As an Appliance Administrator, you can use the Factory Reset feature to reset a Safeguard for Privileged Passwords Appliance to recover from major problems or to clear the data and configuration settings on the appliance. A factory reset of a physical appliance may be initiated from:
- The web client
- The Recovery Kiosk
- The Support Kiosk
- Using the API
A Safeguard for Privileged Passwords virtual appliance is reset by the recovery steps to redeploy and not a factory reset. For more information, see Virtual appliance backup and recovery.
|
|
Caution: Care should be taken when performing a factory reset against a physical appliance, because this operation removes all data and audit history, returning it to its original state when it first came from the factory. Performing a factory reset will NOT reset the BMC/IPMI interface or the IP address. However, the BMC/IPMI interface will need to be reenabled after the reset has completed (for more information, see Lights Out Management (BMC)). The appliance must go through configuration again as if it had just come from the factory. For more information, see Setting up Safeguard for Privileged Passwords for the first time. In addition, performing a factory reset may change the default SSL certificate and default SSH host key. The appliance resets to the current Long Term Support (LTS) version. For example, if the appliance is running version 6.6 (feature release) or 6.0.6 LTS (maintenance Long Term Support release) and then factory reset, the appliance will reset down to 6.0 LTS and you will have to patch up to your desired version. For more information, see Long Term Support (LTS) and Feature Releases. |
Factory reset on a clustered appliance
Performing a factory reset on a clustered hardware appliance will not automatically remove the appliance from a cluster. The recommended best practice is to unjoin an appliance from the cluster before performing a factory reset on the appliance. After the unjoin and factory reset, the appliance must be configured again. For more information, see Setting up Safeguard for Privileged Passwords for the first time.
To perform a factory reset from the web client
- Go to Factory Reset on hardware (not virtual machine):
- Navigate to Appliance Management > Appliance > Factory Reset.
- Click Factory Reset.
-
In the Factory Reset confirmation dialog, enter the words Factory Reset and click Factory Reset.
The appliance will go into Maintenance mode to revert the appliance. If the appliance was in a cluster, you may need to unjoin the factory reset appliance. The factory reset appliance must be configured again. For more information, see Setting up Safeguard for Privileged Passwords for the first time. In addition, when you log in to the appliance, you will be prompted to add your Safeguard for Privileged Passwords licenses.
To perform a factory reset from the Recovery Kiosk
|
|
CAUTION: As part of the factory reset process, you will be performing a challenge response operation. If the challenge response operation is invalidated, try restarting the process to generate a new challenge response. If that fails, contact One Identity Support for assistance. |
- To perform a hardware factory reset, go to the Recovery Kiosk. For more information, see Recovery Kiosk (Serial Kiosk).
-
Select Factory Reset.
-
Press the right arrow.
-
At Name or Email, enter your email or name and press the Tab key (or down arrow).
-
Select Submit.
-
At View Challenge, press the Enter key. Safeguard for Privileged Passwords produces a challenge. (If the challenge is not shown, maximize Putty.)
-
Copy and paste the challenge into a text document and send it to One Identity Support. A challenge response is only good for 48 hours.
IMPORTANT: Do not reboot the machine during the challenge response process.
- When you get the response from One Identity Support, copy and paste the response into the kiosk screen and select Factory Reset. The response is only valid for 24 hours from when it was generated by One Identity.
-
Once the factory reset is completed the appliance will need to be reconfigured.
See the following Knowledge Base Article for details on using the MGMT network interface for factory reset: KB 232766: What are the steps to perform a factory reset from the recovery kiosk or MGMT network interface on physical devices?
To perform a factory reset from the Support Kiosk
|
|
CAUTION: As part of the factory reset process, you will be performing a challenge response operation. To avoid invalidating the challenge response, do NOT navigate away from the page or refresh. If the challenge response operation is invalidated, try restarting the process to generate a new challenge response. If that fails, contact One Identity Support for assistance. |
- To perform a hardware factory reset, on the web management console, click
Support Kiosk. For more information, see Support Kiosk.
- Select Factory Reset. (This option is not available if you are attached to the console of a virtual machine. The options is only available for hardware.)
-
Complete the challenge/response process:
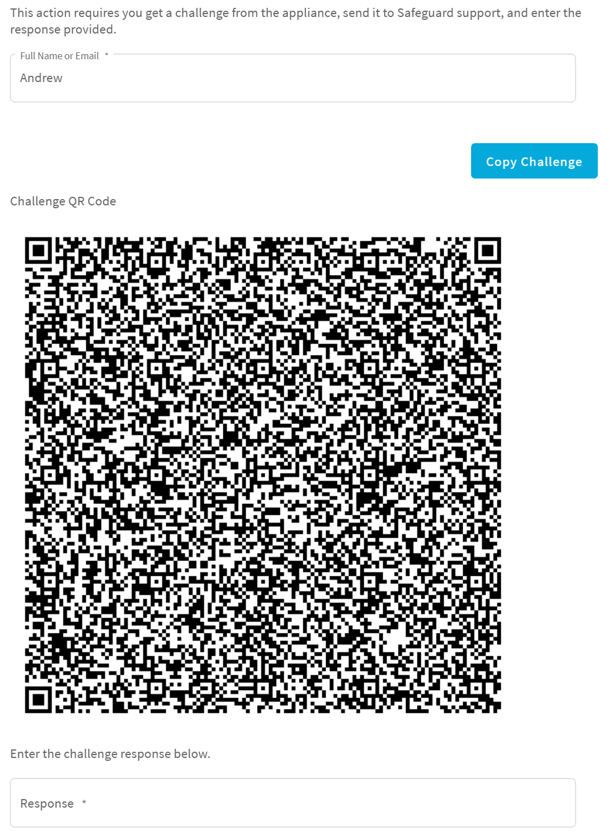
- In Full Name or Email, enter your name or email to receive the challenge question.
- Click Get Challenge.
- To get the challenge response, perform one of the following (see the illustration that follows).
- Click Copy Challenge. The challenge is copied to the clipboard. Send that challenge to Safeguard support. Support will send back a challenge response that is good for 48 hours.
-
Screenshot the QR code and send it to Support. Support will send back a challenge response that is good for 48 hours.
IMPORTANT: Do not reboot the machine during the challenge response process.
-
Use a QR code reader on your phone to get the challenge response.
- When you get the response from One Identity Support, copy and paste the response into the kiosk screen and select Factory Reset.


 web client: The Appliance State will show a red lock icon (
web client: The Appliance State will show a red lock icon ( ).
).  Cluster > Cluster Management.
Cluster > Cluster Management.