Creating a new content policy
The following describes how to create a new content policy that performs an action if a predefined content appears in a connection.
|
|
NOTE:
Using content policies significantly slows down connections (approximately 5 times slower), and can also cause performance problems when using the indexer service. |
Figure 145: Policies > Content Policies — Content policies
To create a new content policy that performs an action if a predefined content appears in a connection
-
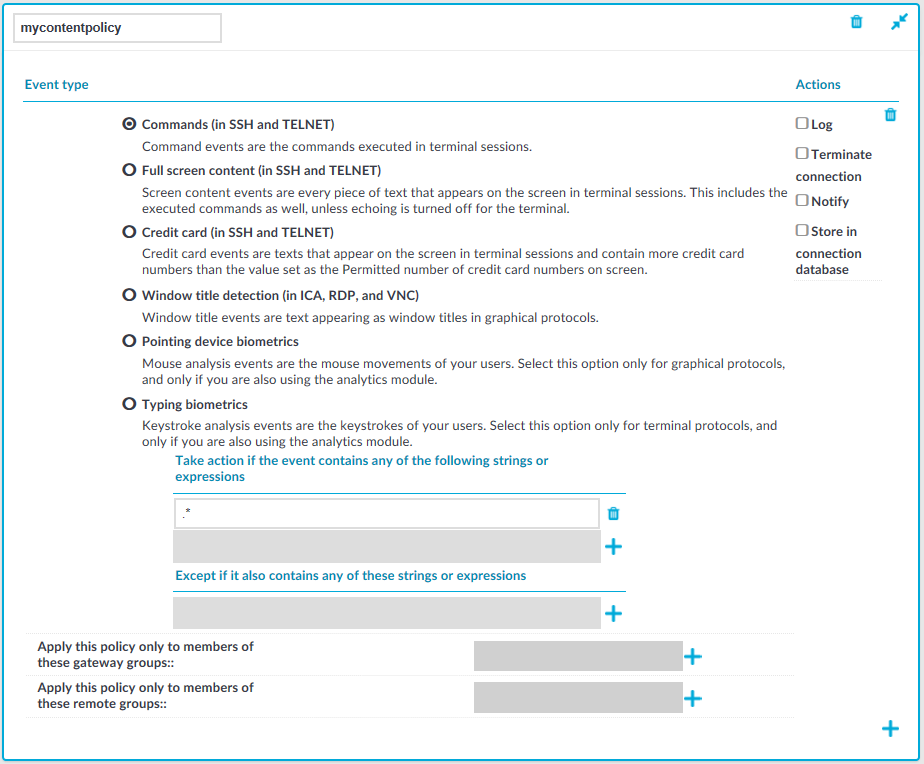
Navigate to Policies > Content Policies, click
and enter a name for the policy.
-
Select the type of event that you want to monitor:
-
Commands: The commands executed in the session-shell channel of SSH connections, or in Telnet connections.
Caution: During indexing, if a separate certificate is used to encrypt the upstream traffic, command detection works only if the upstream key is accessible on the machine running the indexer.
NOTE: Command detection is case-insensitive.
-
Screen content: Every text that appears on the screen. For example, every text that is displayed in the terminal of SSH or Telnet connections. This includes the executed commands as well, unless echoing is turned off for the terminal.
-
Credit card: Process every text that appears on the screen and attempt to detect credit card numbers in SSH or Telnet connections. One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) performs an action if the number of detected credit card numbers exceeds the value set as Permitted number of credit card numbers.
Credit card number detection is based on the Luhn algorithm and lists of known credit card number prefixes.
-
Window title detection: Text appearing as window titles in case of RDP, Citrix ICA, and VNC connections. Note the following points.
Supported themes
-
Windows Classic at 96 and 120 DPI
-
Windows 2012 at 96 and 120 DPI (metro)
-
Windows 7 Normal at 96 and 120 DPI (not aero)
-
Windows 8 at 96 and 120 DPI (metro)
Limitations
-
Windows 10, Windows 2016 Server, and Windows 2019 Server themes are not supported
-
Windows Aero themes are not supported.
-
Windows that do not have an X (close window) button in the top-right corner (or it is not visible) are not detected.
-
Use window title detection for sessions that use a single monitor. The feature works in multi-monitor environments as well, but becomes very slow, therefore it is not recommended.
The configuration JSON file contains the most common window title color schemes.
NOTE: Window title detection is case-insensitive.
NOTE: Do not adjust or modify the following settings unless you know exactly what you are doing. Misconfiguring them will severely decrease the performance of SPS.
-
If a special color is used, open /opt/scb/etc/window-title-default on the server, and add the color scheme in RGB. In case of a single color, enter "to": null. After adding a new color, temporarily disable all traffic going through SPS. Navigate to Basic Settings > System > Traffic control and click Stop in the All services field. Login to SPS as root locally (or remotely using SSH) to access the Console menu. Select Shells > Core Shell, and issue the systemctl restart zorp-core.service command.
