Replacing a node in an SSB HA cluster
This section describes how to replace a unit in an SSB cluster with a new appliance.
To replace a unit in an SSB cluster with a new appliance
-
Verify the HA status on the working node. Select Basic Settings > High Availability. If one of the nodes has broken down or is missing, the Status field displays DEGRADED.
-
Note down the IP addresses of the Heartbeat and the Next hop monitoring interfaces.
-
Perform a full system backup. Before replacing the node, create a complete system backup of the working node. For details, see Data and configuration backups.
-
Check which firmware version is running on the working node. Select Basic Settings > System > Version details and write down the exact version numbers.
-
Log in to your support portal account and download the CD ISO for the same SSB version that is running on your working node.
-
Without connecting the replacement unit to the network, install the replacement unit from the ISO file. Use the IPMI interface if needed.
-
When the installation is finished, connect the two SSB units with an Ethernet cable via the Ethernet connectors labeled as 4 (or HA).
-
Reboot the replacement unit and wait until it finishes booting.
-
Log in to the working node and verify the HA state. Select Basic Settings > High Availability. The Status field should display HALF.
-
Reconfigure the IP addresses of the Heartbeat and the Next hop monitoring interfaces. Click  .
.
-
Click Other node > Join HA.
-
Click Other node > Reboot.
-
The replacement unit will reboot and start synchronizing data from the working node. The Basic Settings > High Availability > Status field will display DEGRADED SYNC until the synchronization finishes. Depending on the size of the hard disks and the amount of data stored, this can take several hours.
-
After the synchronization is finished, connect the other Ethernet cables to their respective interfaces (external to 1 or EXT, management to 2 or MGMT) as needed for your environment.
Expected result
A node of the SSB cluster is replaced with a new appliance.
Resolving an IP conflict between cluster nodes
The IP addresses of the HA interfaces connecting the two nodes are detected automatically, during boot. When a node comes online, it attempts to connect to the IP address 1.2.4.1. If no other node responds until timeout, then it sets the IP address of its HA interface to 1.2.4.1, otherwise (if there is a responding node on 1.2.4.1) it sets its own HA interface to 1.2.4.2.
Replaced nodes do not yet know the HA configuration (or any other HA settings), and will attempt to negotiate it automatically in the same way. If the network is, for any reason, too slow to connect the nodes on time, the replacement node boots with the IP address of 1.2.4.1, which can cause an IP conflict if the other node has also set its IP to that same address previously. In this case, the replacement node cannot join the HA cluster.
To manually assign the correct IP address to the HA interface of a node, perform the following steps:
-
Log in to the node using the IPMI interface or the physical console.
Configuration changes have not been synced to the new (replacement) node, as it could not join the HA cluster. Use the default password of the root user of SSB, see "Installing the SSB hardware" in the Installation Guide.
-
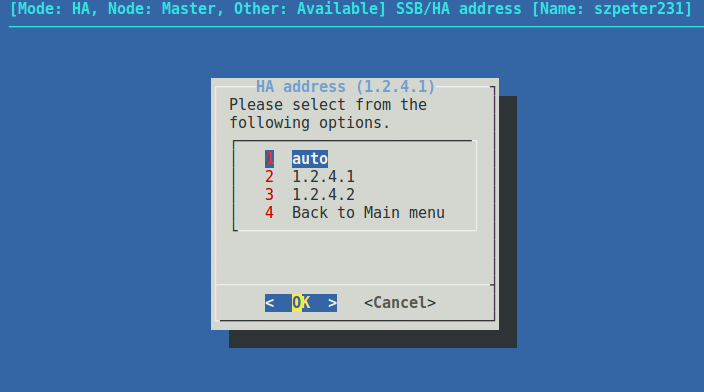
From the console menu, choose 6 HA address.
Figure 167: The console menu

-
Choose the IP address of the node.
Figure 168: The console menu
-
Reboot the node.
Restoring SSB configuration and data
The following procedure describes how to restore the configuration and data of SSB from a complete backup, for example, after a hardware replacement.
|

|
NOTE:
It is possible to receive indexer errors following data restore. Data that was still in the memory of SSB during backup might have been indexed, but as it was not on the hard drive, it was not copied to the remote server.
To make sure that all data is backed up (for example, before an upgrade), shut down syslog-ng before initiating the backup process. |
|

|
NOTE:
Statistics about syslog-ng and logspace sizes are not backed up. As a result, following a data restore, the Basic Settings > Dashboard page will not show any syslog-ng and logspace statistics about the period before the backup. |
To restore the configuration and data of SSB from a complete backup
-
Connect to your backup server and locate the directory where SSB saves the backups. The configuration backups are stored in the config subdirectory in timestamped files. Find the latest configuration file (the configuration files are called SSB-timestamp.config).
-
Connect to SSB.
If you have not yet completed the Welcome Wizard, click Browse, select the configuration file, and click Import.
If you have already completed the Welcome Wizard, navigate to Basic Settings > System > Import configuration > Browse, select the configuration file, and click Import.
-
Navigate to Policies > Backup & Archive/Cleanup. Verify that the settings of the target servers and the backup protocols are correct.
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Management > System backup, click Restore now and wait for the process to finish. Depending on the amount of data stored in the backup, and the speed of the connection to the backup server, this may take a long time.
-
Navigate to Log > Logspaces, and click Restore ALL. Depending on the amount of data stored in the backup, and the speed of the connection to the backup server, this may take a long time.
Configuring the IPMI interface from the BIOS after losing IPMI password
It may happen that you inadvertently lose the IPMI pasword of your SSB. In that case, you will be required to:
-
Shut down SSB.
-
Unplug the SSB physical appliance's power cord.
-
Wait 30 seconds.
-
Replug the power cord.
-
Restart the appliance.
-
Re-configure the IPMI interface from the BIOS.
To confgure IPMI from the BIOS, complete the following steps.
Prerequisites
To apply the procedure outlined here, you will need physical access to a monitor and keyboard.
-
Press the DEL button when the POST screen comes up while the appliance is booting.
Figure 169: POST screen during booting

-
In the BIOS, navigate to the IPMI page.
-
On the IPMI page, select BMC Network Configuration, and press Enter.
Figure 170: IMPI page > BMC Network Configuration option

-
On the BMC Network Configuration page, select Update IPMI LAN Configuration, press Enter, and select Yes.
Figure 171: BMC Network Configuration page > Update IPMI LAN Configuration

-
Stay on the BMC Network Configuration page, select Configuration Address Source, press Enter, and select Static.
Figure 172: BMC Network Configuration page > Configuration Address Source

-
Still on the BMC Network Configuration page, configure the Station IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP Address individually.
Figure 173: BMC Network Configuration page > Station IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway IP Address

-
Press F4 to save the settings, and exit from the BIOS.
About a minute later, you will be able to log in on the IPMI web interface.
 .
.







