-
제목
Active Roles service account minimum permissions -
설명
What are the requirements to assign minimum permissions so that Active Roles will function?
NOTE: For the latest up-to-date information, please refer to the Active Roles Technical Documentation. -
해결 방안
Required Active Directory Permissions and AccessAs Active Roles performs operations on objects on behalf of delegated users, the Active Roles service account which is used to manage the Active Directory domain requires adequate permissions. All internal test scenarios and the One Identity Active Roles Support Model all assume that the domain is being managed using an account that is a member of the Domain Admins role group. If this configuration is not leveraged, then guidance and documentation provided by the One Identity Support Team may not be relevant.
It is possible to separate the tasks performed by the service account from domain management by specifying distinct accounts for the service and for managing the domain. In this configuration scenario, the service account can be configured to run with the minimum permissions specified below, but the proxy account/domain management account should be a member of the Domain Admins role group in order to stay within the One Identity Active Roles Support Model.
If membership in the Domain Admins role group is not possible, then the proxy account must be a member of the Account Operators role group. Additionally, the domain management account MUST have at an absolute minimum:
1. Replicating Directory Changes and Reanimate tombstones extended rights on the domain, as well as List contents and Read all properties on all Active Directory Directory objects in the desired containers: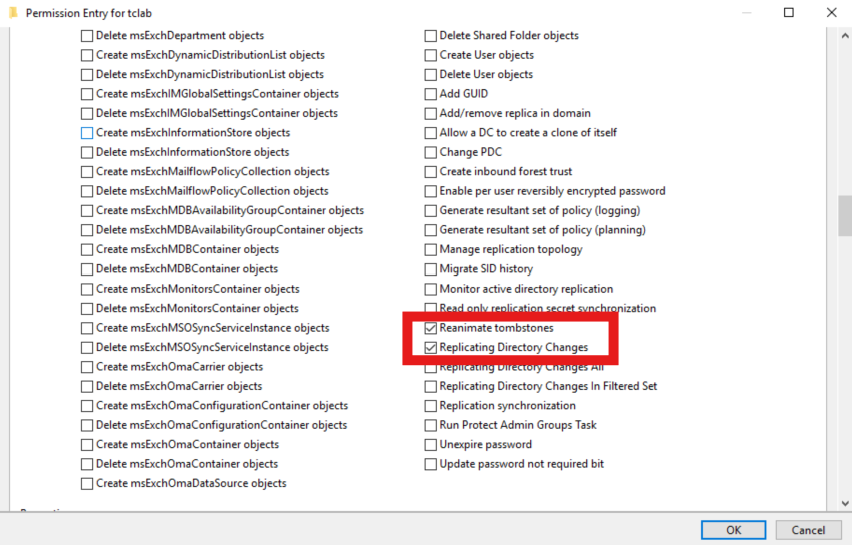
2. In addition to Reanimate Tombstones delegated permission, the following KB from Microsoft outlines the additional steps that must be taken for the Deleted Items to show in Active Roles:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/windows-server/active-directory/non-administrators-view-deleted-object-containerNOTE: It is a requirement for Active Roles to be able to receive and process DirSync notifications that the domain management account must have List contents and Read all properties allowed for This object and all descendant objects as per the attached screenshot. It is not possible to limit this access to a specific descendant object class. Without this list and read access, Active Roles will not receive DirSync notifications when Active Directory objects are changed. This will directly impact operations that require those notifications, just as Active Roles Dynamic Group updates.
NOTE: The Reanimate tombstones extended right is necessary to allow visibility into the Active Directory Recycle Bin. Active Roles requires this because DirSync notifications will come from the destination container - which, in the case of a deleted item, is the Active Directory Recycle Bin. Without this extended right, Active Roles will not be able will not be able to trace object deletions via DirSync and will not clean up Managed Units and Dynamic Groups which explicitly reference deleted objects.
The service account credential has five main roles, two of which are optional:- Accessing local resources on the Active Roles Administration Service host.
- Creating the Service Connection Point in Active Directory (this functionality is non-critical and won't prevent the service from functioning as expected - instead, Active Roles clients won't automatically discover the Active Roles Administration Service. Active Roles Clients will still be able to connect if the service name or IP address is known).
- All script modules are executed under the security context of the Active Roles Service Account.
- Connecting to the Microsoft SQL database (this is optional, as a SQL Authentication credential may also be specified).
