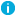
| Platform |
Description |
| WindowsServer |
A name for a group of server operating systems released by Microsoft. |
| SolarisSsh |
A Unix operating system, using an SSH connection. |
| PanosSsh |
An operating system developed by Acorn Computers, using an SSH connection. |
| Aixssh |
A series of proprietary Unix operating systems developed by IBM, using an SSH connection. |
| OdbcMysql |
An open-source relational database management system, using an ODBC Driver. |
| postgres |
An open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). |
| vsphere |
Server virtualization software |
| IloSsh |
HP Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) is a proprietary embedded server management technology, using an SSH connection |
| OdbcSqlServer |
A relational database management system, using an ODBC Driver. |
| ad |
Microsoft Windows Active Directory |
| SonicWall |
SonicWall Secure Mobile Access (SMA) is a unified secure access gateway. |
| Aws |
Amazon Web Services (AWS), an on-demand cloud computing platform. |
| Acf2Tn3270 |
IBM's Access Control Facility (z-Series), using a TN3270 connection. |
| F5BigIpSsh |
A load balancer and a full proxy, using an SSH connection |
| TopSecretTn3270 |
CA TopSecret is a streamlined and scalable mainframe security for IBM's zseries operating system, using a TN3270 connection. |
| OdbcSybase |
Used to manage and analyze information in relational databases, using an ODBC Driver. |
| PixSsh |
Cisco PIX (Private Internet eXchange) is an IP firewall, using an SSH connection. |
| FreeBsdSsh |
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system, using an SSH connection. |
| DracSsh |
Dell Remote Access Controller (DRAC) is an out-of-band management platform, using a SSH connection. |
| Hpuxssh |
Hewlett Packard Unix Operating systems, using a SSH connection. |
| Acf2Ldap |
Access Control Facility, a discretionary access control software security system over LDAP authentications. |
| RacfLdap |
Resource Access Control Facility is an IBM security system that provides access control and auditing functionality for zSeries operating systems over LDAP authentications. |
| SapHana |
A relational database management system. |
| LinuxSsh |
Linux Operating system, using a SSH connection. |
| RacfTn3270 |
IBM's Resource Access Control Facility (z-Series), using a TN3270 connection. |
| SonicSsh |
SonicOS, an operating system for SonicWall network security appliances (firewalls), using a SSH connection. |
| TopSecretLdap |
CA TopSecret is a streamlined and scalable mainframe security for IBM's zseries operating system, using a SSH connection. |
| MongoDb |
MongoDb is a cross-platform document-oriented database program. |
| JunosSsh |
Junos OS is the FreeBSD-based operating system used in Juniper Networks hardware routers, using an SSH connection. |
| SapNetweaver |
SAP NetWeaver is an open application server platform. |
| OdbcOracle |
Oracle Database is a multi-model database management system, using an ODBC driver. |
| As400Tn3270 |
IBM's Application System/400, using a TN3270 driver. |
| FortinetSsh |
Fortinet firewall client, using an SSH connection. |
| Ldap |
A protocol used for accessing Active Directory object, user authentication, and authorization in windows server. |
| MacOsSsh |
Apple Mac Operating system, using a SSH connection. |