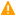
The route of a log message in syslog-ng
Purpose:
The following procedure illustrates the route of a log message from its source on the syslog-ng client to its final destination on the central syslog-ng server.
Figure 1: The route of a log message
Steps:
-
A device or application sends a log message to a source on the syslog-ng client. For example, an Apache web server running on Linux enters a message into the /var/log/apache file.
-
The syslog-ng client running on the web server reads the message from its /var/log/apache source.
-
The syslog-ng client processes the first log statement that includes the /var/log/apache source.
-
The syslog-ng client performs optional operations (message filtering, parsing, and rewriting) on the message, for example, it compares the message to the filters of the log statement (if any). If the message complies with all filter rules, syslog-ng sends the message to the destinations set in the log statement, for example, to the remote syslog-ng server.
Caution: Message filtering, parsing, and rewriting is performed in the order that the operations appear in the log statement.
NOTE: The syslog-ng client sends a message to all matching destinations by default. As a result, a message may be sent to a destination more than once, if the destination is used in multiple log statements. To prevent such situations, use the final flag in the destination statements. For details, see Log statement flags.
-
The syslog-ng client processes the next log statement that includes the /var/log/apache source, repeating Steps 3-4.
-
The message sent by the syslog-ng client arrives from a source set in the syslog-ng server.
-
The syslog-ng server reads the message from its source and processes the first log statement that includes that source.
-
The syslog-ng server performs optional operations (message filtering, parsing, and rewriting) on the message, for example, it compares the message to the filters of the log statement (if any). If the message complies with all filter rules, syslog-ng sends the message to the destinations set in the log statement.
Caution: Message filtering, parsing, and rewriting is performed in the order that the operations appear in the log statement.
-
The syslog-ng server processes the next log statement, repeating Steps 7-9.
NOTE: The syslog-ng application can stop reading messages from its sources if the destinations cannot process the sent messages. This feature is called flow-control and is detailed in Managing incoming and outgoing messages with flow-control.
Modes of operation
The syslog-ng Open Source Edition application has three
Client mode
Figure 2: Client-mode operation
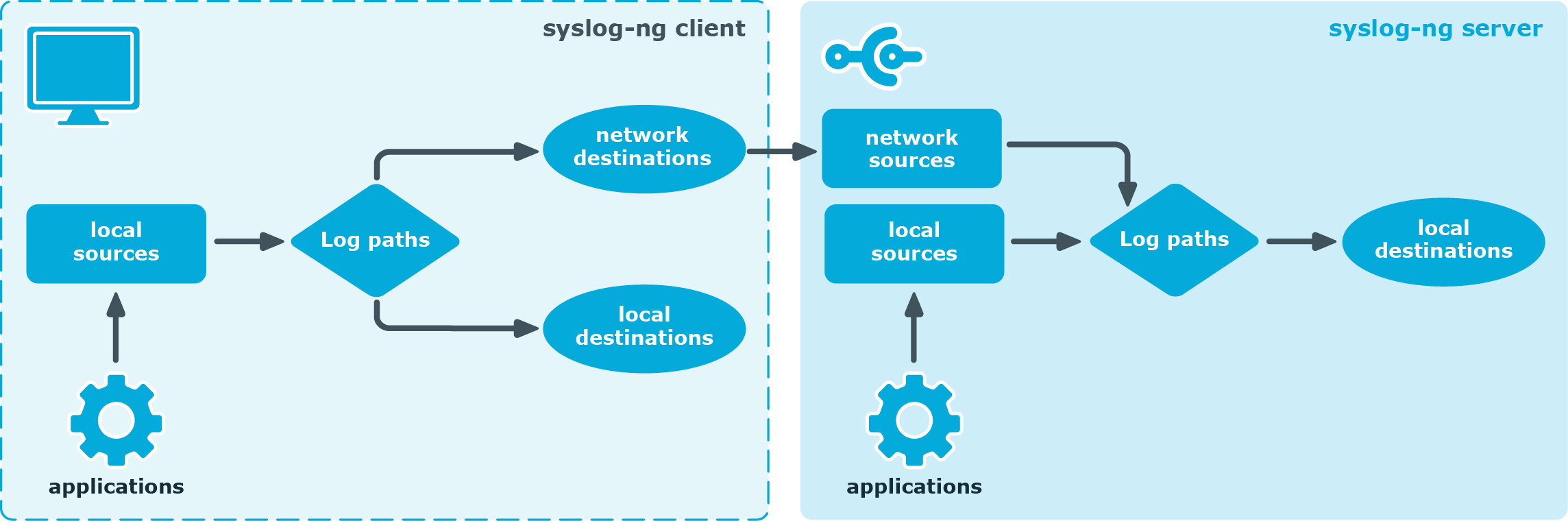
In client mode, syslog-ng collects the local logs generated by the host and forwards them through a network connection to the central syslog-ng server or to a relay. Clients often also log the messages locally into files.
