To react quickly to special requests, you can assign groups directly to computers.
To assign a group directly to computers
-
In the Manager, select the Active Directory > Groups category.
-
Select the group in the result list.
-
Select the Assign computers task.
-
In the Add assignments pane, assign computers.
TIP: In the Remove assignments pane, you can remove assigned computers.
To remove an assignment
- Save the changes.
NOTE: The primary group of a computer is already assigned and is marked as Does not apply yet. Edit the computer's main data to change its primary group.
Related topics
Groups can be assigned directly or indirectly to a computer. Indirect assignment is carried out by allocating the device with which a computer is connected and groups to company structures, like departments, cost centers, locations, or business roles.
To react quickly to special requests, you can assign groups directly to a computer.
To assign a computer directly to groups
-
In the Manager, select the Active Directory > Computers category.
-
Select the computer in the result list.
-
Select Assign groups.
-
In the Add assignments pane, assign the groups.
TIP: In the Remove assignments pane, you can remove the assignment of groups.
To remove an assignment
- Save the changes.
NOTE: The primary group of a computer is already assigned and is marked as Does not apply yet. Edit the computer's main data to change its primary group.
Related topics
When groups are assigned to user accounts an employee may obtain two or more groups, which are not permitted in this combination. To prevent this, you can declare mutually exclusive groups. To do this, you specify which of the two groups should apply to the user accounts if both are assigned.
It is possible to assign an excluded group at any time either directly, indirectly, or with an IT Shop request. One Identity Manager determines whether the assignment is effective.
NOTE:
- You cannot define a pair of mutually exclusive groups. That means, the definition "Group A excludes group B" AND "Group B excludes groups A" is not permitted.
- You must declare each group to be excluded from a group separately. Exclusion definitions cannot be inherited.
- One Identity Manager does not check if membership of an excluded group is permitted in another group ( table).
The effectiveness of the assignments is mapped in the ADSAccountInADSGroup and BaseTreeHasADSGroup tables by the XIsInEffect column.
Example: The effect of group memberships
- Group A is defined with permissions for triggering requests in a domain. A group B is authorized to make payments. A group C is authorized to check invoices.
- Group A is assigned through the "Marketing" department, group B through "Finance", and group C through the "Control group" business role.
Clara Harris has a user account in this domain. She primarily belongs to the "Marketing" department. The "Control group" business role and the "Finance" department are assigned to her secondarily. Without an exclusion definition, the user account obtains all the permissions of groups A, B, and C.
By using suitable controls, you want to prevent an employee from being able to trigger a request and to pay invoices. That means, groups A, B, and C are mutually exclusive. An employee that checks invoices may not be able to make invoice payments as well. That means, groups B and C are mutually exclusive.
Table 15: Specifying excluded groups (ADSGroupExclusion table)
|
Group A |
|
|
Group B |
Group A |
|
Group C |
Group B |
Table 16: Effective assignments
|
Ben King |
Marketing |
Group A |
|
Jan Bloggs |
Marketing, finance |
Group B |
|
Clara Harris |
Marketing, finance, control group |
Group C |
|
Jenny Basset |
Marketing, control group |
Group A, Group C |
Only the group C assignment is in effect for Clara Harris. It is published in the target system. If Clara Harris leaves the "control group" business role at a later date, group B also takes effect.
The groups A and C are in effect for Jenny Basset because the groups are not defined as mutually exclusive. That means that the employee is authorized to trigger requests and to check invoices. If this should not be allowed, define further exclusion for group C.
Table 17: Excluded groups and effective assignments
|
Jenny Basset
|
Marketing |
Group A |
|
Group C
|
|
Control group |
Group C |
Group B
Group A |
Prerequisites
-
The QER | Structures | Inherite | GroupExclusion configuration parameter is set.
In the Designer, set the configuration parameter and compile the database.
NOTE: If you disable the configuration parameter at a later date, model components and scripts that are not longer required, are disabled. SQL procedures and triggers are still carried out. For more information about the behavior of preprocessor relevant configuration parameters and conditional compiling, see the One Identity Manager Configuration Guide.
-
Mutually exclusive groups belong to the same domain
To exclude a group
-
In the Manager, select the Active Directory > Groups category.
-
Select a group in the result list.
-
Select the Exclude groups task.
-
In the Add assignments pane, assign the groups that are mutually exclusive to the selected group.
- OR -
In the Remove assignments pane, remove the groups that are no longer mutually exclusive.
- Save the changes.