- Synchronizing native permissions to Active Directory (this is required only if Active Roles is configured to do so).
NOTE: For the necessary Microsoft SQL Server permissions, please see the Active Roles Installation Guide under the section titled SQL Server permissions
Access to the Administration Service ComputerThe service account must be a member of the local Administrators group on the computer running the Active Roles Administration service.
Service Publication in Active Directory
For Active Roles clients to discover available Active Role services, the service account must be able to publish itself in Active Directory. On the Aelita sub-container, under the System container in the domain, grant the following rights:- Create Container Objects
- Create ServiceConnectionPoint Objects
Access to Managed Domains
The service account must have at least Read Permissions in any Managed Domain. In addition, the service account must have Modify Permissions rights on the Active Directory objects and containers where the Active Roles security synchronization feature will be utilized.Access to Exchange OrganizationsTo manage Exchange recipients on Exchange Server 2019, 2016, or 2013, the service account or the override account must be configured to have sufficient rights in the Exchange organization. The rights must be delegated to the service account if an override account is not used; otherwise, the rights must be delegated to the override account.
To configure the service account or the override account
1. Add the account to the Recipient Management role group.
For instructions for Exchange 2019, see “Add Members to a Role Group” at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-in/library/jj657492(v=exchg.160).aspx .
2. Add the account to the Account Operators domain security group.
3. Enable the account to use remote Exchange Management Shell.
For instructions for Exchange 2019, see “Enable Remote Exchange Management Shell for a User” at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd335083(v=exchg.160).aspx .
4. Ensure that the account can read Exchange configuration data (see Permission to read Exchange configuration data).
5.Restart the Administration Service after you have changed the configuration of the account: Start Active Roles Configuration Center (see “Running Configuration Center” in the Active Roles Administration Guide), go to the Administration Service page in the Configuration Center main window, and then click the Restart button at the top of the Administration Service page.
NOTE:- For instructions for Exchange 2013, 2016, and 2019, see the relevant Microsoft Exchange pages at https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library .
- ARS service account must be a part of Recipient Management group to run exchange hybrid commands.
Permission to read Exchange configuration dataTo perform Exchange recipient management tasks, Active Roles requires read access to Exchange configuration data in Active Directory. This requirement is met if the service account (or the override account, if specified) has administrator rights (for example, is a member of the Domain Admins or Organization Management group). Otherwise, you should give the account the Read permission in the Microsoft Exchange container. You can do this by using the ADSI Edit console as follows (these instructions apply to the ADSI Edit console that ships with Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, or Windows Server 2022):
- Open the ADSI Edit console and connect to the Configuration naming context.
- In the ADSI Edit console, navigate to the Configuration | Services container, right-click Microsoft Exchange in that container, and then click Properties.
- On the Security tab in the Properties dialog box that appears, click Advanced.
- On the Permissions tab in the Advanced Security Settings dialog box, click Add.
- On the Permission Entry page, configure the permission entry:
- Click the Select a principal link, and select the desired account.
- Verify that the Type box indicates Allow.
- Verify that the Applies onto box indicates This object and all descendant objects.
- In the Permissions area, select the List contents and Read all properties check boxes.
- Click OK.
- Click OK to close the Advanced Security Settings dialog box, and then click OK to close the Properties dialog box.
Support for remote Exchange Management ShellWhen performing Exchange recipient management tasks on Exchange Server 2013 or later, Active Roles uses remote Exchange Management Shell to communicate with Exchange Server, so you do not need to install the Exchange management tools on the computer running the Administration Service.
To use remote Exchange Management Shell, the Administration Service must be running on a computer that has:
- Windows Server 2016 or a later.
- Microsoft .NET Framework 4.7.2 installed see https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=53321).
- Windows Management Framework 5.1 installed (see “Windows Management Framework 5.1” at https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54616).
Remote Shell also requires the following:
- TCP port 80 must be open between the computer running the Administration Service and the remote Exchange server.
- The user account the Administration Service uses to connect to the remote Exchange server (the service account or the override account) must be enabled for remote Shell. To enable a user account for remote Shell, update that user account by using the
Set-Usercmdlet with the RemotePowerShellEnabled parameter set to $True. - Windows PowerShell script execution must be enabled on the computer running the Administration Service. To enable script execution for signed scripts, run the Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned command in an elevated Windows PowerShell window.
-
변경 요청
223920 -
첨부 파일
