This section describes getting the status information of the disk-buffer files used in syslog-ng Premium Edition ( syslog-ng PE ).
Command syntax
The basic command syntax for getting the status information of the disk-buffer files used in syslog-ng PE looks like the following:
/opt/syslog-ng/bin/dqtool info DISK-BUFFER_FILE
Example commands
The following example commands describe how you can get the status information of two different types of disk-buffer files (namely, empty normal disk-buffer files, and non-empty reliable disk-buffer queue files).
Example commands for empty, normal disk-buffer files, and non-empty, reliable disk-buffer queue files
-
Empty, normal disk-buffer file
/opt/syslog-ng/bin/dqtool info /opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00000.qf
Disk-buffer state loaded; filename='/opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00000.qf', number_of_messages='0'
-
Non-empty, reliable disk-buffer queue file
/opt/syslog-ng/bin/dqtool info /opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00000.rqf
Reliable disk-buffer state loaded; filename='/opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00000.rqf', number_of_messages='10'
One-liner command to get the state of disk-buffer files in the default directory
You can use the following one-liner command to get the state of disk-buffer files in the default directory:
for qfile in /opt/syslog-ng/var/*.?(r)qf ; do /opt/syslog-ng/bin/dqtool info $qfile 2>&1 ; done
This section describes printing the content of the disk-buffer files used in syslog-ng Premium Edition ( syslog-ng PE ).
Command syntax
The command syntax for printing the content of the disk-buffer files used in syslog-ng PE looks like the following:
/opt/syslog-ng/bin/dqtool cat DISK-BUFFER_FILE
Short example output for printed content
Example: short output that shows the printed content of the disk-buffer files used in syslog-ng PE
The following short output example shows the printed content of the disk-buffer files used in syslog-ng PE :
/opt/syslog-ng/bin/dqtool cat /opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00000.rqf
Reliable disk-buffer state loaded; filename='/opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00000.rqf', queue_length='2952', size='-437712'
Jul 31 12:33:48.226 10.21.10.10 <382019-07-31T12:33:36 localhost prg00000[1234]: seq: 0000000838, thread: 0000, runid: 1564569216, stamp: 2019-07-31T12:33:36 PADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADDPADD
...
This section describes orphan disk-buffer files used in syslog-ng Premium Edition ( syslog-ng PE ).
In certain situations (for example, after modifying the disk-buffer configuration or losing the persist information), syslog-ng PE creates a new disk-buffer file instead of using the already existing one. In these situations, the already existing disk-buffer file becomes a so-called orphan disk-buffer file.
NOTE: The syslog-ng PE application does not store messages in orphan disk-buffer files or forward the messages stored in the disk-buffer file.
Discovering the new disk-buffer files (orphan disk-buffer files)
To discover orphan disk-buffer files, get the list of disk-buffer files from the persist file, then compare the list with the contents of the disk-buffer files' saving directory.
For more information about how you can get the list of disk-buffer files from the persist file, see Getting the list of disk-buffer files).
Example: difference between the list of disk-buffer files from the persist file and the content of the disk-buffer files' saving directory
The following examples show the difference between the list of disk-buffer files from the persist file and the content of the disk-buffer files' saving directory.
Disk-buffer file list from persist file:
afsocket_dd_qfile(stream,10.21.10.112:514) = { "queue_file": "/opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00001.rqf" }
Disk-buffer files' saving directory content:
# ls -l /opt/syslog-ng/var/*qf
-rw------- 1 root root 2986780 Jul 31 12:30 /opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00000.qf
-rw------- 1 root root 2000080 Jul 31 12:31 /opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00000.rqf
-rw------- 1 root root 4096 Aug 1 11:09 /opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00001.rqf
The disk-buffer files syslog-ng-00000.qf and syslog-ng-00000.rqf don't exist in the persist file. These two files are the orphan disk-buffer files.
For more information about orphan disk-buffer files and how to process the messages in orphan disk-buffer files using a separate syslog-ng PE instance, see How to process messages from an orphan disk-buffer file using a separate syslog-ng PE instance.
This section describes how to read messages from an orphan disk-buffer file by using a separate syslog-ng Premium Edition ( syslog-ng PE ) process running parallel to the already running syslog-ng PE instance.
Orphan disk-buffer files
In certain situations (for example, after modifying the disk-buffer configuration or losing the persist information), syslog-ng PE creates a new disk-buffer file instead of using the already existing one. In these situations, the already existing disk-buffer file becomes a so-called orphan disk-buffer file.
NOTE: The syslog-ng PE application does not store messages in orphan disk-buffer files or forward the messages stored in the disk-buffer file.
Processing the messages from an orphan disk-buffer file by using a separate syslog-ng PE instance
When syslog-ng PE creates orphan disk-buffer files, you can start a separate syslog-ng PE instance parallel to the syslog-ng PE instance already running, and use the following resolution process to process the messages in the orphan disk-buffer file.
|
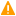
|
Caution:
Before starting a separate syslog-ng PE instance to process the messages from the orphan disk-buffer file, consider the following:
- During the resolution process, a separate syslog-ng PE instance will be started with its temporary files beside the syslog-ng PE instance already running.
