Use the Active Roles Administration Center to view or modify the tenant type of an existing Azure AD tenant. This is useful if you need to change the default domain settings of an Azure tenant due to an IT or organizational change.
NOTE: Consider the following limitations when modifying the properties of the selected Azure AD tenant:
-
If you set the tenant type of an on-premises or hybrid Azure AD to Federated Domain or Synchronized Identity Domain, then the Azure properties fields of the objects (Azure users, Azure guest users, groups and contacts) in the Azure tenant will be disabled and cannot be edited in the Active Roles Web Interface.
-
You cannot modify the tenant ID and the authentication settings of the Azure AD tenant.
To view or modify the Azure AD tenant properties
-
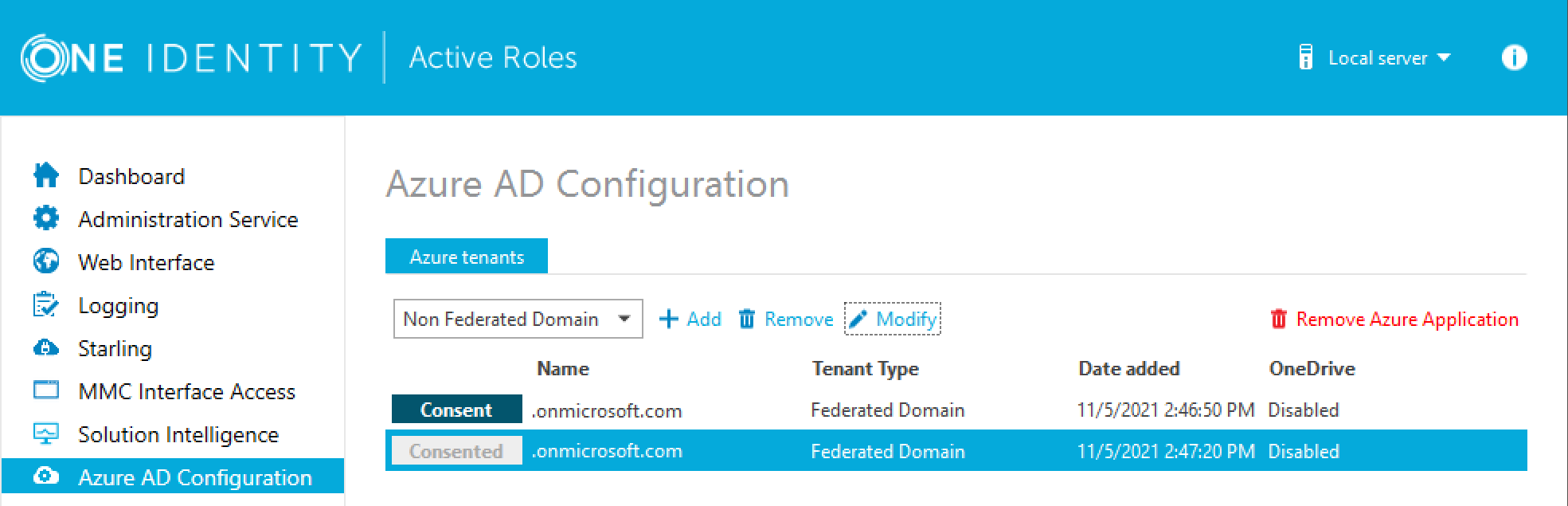
In the [Product Name] Configuration Center, on the left pane, click Azure AD Configuration.
The list of existing Azure AD tenants appears.
-
Select the Azure AD tenant you want to view or modify, then click Modify.
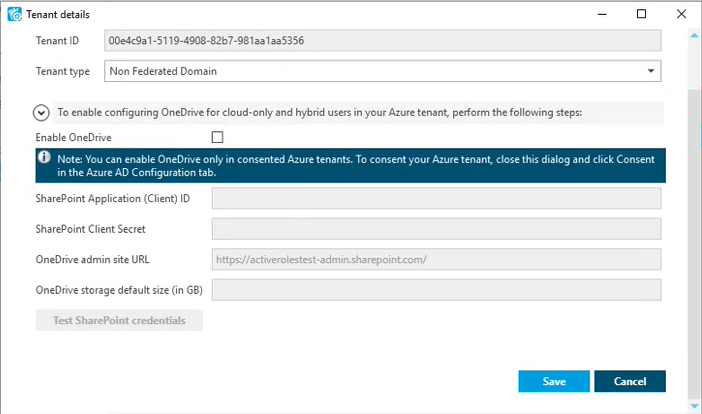
The Tenant details window appears.