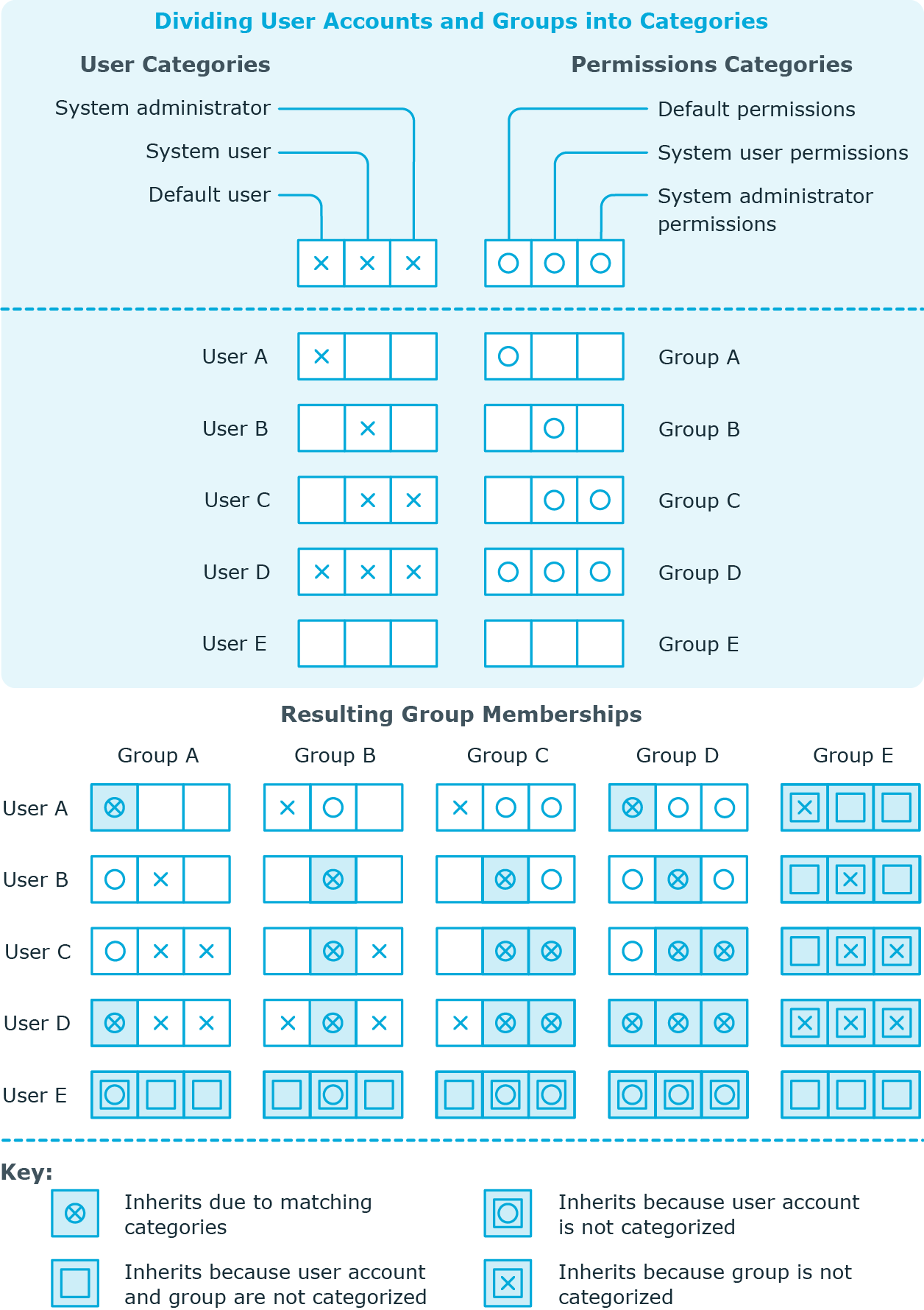
Groups and be selectively inherited by user accounts and contacts in One Identity Manager. The groups and user accounts (contacts) are divided into categories in the process. The categories can be freely selected and are specified using a mapping rule. Each category is given a specific position within the template. The mapping rule contains tables that map the user accounts (contact) and the groups. Specify your categories for user account (contacts) in the table for user accounts (contacts). Enter your categories for groups in the group table. Each table contains the Position 1 to Position 31 category positions.
Every user account (contact) can be assigned to one or more categories. Each group can also be assigned to one or more categories. If at least one user account (contact) category position matches an assigned structural profile, the structural profile is inherited by the user account (contact). If the group or user account (contact) is not in classified into categories, the group is also inherited by the user account (contact).
NOTE: Inheritance through categories is only taken into account when groups are assigned indirectly through hierarchical roles. Categories are not taken into account when assigning groups to user accounts and contacts.
Table 18: Category examples
|
1 |
Default user |
Default entitlements |
|
2 |
System users |
System user entitlements |
|
3 |
System administrator |
System administrator entitlements |
Figure 2: Example of inheriting through categories.
To use inheritance through categories
-
In the Manager, define the categories in the domain.
-
Assign categories to user accounts and contacts through their main data.
-
Assign categories to groups through their main data.
Related topics
.

