The snmp() driver sends SNMP traps using the Simple Network Management Protocol version 2c or version 3. Incoming log messages can be converted to SNMP traps, as the fields of the SNMP messages can be customized using syslog-ng PE macros.
The snmp() driver is available in syslog-ng PE version 7.0.20 and later.
NOTE: The snmp destination driver currently supports sending SNMP traps only using the UDP transport protocol.
The snmp() driver requires the host(), trap-obj(), and snmp-obj() options to be set, as well as the engine-id() and version() options when using the SNMPv3 protocol. For the list of available optional parameters, see snmp() destination options.
NOTE:To use the snmp() driver, the scl.conf file must be included in your syslog-ng PE configuration:
@include "scl.conf"
Declaration
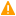
destination d_snmp {snmp(host() trap-obj() snmp-obj() ...);};
|
|
Caution:
If syslog-ng PE cannot resolve the destination hostname during startup, it will try to resolve the hostname again when the next message to be sent as an SNMP trap is received. However, if this name resolution fails, the trap will be dropped. |
NOTE: The snmp() destination driver does not generate MARK signals itself, but can receive and forward MARK signals.
Example: Using the snmp() destination driver
The following example defines an SNMP destination that uses the SNMPv2c protocol.
destination d_snmpv2c{
snmp(
version('v2c')
host('192.168.1.1')
trap-obj('.1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.4.1.0', 'Objectid', '.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.2.1')
snmp-obj('.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.1.0', 'Octetstring', 'Test SNMP trap')
snmp-obj('.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.2.0', 'Octetstring', 'admin')
snmp-obj('.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.3.0', 'Ipaddress', '192.168.1.1')
);
};
The following example defines an SNMP destination that uses the SNMPv3 protocol and uses macros to fill the values of the SNMP objects.
destination d_snmpv3{
snmp(
version('v3')
host('192.168.1.1')
port(162)
engine-id('0xdeadbeefde')
auth-username('myusername')
auth-password('password')
enc-algorithm('AES')
enc-password('password')
trap-obj('.1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.4.1.0', 'Objectid', '.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.2.1')
snmp-obj('.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.1', 'Octetstring', '${MESSAGE}')
snmp-obj('.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.2', 'Octetstring', 'admin')
snmp-obj('.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.3', 'Ipaddress', '${SOURCEIP}')
);
};
This driver sends SNMP traps using the SNMP v2c or v3 protocol.
The snmp() destination has the following options:
auth-algorithm()
| Type: |
SHA|sha |
| Default: |
SHA |
Description: The authentication method to use. Lowercase values (for example, sha) can be used as well.
This option is used with the SNMPv3 protocol.
auth-password()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
empty string |
Description: The password used for authentication. If the auth-username() option is set but the auth-password() is empty, syslog-ng PE will try to authenticate with an empty password.
This option is used with the SNMPv3 protocol.
auth-username()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
empty string |
Description: The username used to authenticate on the SNMP server. If this parameter is set, syslog-ng PE will try to authenticate on the SNMP server.
This option is used with the SNMPv3 protocol.
community()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
public |
Description: The community string used for SNMPv2c authentication.
This option is used with the SNMPv2c protocol.
enc-algorithm()
| Type: |
AES|aes |
| Default: |
AES |
Description: The encryption method used to encrypt the SNMP traffic. Lowercase values (for example, aes) can be used as well.
This option is used with the SNMPv3 protocol.
enc-password()
Description: The password used for the encryption. Encryption is used only if the enc-password() is not empty.
This option is used with the SNMPv3 protocol.
engine-id()
| Type: |
number (hexadecimal number) |
| Default: |
|
Description: The engine ID is a hexadecimal number between 5 and 32 characters long, starting with 0x. for example, 0xABABABABAB.
This option is a required parameter when using the SNMPv3 protocol.
host()
| Type: |
hostname or IP address |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: Hostname of the SNMP server.
log-fifo-size()
| Type: |
number |
| Default: |
Use global setting. |
Description: The number of messages that the output queue can store.
port()
| Type: |
number (port number) |
| Default: |
162 |
Description: The port number to connect to.
snmp-obj()
| Type: |
<oid_of_the_object>, <type_of_the_object>, <value_of_the_object> |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: The snmp-obj() option can be used to create custom SNMP trap elements. To create a trap element, specify the OID, type, and value of the element in the snmp-obj() option. To send SNMP traps, at least one snmp-obj() option must be defined. The snmp-obj() option requires the following parameters. Note that syslog-ng PE does not validate the values of these elements.