-
(Optional) To change the domain type of the Azure tenant, select the applicable type from the Tenant type drop-down list.
-
Non-Federated Domain: When selected, on-premises domains are not registered in Azure AD, and Azure AD Connect is not configured. Azure users and Azure guest users are typically created with the onmicrosoft.com UPN suffix.
-
Federated Domain: On-premises domains are registered in Azure AD and Azure AD Connect. Also, Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) is configured. Azure users and Azure guest users are typically created with the UPN suffix of the selected on-premises domain.
-
Synchronized Identity Domain: On-premises domains may or may not be registered in Azure AD. Azure AD Connect is configured. Azure users and Azure guest users can be created either with the selected on-premises domain, or with the onmicrosoft.com UPN suffix.
-
(Optional) To enable, disable or modify the provisioned OneDrive storage of the Azure tenant, select or deselect Enable OneDrive, and (when selected), configure the SharePoint and OneDrive settings listed in the Tenant details window. For more information on configuring OneDrive storage in an Azure tenant, see Enabling OneDrive in an Azure tenant.
-
To close the Tenant details window without any changes, click Cancel. To apply your changes, click Save.
You can use the Active Roles Configuration Center to delete an Azure AD tenant. This is typically required when an Azure tenant and its directory objects become obsolete because of organizational reasons.
To remove an Azure AD tenant
-
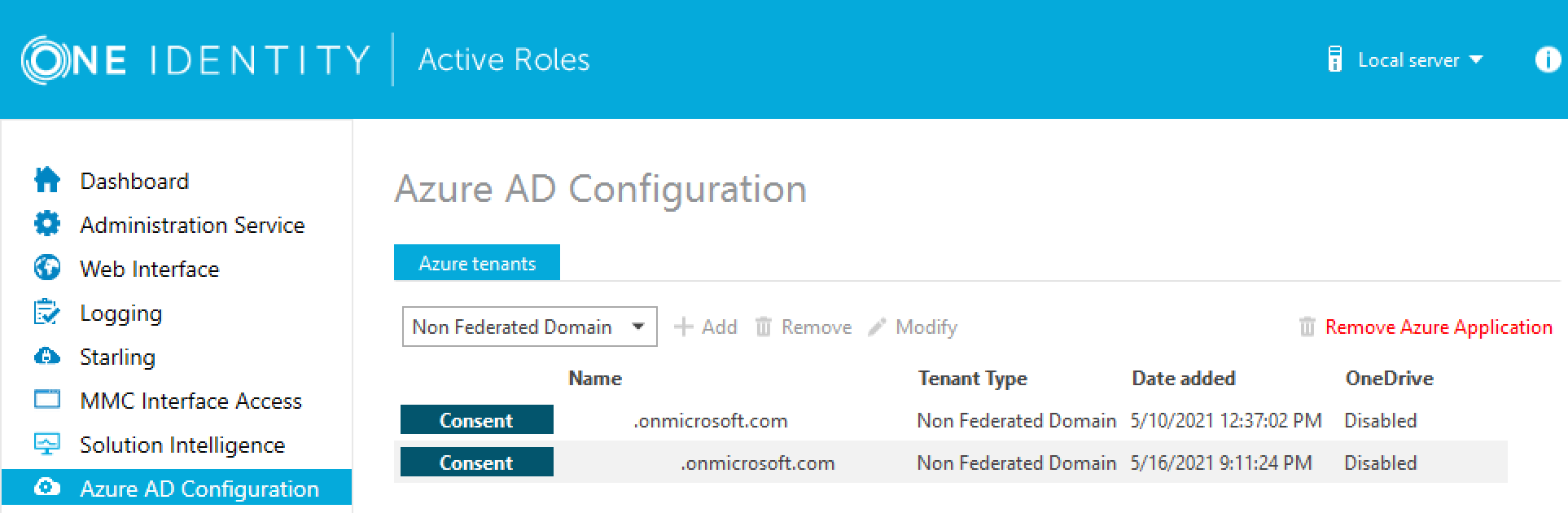
In the [Product Name] Configuration Center, on the left pane, click Azure AD Configuration.
The list of existing Azure tenants appears.
-
On the Azure AD Configuration page, from the list of Azure tenants, select the tenant that you want to remove.