- An incorrect startup command and incorrect configurations may cause issues for the syslog-ng PE instance already running.
- The disk-buffer file stores processed log messages in the format in which they would have been sent out to the destination.
- The disk-buffer file doesn't store information about the destination.
|
To process the messages from an orphan disk-buffer file using a separate syslog-ng PE instance,
-
Identify the orphan disk-buffer files and make a record of them. For more information, see How to get information about disk-buffer files.
It is important to know the type of the disk-buffer file. Disk-buffer file types can be normal (.qf) or reliable (.rqf).
In the examples during this process, the /opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00005.rqf orphan reliable disk-buffer file is used.
-
Determine the destination of the logs. The content of the disk-buffer may help you determine the logs' destination. For more information, see How to get information about disk-buffer files.
In the examples during this process, the destination 10.21.10.20 is used with the standard network() port 514.
-
Create a directory for the temporary instance. In the examples during this process, the /tmp/qdisk directory is used.
mkdir /tmp/qdisk
|

|
Caution:
Make sure that there is sufficient disk space in the directory. The minimum recommended disk space in the directory is equal to the size of the orphan disk-buffer file. |
If you want to use a different temporary directory (that is, other than /tmp/qdisk), create a symbolic link between /tmp/qdisk and the temporary directory you want to use with ln -s /path/to/tempdir /tmp/qdisk. This will allow you to use the commands in this resolution process.
If you will not use a different temporary directory, use the /tmp/qdisk temporary directory in the example commands and file names.
-
Create the configuration file /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.conf for the temporary instance with the following content.
Example: creating the /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.conf configuration file for the temporary instance
@version:7.0
@include "scl.conf"
options {
keep-hostname(yes);
keep-timestamp(yes);
};
destination d_destination {
# ADD YOUR DESTINATION HERE
};
log {
destination(d_destination);
};
-
Add your destination statement with disk-buffer() to the configuration file. You can copy the destination statement from your running syslog-ng PE configuration.
|

|
Caution:
Add the dir() option and set the disk-buffer file's destination directory to the temporary directory (that is, /tmp/qdisk) in your destination statement. |
Example: adding the destination statement with disk-buffer() to the configuration file
network("10.21.10.20"
disk-buffer(
disk-buf-size(1048576)
reliable(yes)
dir(/tmp/qdisk/)
);
-
Start the temporary syslog-ng PE instance in the foreground.
syslog-ng -Fe -f /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.conf -R /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.persist -c /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.ctl
The syslog-ng PE application will log to the console, so you will see any potential error that may occur during startup.
The following example output displays that an empty disk-buffer file has been created and the connection to the remote destination has been established.
Example: output displaying newly created empty disk-buffer file and connection established to remote destination
Follow-mode file source not found, deferring open; filename='/no_such_file_or.dir'
Reliable disk-buffer state saved; filename='/tmp/qdisk/syslog-ng-00000.rqf', qdisk_length='0'
No server license found, running in client mode;
syslog-ng starting up; version='7.0.20', cfg-fingerprint='eaa03b9efb88b87d7c1b0ce7efd042ed8ac0c013', cfg-nonce-ndx='0', cfg-signature='c0327a7f7e6418ce0399a75089377dfb662bb072'
FIPS information; FIPS-mode='disabled'
Syslog connection established; fd='7', server='AF_INET(10.21.10.20:514)', local='AF_INET(0.0.0.0:0)'
-
To stop syslog-ng PE , press CTRL+C.
-
Overwrite the empty disk-buffer file with the orphan disk-buffer file.
mv /opt/syslog-ng/var/syslog-ng-00005.rqf /tmp/qdisk/syslog-ng-00000.rqf
-
Start syslog-ng PE using the command used in Start the temporary syslog-ng PE instance in the foreground step.
syslog-ng -Fe -f /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.conf -R /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.persist -c /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.ctl
-
Open another terminal and check the progress by using one of the following methods.
-
Checking the number of stored logs in the disk-buffer (that is, the last number from the output).
/opt/syslog-ng/sbin/syslog-ng-ctl stats -c /tmp/qdisk/qdisk.ctl | grep 'dst.*queued'
-
Checking the status of the disk-buffer file.
/opt/syslog-ng/bin/dqtool info /tmp/qdisk/syslog-ng-00000.rqf
An empty disk-buffer file will look similar to this:
Example: empty disk-buffer file status message
When checking the status of the disk-buffer files, the terminal will display a similar status message for an empty disk-buffer file:
Reliable disk-buffer state loaded; filename='/tmp/qdisk/syslog-ng-00000.rqf', queue_length='0', size='0'
-
Press CTRL+C to stop syslog-ng PE .
-
Check the state of the orphan disk-buffer file. For more information, see How to get information about disk-buffer files.
-
If you have more than one orphan disk-buffer file, repeat the steps following the syslog-ng PE stop (that is, the steps beginning from overwriting the empty disk-buffer file with the orphan disk-buffer file) for each orphan disk-buffer file.
-
Remove the temporary directory.
Example: command for removing the temporary directory
The following command removes the /mp/qdisk temporary directory:
rm -rf /tmp/qdisk