-
<oid_of_the_object>: The object id of the SNMP object, for example, .1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.1.
-
<type_of_the_object>: The type of the object specified as an ASN.1 primitive. One of: Integer, Timeticks, Octetstring, Counter32, Ipaddress, Objectid. The type names are not case sensitive.
-
<value_of_the_object>: The value of the object as a string. The macros of syslog-ng PE can be used to set these values, making it possible to transfer the content and other metadata from the the syslog message to the SNMP trap. Note that if the value of an Integer, Counter32 or Timeticks object is not a number (for example, is an empty string or other not-number string), syslog-ng PE will automatically replace the value with 0. The values of other types of objects are not validated.
Example: Defining SNMP objects
The following are SNMP object definitions:
snmp-obj('.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.3', 'Ipaddress', '192.168.1.1')snmp-obj('.1.3.6.1.4.1.18372.3.1.1.1.1.2', 'Octetstring', '${MESSAGE}')
time-zone()
| Type: |
name of the timezone, or the timezone offset |
| Default: |
unspecified |
Description: Convert timestamps to the timezone specified by this option. If this option is not set, then the original timezone information in the message is used. Converting the timezone changes the values of all date-related macros derived from the timestamp, for example, HOUR. For the complete list of such macros, see Date-related macros.
The timezone can be specified as using the name of the (for example, time-zone("Europe/Budapest")), or as the timezone offset in +/-HH:MM format (for example, +01:00). On Linux and UNIX platforms, the valid timezone names are listed under the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory.
trap-obj()
| Type: |
<oid_of_the_object>, "Objectid", <value_of_the_object> |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: The trap-obj() is a specialized version of the snmp-obj() option that is used to identify the SNMP trap object. The type of the trap object is always Objectid. The <oid_of_the_object> and the <value_of_the_object> parameters are identical to the respective parameters of the snmp-obj() option. For details on these parameters, see snmp-obj().
NOTE: Using the trap-obj() object is equivalent to using the snmp-obj() with the Objectid type.
version()
| Type: |
v2c|v3 |
| Default: |
v2c |
Description: Specifies which version of the SNMP protocol to use.
NOTE: The syslog-ng PE application will accept any valid option for the snmp() destination, but will only use the ones relevant to the selected protocol version, any other option will be ignored. For example, if the version("v2c") engine-id("0xABABABABAB") community("mycommunity") options are set, syslog-ng PE will accept every option, but process only the community() option, because engine-id() applies only to SNMPv3.
The destination is aimed at a fully controlled local, or near-local, trusted SMTP server. The goal is to send mail to trusted recipients, through a controlled channel. It hands mails over to an SMTP server, and that is all it does, therefore the resulting solution is as reliable as sending an email in general. For example, syslog-ng PE does not verify whether the recipient exists.
The smtp() driver sends email messages triggered by log messages. The smtp() driver uses SMTP, without needing external applications. You can customize the main fields of the email, add extra headers, send the email to multiple recipients, and so on.
The subject(), body(), and header() fields may include macros which get expanded in the email. For more information on available macros see Macros of syslog-ng PE.
The smtp() driver has the following required parameters: host(), port(), from(), to(), subject(), and body(). For the list of available optional parameters, see smtp() destination options.
NOTE: To use this destination, syslog-ng Premium Edition (syslog-ng PE) must run in server mode. Typically, only the central syslog-ng PE server uses this destination. For more information on the server mode, see Server mode.
NOTE: The smtp() destination driver is available only in 5 F2 and later.
Declaration
smtp(host() port() from() to() subject() body() options());
Example: Using the smtp() driver
The following example defines an smtp() destination using only the required parameters.
destination d_smtp {
smtp(
host("localhost")
port(25)
from("syslog-ng alert service" "noreply@example.com")
to("Admin #1" "admin1@example.com")
subject("[ALERT] Important log message of $LEVEL condition received from $HOST/$PROGRAM!")
body("Hi!\nThe syslog-ng alerting service detected the following important log message:\n $MSG\n-- \nsyslog-ng\n")
);
};
The following example sets some optional parameters as well.
