Control access rights are provided as an optional setting during the installation of the Defender Administration Console. Control access rights can be combined with the delegated administration privileges assigned to security groups or users.
The Defender control access rights act as an additional layer of administration security, allowing you to enable or disable the token-related buttons provided below the Tokens list on the Defender tab in the Properties dialog for a Defender user:
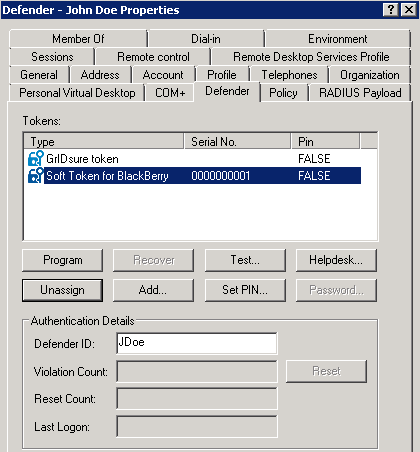
With control access rights, you can enable or disable the following buttons:
- Program Allows you to program the selected token for the user.
- Recover Unlocks the selected token.
- Test Starts a non-intrusive test to verify the token’s response.
- Helpdesk Allows you to reset the token or assign a temporary token response to the user.
- Unassign Unassigns the selected token from the user.
- Add Assigns a new token to the user.
- Set PIN Sets a PIN for the selected token.
- Password Allows you set up a new or change the existing Defender password for the user.
To assign control access rights to users
- Use the Defender Administration Console to enable the Security tab for the Defender users. By default, the Security tab is disabled.
Do the following:
- On the computer where the Defender Administration Console is installed, open the Active Directory Users and Computers tool (dsa.msc).
- In the left pane, expand the appropriate domain node, and then click to select the Defender container.
- On the menu bar, click View, and then click Advanced Features.
- In the left pane (console), locate the organizational unit that holds the Defender users to whom you want to assign control access rights.
- Right-click the OU, and then on the shortcut menu click Properties.
- In the dialog box that opens, click the Security tab, and then click Advanced.
- Click Add to add the security group or user account.
- In the Permission Entry for Users dialog box, use the following elements:
- Apply on Select the target for the permissions you are going to select (user objects or descendant user objects).
- Permissions list Select the check boxes next to the permissions you want to assign.
- Click OK to apply your changes.
To remove control access rights from a group of users
- In the Advanced Security Settings dialog box, click to select the appropriate entry in the Permission entries list.
- Click the Remove button below the list, and then click OK.
