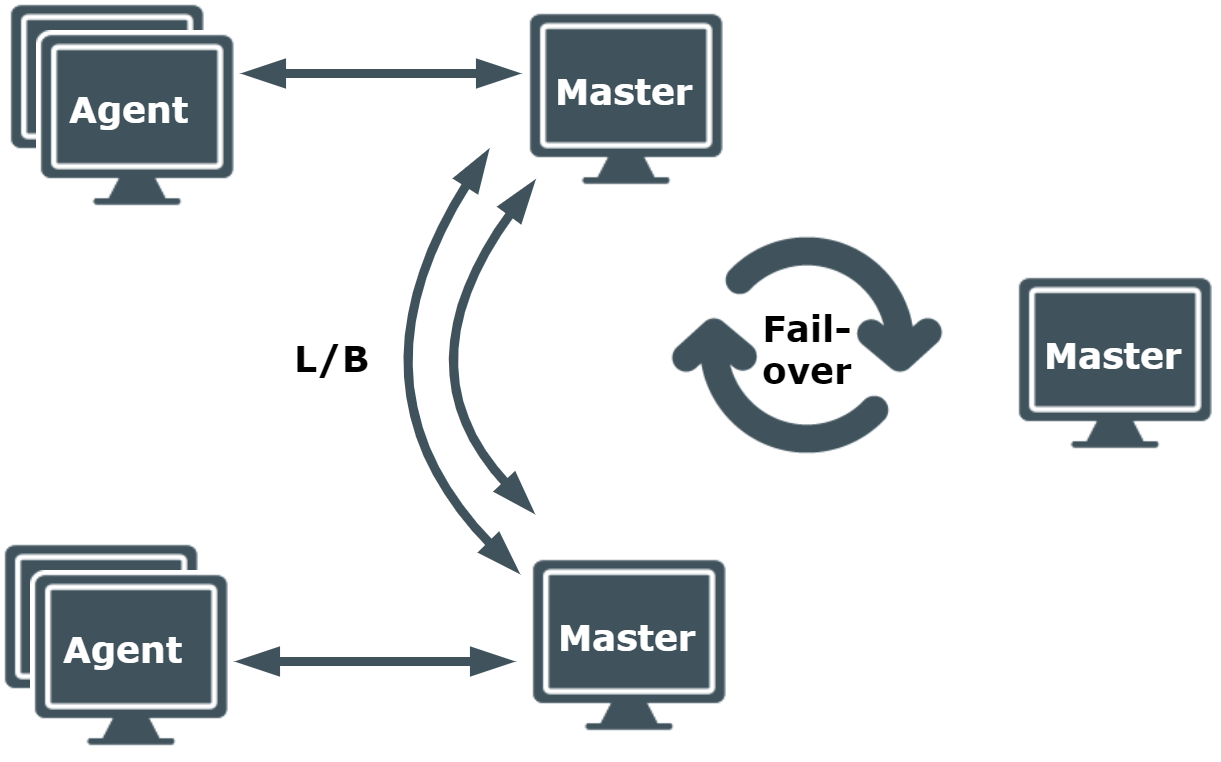
This is an example of how a large business might deploy Privilege Manager for Unix. Some global companies prefer to fragment their requirement and deploy multiple instances as shown in the medium-sized business model.
This example comprises three policy servers, two are balancing the load of multiple agents. This may be necessary if there is a high level of audit and/or a significant volume of requested elevated privilege. Further, there is an additional policy server configured as a failover should one or both policy servers become unavailable.
