Active Roles offers these key security and administration elements:
- Trustees Users or groups that have permissions to administer users, groups, computers, or other directory objects.
- Permissions and Roles Permissions are grouped in Access Templates (roles) to define how a Trustee can manage directory objects.
- Managed Units Collections of directory objects delegated to Trustees for administration.
The directory administrator defines which users or groups are designated as Trustees, which roles and permissions are assigned to Trustees, and what objects are included in Managed Units.
Managed Units are used to determine the directory objects that a Trustee can administer. As a Trustee, you can administer Managed Units for which you have assigned permissions. Managed Units containing objects you are authorized to administer are displayed under Managed Units in the console tree.
When you select a Managed Unit in the console tree, the details pane displays a list of objects included in that Managed Unit. To administer objects, select them from the list and use the commands on the Action menu.
If a Managed Unit includes a container, such as an Organizational Unit, the container is displayed under the Managed Unit in the console tree. When you select a container in the console tree, the details pane lists all child objects and sub-containers held in that container.
The Active Roles console makes it possible to apply a filter to display only the objects that match the filtering criteria. To apply a filter, select an Active Directory object or container and click the Filter button on the toolbar:  . This displays the Filter Options dialog box where you can set up a filter. After you set up a filter, the filtering criteria immediately take effect on all lists of Active Directory objects in the Active Roles console.
. This displays the Filter Options dialog box where you can set up a filter. After you set up a filter, the filtering criteria immediately take effect on all lists of Active Directory objects in the Active Roles console.
To sort objects in the details pane
- Click a column heading to sort by the contents of that column.
- Click the column heading again to switch between ascending and descending sort order.
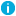
To add or remove columns in the details pane
- On the View menu, click Choose Columns or Add/Remove Columns.
- Do the following, and then click OK:
- To add a column, in Available columns, click the column you want to display, and then click Add.
- To remove a column, in Displayed columns, click the column you want to hide, and then click Remove.
- To re-order columns, click a column name in Displayed columns, and then click Move Up or Move Down to change the position of the column.
|
|
NOTE: In the advanced details pane, you can add or remove columns from a list in the upper sub-pane or in the lower sub-pane: click the list in the sub-pane you want to modify, and then follow the steps above. |
Filter options help you search for particular objects in the details pane. You can view all objects or only objects of selected type, configure the number of items that can be displayed for each folder, or create custom filters using object attributes and LDAP queries.
To select view filter options
- On the View menu, click Filter Options.
- Do one of the following, and then click OK:
- To view all objects, click Show all types of objects. With this option, the filter is turned off.
- To view objects of certain types, click Show only the following types of objects, and select check boxes next to the types of objects you want to view.
- To view objects that match custom filtering criteria, click Create custom filter. Then, Customize and configure your filtering criteria by using the instructions outlined in Steps for building a custom search.
- Optionally, in Maximum number of items displayed per folder, modify the maximum number of objects that can be displayed in the console. The default maximum number of objects displayed in the console is 2,000 objects.
In the Active Roles console you can search for objects of different types using the Find window. To access the Find window, right-click a container and click Find.
From the In list, you can select the container or Managed Unit you want to search. The list includes the container that you selected before activating the Find window. To add containers to the list, click Browse. From the Find list, you can select the type of the objects you want to find.
When you select an object type, the Find window changes accordingly. For example, Users, Contacts, and Groups searches for users, contacts, or groups using criteria such as user name, a note describing a contact, or the name of a group. In the Find list, Active Roles splits the Users, Contacts, and Groups category into three, providing the option for a more streamlined search.
By selecting Custom Search from the Find list, you can build custom search queries using advanced search options:
Using the Find window, you can search for any directory objects, such as users, groups, computers, Organizational Units, printers or shared folders. It is also possible to search for Active Roles configuration objects such as Access Templates, Managed Units, and Policy Objects. When you search for Access Templates, Policy Objects or Managed Units and select an appropriate object type from the Find list, the relevant container appears in the In list.
Once the search has completed, the objects matching the search criteria (search results) are listed at the bottom of the Find window. You can quickly find an object in the search results list by typing a few characters. This will select the first name that matches what you typed.
Once you have found the object, you can manage it by right-clicking the entry in the search results list, and then clicking commands on the shortcut menu.

 . This displays the Filter Options dialog box where you can set up a filter. After you set up a filter, the filtering criteria immediately take effect on all lists of Active Directory objects in the
. This displays the Filter Options dialog box where you can set up a filter. After you set up a filter, the filtering criteria immediately take effect on all lists of Active Directory objects in the 