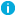
multi-line-prefix()
| Type: | regular expression starting with the ^ character |
| Default: | empty string |
Description: Use the multi-line-prefix() option to process multi-line messages, that is, log messages that contain newline characters (for example, Tomcat logs). Specify a string or regular expression that matches the beginning of the log messages (always start with the ^ character). Use as simple regular expressions as possible, because complex regular expressions can severely reduce the rate of processing multi-line messages. If the multi-line-prefix() option is set, syslog-ng OSE ignores newline characters from the source until a line matches the regular expression again, and treats the lines between the matching lines as a single message. See also the multi-line-garbage() option.
|
|
TIP:
|
Example: Processing Tomcat logs
The log messages of the Apache Tomcat server are a typical example for multi-line log messages. The messages start with the date and time of the query in the YYYY.MM.DD HH:MM:SS format, as you can see in the following example.
2010.06.09. 12:07:39 org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina start
SEVERE: Catalina.start:
LifecycleException: service.getName(): "Catalina"; Protocol handler start failed: java.net.BindException: Address already in use null:8080
at org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector.start(Connector.java:1138)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService.start(StandardService.java:531)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer.start(StandardServer.java:710)
at org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina.start(Catalina.java:583)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap.start(Bootstrap.java:288)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.commons.daemon.support.DaemonLoader.start(DaemonLoader.java:177)
2010.06.09. 12:07:39 org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina start
INFO: Server startup in 1206 ms
2010.06.09. 12:45:08 org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol pause
INFO: Pausing Coyote HTTP/1.1 on http-8080
2010.06.09. 12:45:09 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService stop
INFO: Stopping service Catalina
To process these messages, specify a regular expression matching the timestamp of the messages in the multi-line-prefix() option. Such an expression is the following:
source s_file{file("/var/log/tomcat6/catalina.2010-06-09.log" follow-freq(0) multi-line-mode(regexp) multi-line-prefix("[0-9]{4}\.[0-9]{2}\.[0-9]{2}\.") flags(no-parse));};
};
Note that flags(no-parse) is needed to prevent syslog-ng OSE trying to interpret the date in the message.