tls-security-settings
To configure TLS security settings on both the Client side and the Server side, proceed to TLS security settings.
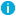
Figure 326: <Protocol> Control > Settings > TLS security settings - configuring TLS security settings
-
Cipher strength specifies the cipher string OpenSSL will use. The following settings options are possible:
-
Recommended: this setting only uses ciphers with adequate security level.
-
Custom: this setting allows you to specify the list of ciphers you want to permit SPS to use in the connection. This setting is only recommended in order to ensure compatibility with older systems. For more details on customizing this list, check the 'openssl-ciphers' manual page on your SPS appliance.
For example: ALL:!aNULL:@STRENGTH
-
-
Minimum TLS version specifies the minimal TLS version SPS will offer during negotiation. The following settings options are possible:
-
TLS 1.2: this setting will only offer TLS version 1.2 during negotiation. This is the recommended setting.
-
TLS 1.1: this setting will offer TLS version 1.1 and later versions during negotiation.
-
TLS 1.0: this setting will offer TLS version 1.0 and later versions during negotiation.
-
|
|
NOTE:
Note that SPS only permits TLS-encrypted connections. SSLv3 is not supported. |