-
Click Remove.
-
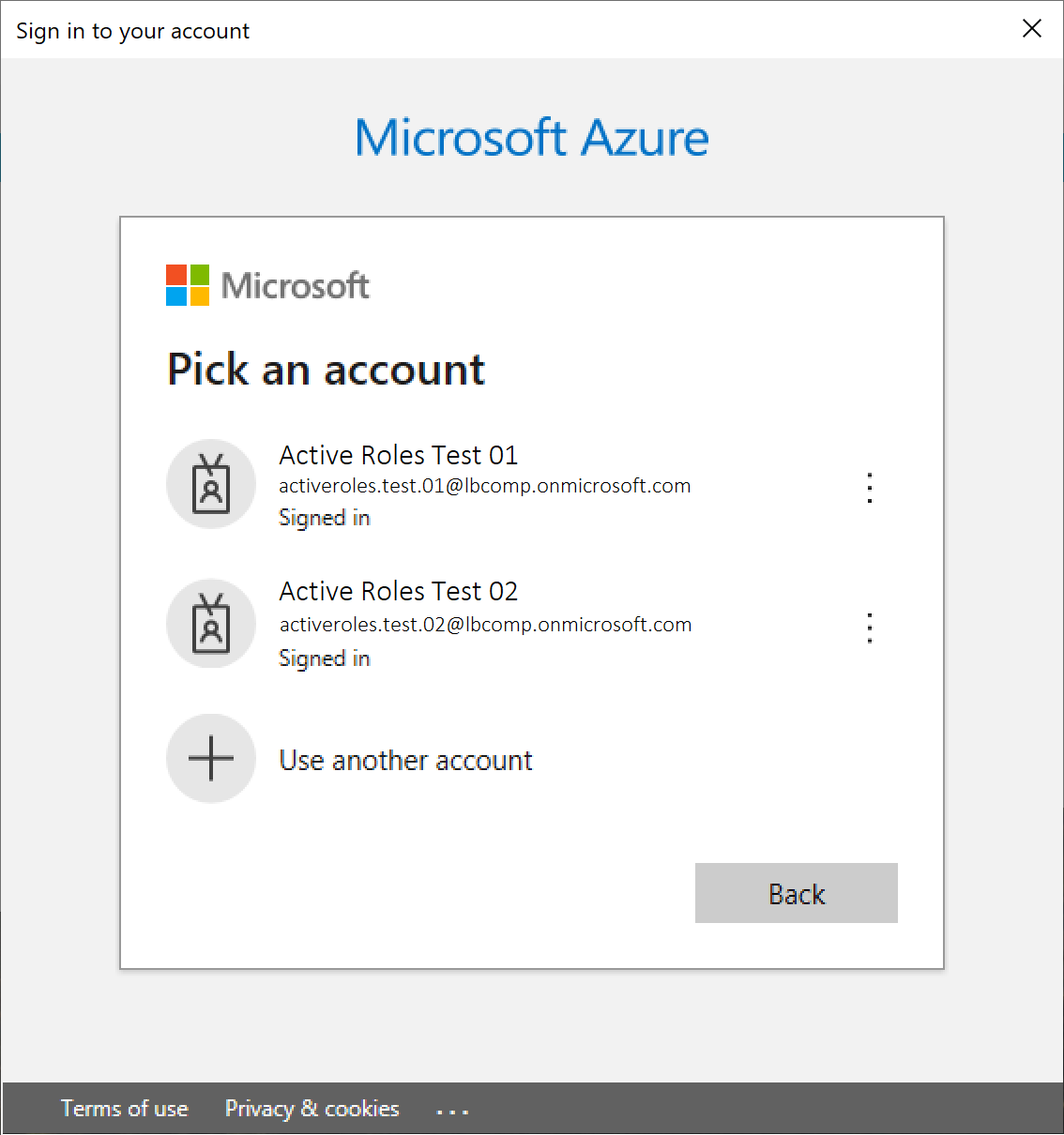
Authenticate your Azure AD administrator account.
-
If you already used one or more Azure AD administrator accounts on your PC, select your account from the Pick an account list, then provide the account password. If you do not find your account in the list, specify your account by clicking Use another account.
-
If you have not used any Azure AD administrator accounts yet on the PC (for example, because you are configuring a fresh Active Roles installation), specify your account user name in the Sign in field, then provide your password.