-
The minimum and maximum height and the minimum width of the window title are determined in pixels, as "minheight", "maxheight" and "minwidth".
-
-
Pointing device biometrics: Select this option only for graphical protocols, and only if you are also using One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Analytics (SPA). SPA can analyze mouse movement patterns of your users as a biometric identity verification method to protect against account theft. For details, see the One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Analytics website.
-
Typing biometrics: Select this option only for terminal-based protocols, and only if you are also using One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Analytics (SPA). SPA can analyze the typing patterns of your users as a biometric identity verification method to protect against account theft. For details, see the One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Analytics website.
-
-
Select Take action if the event contains any of the following strings or expressions, click
and enter a string or regular expression. SPS will perform an action if this expression is found in the connection, unless it is listed in the Except if it also contains any of these strings or expressions list. For example, SPS can terminate the connection if the user issues the rm -rf * in an SSH connection. Repeat this step to add further expressions if needed.
-
Use Perl Compatible Regular Expressions (PCRE).
-
The following characters must be escaped using a backslash character: '(single-quote). For example, instead of .*' use .*\'
-
SPS uses substring search to find the expression in the content. That is, SPS finds the expression even if there is more content before or after the matching part. For example, the conf pattern will match the following texts: conf, configure, reconfigure, arcconf, and so on.
-
Using complicated regular expressions or using many regular expressions will affect the performance of SPS.
-
If the multiple expressions are set, SPS processes them one after the other, and stops processing the content if the first match is found, even if other expressions would also match the content. Therefore, when using multiple expressions, start with the most specific one, and add general expressions afterward.
Example: Sample regular expressions for content policies
The following simple regular expressions are samples to demonstrate what kinds of events that can be detected using content policies.
-
The enable command on Cisco devices: the user enters privileges mode.
-
The conf term command on Cisco devices: the user configures the networking parameters of the device.
-
The sudo and su - commands: the user enters privileged mode Linux and other UNIX platforms.
-
-
To add an exception to the Take action if the event contains any of the following strings or expressions rule, select Except if it also contains any of these strings or expressions, click
and enter a string or regular expression. SPS will not perform any action if this expression is found in the connection. For example, to permit the users to delete only the /tmp directory in an SSH connection, enter rm -rf /tmp. Repeat this step to add further expressions if needed.
Example: Sample content policies using Ignore rules
The following expressions can be used to perform an action if any SQL command is used in MySQL, except for the select and help commands:
-
Into the Take action if the event contains any of the following strings or expressions expression, enter mysql>.*
-
Add two Except if it also contains any of these strings or Except if it also contains any of these strings or Except if it also contains any of these strings or expressions expressions: mysql> select.* and mysql> help.*
-
-
Select the action to perform.
-
Log: Send a log message into the system logs. The log message includes the expression that matched the content. On log level 6, the message includes the matching content as well.
-
Terminate connection: Immediately terminate the connection. When using the Terminate connection action for the Command event type, and a command matches an expression, the connection is terminated before the command is executed. When using the Terminate connection action, note the following points.
-
Select the Log or Notify action as well so that it is easy to find out why a connection was terminated.
-
If the connection is terminated by a content policy, the Verdict of the connection becomes ACCEPT-TERMINATED.
-
-
Notify: Send an e-mail or SNMP alert about the event. To configure the alerts, navigate to Basic Settings > Alerting & Monitoring and set the required alerts for the Real time audit event detected (scbAuditRealTime) event.
-
Store in connection database: Add the event to the SPS connection database. These events are displayed in the Alerts column of the Search page. If the column is not visible, click Customize columns....
-
-
To apply the content policy only for users belonging to specific groups, select Apply this policy only to members of these gateway groups or Apply this policy only to members of these remote groups,
and specify the usergroups as needed. If Apply this policy only to members of these gateway groups or Apply this policy only to members of these remote groups is set, the content policy is applied only to connections of these usergroups.
-
To add a new rule to the policy, click
and repeat Steps 2-6.
Note that if you have more than one rules in a policy, SPS evaluates them as follows.
-
SPS evaluates the first (top) rule.
-
If the rule contains Apply this policy only to members of these gateway groups or Apply this policy only to members of these remote groups restrictions, SPS checks if the current user belongs to any of the specified groups. If the groups do not match, SPS skips the rule.
-
If the content matches any entry of the Except if it also contains any of these strings or expressions list, SPS skips the rule.
-
If the content matches any entry of the Take action if the event contains any of the following strings or expressions list, SPS performs the action configured for the rule. Otherwise, SPS skips the rule.
-
If the current rule did not match the content, SPS evaluates the next rule of the policy (if any).
-
-
Click
. A new content policy is created.
-
To use the content policy created in the previous steps, select the policy in the channel policy that is used to control the connections.
NOTE: It is not required to enable auditing to use content policies.