destination d_smtp {
smtp(
host("localhost")
port(25)
from("syslog-ng alert service" "noreply@example.com")
to("Admin #1" "admin1@example.com")
to("Admin #2" "admin2@example.com")
cc("Admin BOSS" "admin.boss@example.com")
bcc("Blind CC" "blindcc@example.com")
subject("[ALERT] Important log message of $LEVEL condition received from $HOST/$PROGRAM!")
body("Hi!\nThe syslog-ng alerting service detected the following important log message:\n $MSG\n-- \nsyslog-ng\n")
header("X-Program", "$PROGRAM")
);
};
Example: Simple email alerting with the smtp() driver
The following example sends an email alert if the eth0 network interface of the host is down.
filter f_linkdown {
match("eth0: link down" value("MESSAGE"));
};
destination d_alert {
smtp(
host("localhost") port(25)
from("syslog-ng alert service" "syslog@localhost")
reply-to("Admins" "root@localhost")
to("Ennekem" "me@localhost")
subject("[SYSLOG ALERT]: eth0 link down")
body("Syslog received an alert:\n$MSG")
);
};
log {
source(s_local);
filter(f_linkdown);
destination(d_alert);
};
The smtp() sends email messages using SMTP, without needing external applications. The smtp() destination has the following options:
body()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: The BODY field of the email. You can also use macros in the string. Use \n to start a new line. For example:
body("syslog-ng PE received the following alert from $HOST:\n$MSG")
bcc()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: The BCC recipient of the email (contents of the BCC field). You can specify the email address, or the name and the email address. Set the bcc() option multiple times to send the email to multiple recipients. For example: bcc("admin@example.com") or bcc("Admin" "admin@example.com") or bcc("Admin" "admin@example.com") bcc("Admin2" "admin2@example.com")
You can also use macros to set the value of this parameter.
cc()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: The CC recipient of the email (contents of the CC field). You can specify the email address, or the name and the email address. Set the cc() option multiple times to send the email to multiple recipients. For example: cc("admin@example.com") or cc("Admin" "admin@example.com") or cc("Admin" "admin@example.com") cc("Admin2" "admin2@example.com")
You can also use macros to set the value of this parameter.
disk-buffer()
Description: This option enables putting outgoing messages into the disk-buffer file of the destination to avoid message loss in case of a system failure on the destination side. It has the following options:
| dir() |
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
N/A |
|
Description: Defines the folder where the disk-buffer files are stored.
Note that changing the value the dir() option will not move or copy existing files from the old directory to the new one.
|

|
Caution:
When creating a new dir() option for a disk-buffer file, or modifying an existing one, make sure you delete the persist file.
syslog-ng PE creates disk-buffer files based on the path recorded in the persist file. Therefore, if the persist file is not deleted after modifying the dir() option, then following a restart, syslog-ng PE will look for or create disk-buffer files in their old location. To ensure that syslog-ng PE uses the new dir() setting, the persist file must not contain any information about the destinations which the disk-buffer file in question belongs to. | |
| disk-buf-size() |
| Type: |
number [bytes] |
| Default: |
|
| Description: This is a required option. The maximum size of the disk-buffer file in bytes. The minimum value is 1048576 bytes. If you set a smaller value, the minimum value will be used automatically. It replaces the old log-disk-fifo-size() option. |
| mem-buf-length() |
| Type: |
number [messages] |
| Default: |
10000 |
| Description: Use this option if the option reliable() is set to no. This option contains the number of messages stored in overflow queue. It replaces the old log-fifo-size() option. It inherits the value of the global log-fifo-size() option if provided. If it is not provided, the default value is 10000 messages. Note that this option will be ignored if the option reliable() is set to yes. |
| mem-buf-size() |
| Type: |
number [bytes] |
| Default: |
163840000 |
| Description: Use this option if the option reliable() is set to yes. This option contains the size of the messages in bytes that is used in the memory part of the disk-buffer file. It replaces the old log-fifo-size() option. It does not inherit the value of the global log-fifo-size() option, even if it is provided. Note that this option will be ignored if the option reliable() is set to no. |
| quot-size() |
| Type: |
number [messages] |
| Default: |
1000 |
|
Description: The number of messages stored in the output buffer of the destination. Note that if you change the value of this option and the disk-buffer file already exists, the change will take effect when the disk-buffer file becomes empty. |
| reliable() |
| Type: |
yes|no |
| Default: |
no |
|
Description: If set to yes, syslog-ng PE cannot lose logs in case of reload/restart, unreachable destination or syslog-ng PE crash. This solution provides a slower, but reliable disk-buffer option. It is created and initialized at startup and gradually grows as new messages arrive. If set to no, the normal disk-buffer option will be used. This provides a faster, but less reliable disk-buffer option.
|

|
Caution: Hazard of data loss!