NOTE: Make sure to specify the account used for adding the Azure tenant (that is, the account name listed under the Name column of the Azure tenant). Authenticating with another account will result in an error.
-
The Azure tenant and all the related domains and applications are then deleted upon successful login.
-
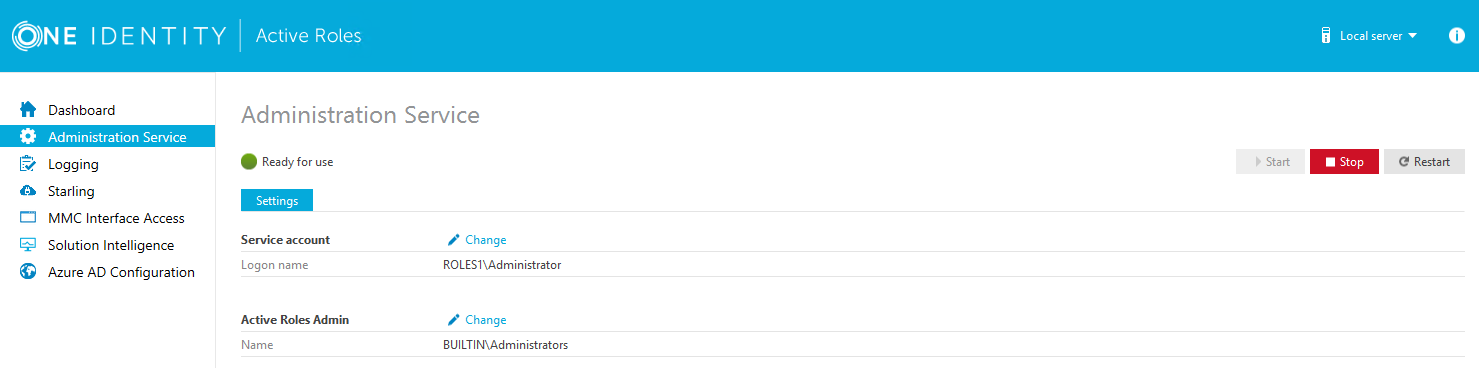
To apply the changes, you must restart the Administration Service, as indicated on the user interface. To restart the Administration Service, open the Configuration Center, click Administration Service on the left pane, then either click Restart, or first click Stop and then Start.
-
(Optional) If you want to force the deletion of the Active Roles Azure application on the Azure Portal for the removed Azure tenant, click Remove Azure Application and log in with the credentials of the removed Azure tenant.
This is typically recommended as an extra housekeeping and security measure if the removed Azure tenant has been previously managed either in earlier Active Roles versions or on other machines as well, but the Azure tenant has not been removed from those Active Roles installations prior to uninstalling them (leaving their client secret intact on the Azure Portal).
|
|
CAUTION: Using the Remove Azure Application option will result in all Active Roles installations losing access to the specified Azure tenant. If this happens, users managing the Azure tenant in another Active Roles installation (for example, on another machine) can regain access to the Azure tenant if they:
-
Remove the Azure tenant in the Azure AD Configuration tab of their Active Roles Configuration Center.
-
Add the Azure tenant again, as described in Configuring a new Azure tenant and consenting Active Roles as an Azure application. |
-
To confirm removal, check if the removed Azure tenant has disappeared from the list of Azure tenants in the Azure AD Configuration page of the Active Roles Configuration Center, and from the Directory Management > Tree > Azure node of the Active Roles Web Interface.
Active Roles Management Shell enables you to perform the following configuration tasks to manage Hybrid AD:
Use the Active Roles Management Shell to add an Azure AD tenant. To do so, run the New-QADAzureConfigObject cmdlet on the Management Shell interface.
Description
New-QADAzureConfigObject lets you add an Azure AD tenant to Active Directory.
Usage Recommendations
Use New-QADAzureConfigObject to add an Azure AD tenant using the tenant ID provided by Microsoft for the default tenant (created at the time of the Microsoft Azure subscription).
Syntax
New-QADAzureConfigObject -type 'AzureTenant' -name 'Azuretenantname' -AzureTenantId 'AzureTenantGUID' -AzureTenantDescription 'AzureTenantDescription' -AzureAdminUserID 'AzureGlobalAdminUserID' -AzureAdminPassword 'AzureGlobalIDPassword' -AzureADTenantType 'AzureTenantType'
Parameters
The New-QADAzureConfigObject cmdlet has the following parameters.