Relay mode
Figure 3: Relay-mode operation
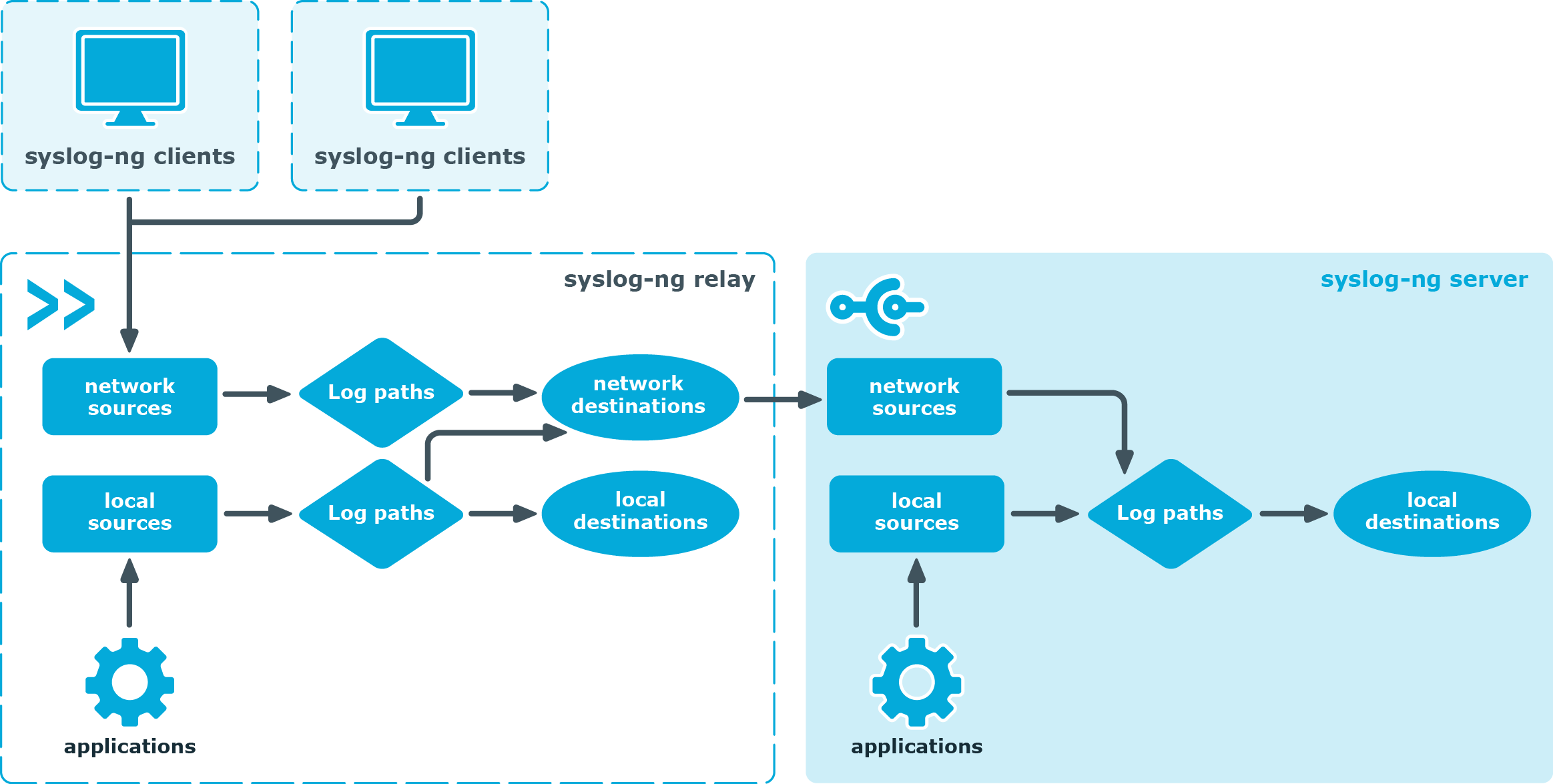
In relay mode, syslog-ng receives logs through the network from syslog-ng clients and forwards them to the central syslog-ng server using a network connection. Relays also log the messages from the relay host into a local file, or forward these messages to the central syslog-ng server.