If you change the value of reliable() option when there are messages in the disk-buffer file, the messages stored in the disk-buffer file will be lost. | |
| truncate-size-ratio() |
| Type: |
number (for percentage) between 0 and 1 |
| Default: |
0.1 (10%) |
|
Description: Limits the truncation of the disk-buffer file. Truncating the disk-buffer file can slow down disk I/O operations, but it saves disk space. As a result, syslog-ng PE only truncates the file if the possible disk gain is more than truncate-size-ratio() times disk-buf-size().
|

|
Caution:
One Identity recommends that you do not modify the value of the truncate-size-ratio() option unless you are fully aware of the potential performance implications. | |
Example: Examples for using disk-buffer()
In the following case, reliable disk-buffer() is used.
destination d_demo {
network("127.0.0.1"
port(3333)
disk-buffer(
mem-buf-size(10000)
disk-buf-size(2000000)
reliable(yes)
dir("/tmp/disk-buffer")
)
);
};
In the following case normal disk-buffer() is used.
destination d_demo {
network("127.0.0.1"
port(3333)
disk-buffer(
mem-buf-length(10000)
disk-buf-size(2000000)
reliable(no)
dir("/tmp/disk-buffer")
)
);
};
from()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: The sender of the email (contents of the FROM field). You can specify the email address, or the name and the email address. For example:
from("admin@example.com")
or
from("Admin" "admin@example.com")
If you specify the from() option multiple times, the last value will be used. Instead of the from() option, you can also use sender(), which is just an alias of the from() option.
You can also use macros to set the value of this parameter.
header()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: Adds an extra header to the email with the specified name and content. The first parameter sets the name of the header, the second one its value. The value of the header can contain macros. Set the header() option multiple times to add multiple headers. For example:
header("X-Program", "$PROGRAM")
When using the header option, note the following points:
-
Do not use the header() option to set the values of headers that have dedicated options. Use it only to add extra headers.
-
If you set the same custom header multiple times, only the first will be added to the email, other occurrences will be ignored.
-
It is not possible to set the DATE, Return-Path, Original-Recipient, Content-*, MIME-*, Resent-*, Received headers.
host()
| Type: |
hostname or IP address |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: Hostname or IP address of the SMTP server.
NOTE: If you specify host="localhost", syslog-ng PE will use a socket to connect to the local SMTP server. Use host="127.0.0.1" to force TCP communication between syslog-ng PE and the local SMTP server.
log-fifo-size()
| Type: |
number |
| Default: |
Use global setting. |
Description: The number of messages that the output queue can store.
port()
Description: The port number of the SMTP server.
reply-to()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: Replies of the recipient will be sent to this address (contents of the REPLY-TO field). You can specify the email address, or the name and the email address. Set the reply-to() option multiple times to send the email to multiple recipients. For example: reply-to("admin@example.com") or reply-to("Admin" "admin@example.com") or reply-to("Admin" "admin@example.com") reply-to("Admin2" "admin2@example.com")
You can also use macros to set the value of this parameter.
retries()
| Type: |
number [of attempts] |
| Default: |
3 |
Description: The number of times syslog-ng PE attempts to send a message to this destination. If syslog-ng PE could not send a message, it will try again until the number of attempts reaches retries(), then drops the message.
subject()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
n/a |
Description: The SUBJECT field of the email. You can also use macros. For example:
subject("[SYSLOG ALERT]: Critical error message received from $HOST")
If you specify the subject() option multiple times, the last value will be used.
throttle()
Description: Sets the maximum number of messages sent to the destination per second. Use this output-rate-limiting functionality only when using the disk-buffer option as well to avoid the risk of losing messages. Specifying 0 or a lower value sets the output limit to unlimited.
to()
| Type: |
string |
| Default: |
localhost |
Description: The recipient of the email (contents of the TO field). You can specify the email address, or the name and the email address. Set the to() option multiple times to send the email to multiple recipients. For example: to("admin@example.com") or to("Admin" "admin@example.com") or to("Admin" "admin@example.com") to("Admin2" "admin2@example.com")
You can also use macros to set the value of this parameter.