-
type (string): Specifies the object class of the directory object to be created (such as User or Group). The cmdlet creates a directory object of the object class specified with this parameter.
Table 6: Parameter: type (string)
|
Required |
true |
|
Position |
named |
|
Accepts pipeline input |
false |
|
Accepts wildcard characters |
false |
-
name (string): Sets the name attribute to the value of this parameter on the new object created by New-QADAzureConfigObject in the directory.
Table 7: Parameter: name (string)
|
Required |
true |
|
Position |
named |
|
Accepts pipeline input |
false |
|
Accepts wildcard characters |
false |
-
AzureTenantId (string): Specifies the Azure AD tenant ID obtained from the default tenant (created after subscribing to Microsoft Azure).
NOTE: The Azure AD ID value configured for this parameter must match the tenant ID configured on the Azure AD side. Otherwise, attempts to create an Azure AD application or manage Azure AD objects will fail.
Table 8: Parameters: AzureTenantId (string)
|
Required |
true |
|
Position |
named |
|
Accepts pipeline input |
false |
|
Accepts wildcard characters |
false |
-
AzureTenantDescription: Specifies the required description of the Azure AD tenant.
Table 9: AzureTenantDescription
|
Required |
false |
|
Position |
named |
|
Accepts pipeline input |
false |
|
Accepts wildcard characters |
false |
-
AzureAdminUserID: Specifies the administrative user name for Microsoft Azure AD.
NOTE: The administrative user must have the required privileges (for example, License Administrator, User Administrator or Groups Administrator roles) to perform license management or Azure user, guest user, and group management.
For more information on the available privileges and for an overview of the various Azure and Azure AD administrative roles, see Azure AD built-in roles and Classic subscription administrator roles, Azure roles, and Azure AD roles in the official Microsoft documentation.
Table 10: Parameters: AzureAdminUserID
|
Required |
true |
|
Position |
named |
|
Accepts pipeline input |
false |
|
Accepts wildcard characters |
false |
-
AzureAdminPassword: Specifies the administrative user password for Microsoft Azure AD.
Table 11: Parameters: AzureAdminPassword
|
Required |
true |
|
Position |
named |
|
Accepts pipeline input |
false |
|
Accepts wildcard characters |
false |
-
AzureADTenantType: Specifies the Azure AD tenant type (Federated, Non-Federated, or Synchronized Identity).
NOTE: Make sure that you select the tenant type corresponding to your organization environment.
Table 12: Parameters: AzureADTenantType
|
Required |
true |
|
Position |
named |
|
Accepts pipeline input |
false |
|
Accepts wildcard characters |
false |
| Accepts value |
- Federated
- NonFederated
- SynchronizedIdentity
|
Examples
See the following use cases for examples on how to use this cmdlet.
Example: Creating a new Azure AD tenant with a local user
To create a new Azure AD tenant with a locally logged on user
-
Connect to any available domain controller with the credentials of your local user.
-
Create a new Azure AD tenant with the following New-QADAzureConfigObject cmdlet:
C:\PS> New-QADAzureConfigObject -type 'AzureTenant' -name 'CompanyAzuretenant' -AzureTenantId 'CompanyAzureTenantID' -AzureTenantDescription 'Azure tenant for Company' -AzureAdminUserID 'AzureAdminUser1' -AzureAdminPassword 'AzureAdminPassword1’ -AzureADTenantType 'AzureTenantType'
Example: Creating a new Azure AD tenant with a specific user and then disconnecting
To create a new Azure AD tenant with a specific user and then disconnect
-
Connect to any available domain controller:
C:\PS> $pw = read-host "Enter password" -AsSecureString
-
Connect to the local Administration Service with a specific user of your choice:
C:\PS> connect-qadService -service 'localhost' -proxy -ConnectionAccount 'company\administrator' -ConnectionPassword $pw
-
Create the new Azure AD tenant:
C:\PS> New-QADAzureConfigObject -type 'AzureTenant' -name 'CompanyAzuretenant' -AzureTenantId 'CompanyAzureTenantID' -AzureTenantDescription 'Azure tenant for Company' -AzureAdminUserID 'AzureAdminUser1' -AzureAdminPassword 'AzureAdminPassword1’ -AzureADTenantType 'AzureTenantType'
-
Once the Azure AD tenant is created, disconnect your user:
C:\PS> disconnect-qadService