Figure 5: Large business implementation: Minimum 3 Masters and less than 1000 Agents
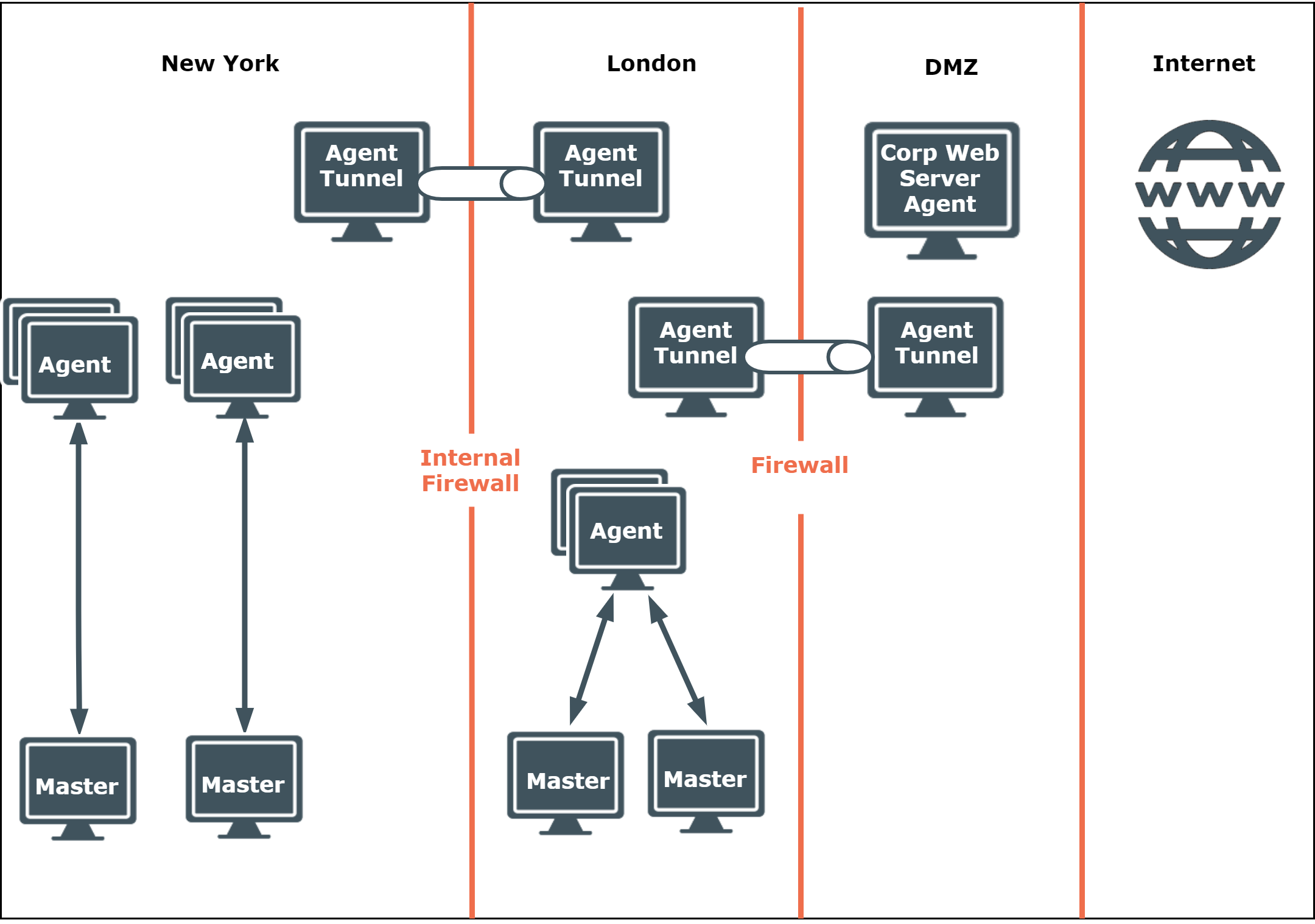
This example is based on an organization with offices in London and New York. Again, as with the medium-sized business example, the web servers and corporate web-based applications reside in a DMZ. The requirement to run commands at an elevated level from inside the firewall remains.
Access to the web server and web applications is predominantly, but not exclusively, from the London office. Privilege Manager for Unix tunnelling components are used to breach the firewall to the DMZ.
In addition, internal firewalls are located between the offices in London and New York, and tunneling components are deployed to enable access from office to office and indeed from anywhere to the DMZ.
Within each office, multiple policy servers are configured for load balancing, with each policy server serving a number of agents.
Figure 6: Enterprise deployment implementation: Minimum 4 Masters and 1000 Agents and above
You can extend each of the models described above by, for example, adding more policy servers, configuring additional load balancing, assigning dedicated audit, logging and reporting servers. The models provide a small indication of the flexibility and modular way in which you can configure and implement Privilege Manager for Unix to meet the precise requirements of any size business.
Installation and Configuration
This is an overview of the steps necessary to set up your environment to use Privilege Manager for Unix software:
To configure a primary policy server
-
Check the server for installation readiness.
-
Install the Privilege Manager for Unix policy server package.
-
Configure the primary policy server.
-
Join the primary policy server to policy group.
To configure a secondary policy server
-
Check the host for installation readiness.
-
Install the Privilege Manager for Unix policy server package.
-
Configure the secondary policy server.
-
Join the PM Agent to the secondary policy server.
To install the PM Agent on a remote host
-
Check the remote host for installation readiness.
-
Install the Privilege Manager for Unix software on the remote host.
-
Join the PM Agent to the policy server.
The following topics walk you through these steps.
To download the Privilege Manager for Unix software packages
-
Go to https://support.oneidentity.com/privilege-manager-for-unix .
-
On the Product Support - Privilege Manager for Unix page, click Software Downloads under Self Service Tools in the left pane.
-
On the Privilege Manager for Unix - Download Software page, click Download to the right of the version to be downloaded.
For more information about Privilege Manager for Unix native platform install packages, see Installation Packages.
-
Read the License Agreement, select the I have read and accept the agreement option, and click Submit.
-
Download the relevant package from the web page. The Privilege Manager for Unix server package includes the PM Agent and the Sudo Plugin components.


