongoDB server, it retrieves the list of replicas (from the replSet option of the server), and appends this list to the servers() option.
Caution: -
This means that syslog-ng OSE can send log messages to addresses that are not listed in its configuration.
-
Make sure to include the address of your master server in your syslog-ng OSE configuration file, otherwise you risk losing log messages if all the addresses listed in the syslog-ng OSE configuration are offline.
-
Addresses retrieved from the MongoDB servers are not stored, and can be lost when syslog-ng OSE is restarted. The retrieved addresses are not lost if the server() option of the destination was not changed in the configuration file since the last restart.
-
The failover mechanism used in the mongodb() driver is different from the client-side failover used in other drivers.
-
-
The syslog-ng OSE application attempts to connect another server if the servers() list contains at least two addresses, and one of the following events happens:
-
The safe-mode() option is set to no, and the MongoDB server becomes unreachable.
-
The safe-mode() option is set to yes, and syslog-ng OSE cannot insert a log message into the database because of an error.
In such case, syslog-ng OSE starts to connect the addresses in from the servers() list (starting from the first address) to find the new master server, authenticates on the new server (if needed), then continues to send the log messages to the new master server.
During this failover step, one message can be lost if the safe-mode() option is disabled.
-
-
If the original master becomes accessible again, syslog-ng OSE will automatically connect to the original master.