Default message sources in SSB
The syslog-ng Store Box (SSB) appliance automatically accepts messages from the following built-in sources:
Figure 121: Log > Sources — Default message sources in SSB

-
legacy: Accepts UDP messages using the legacy BSD-syslog protocol on the port 514.
-
tcp: Accepts TCP messages using the IETF-syslog protocol (RFC 5424) on port 601.
-
tls: Accepts TLS-encrypted messages using the IETF-syslog protocol on port 6514. Mutual authentication is required: the client must show a (not necessarily valid) certificate, SSB sends the certificate created with the Welcome Wizard.
-
tcp_legacy: Accepts TCP messages using the BSD-syslog protocol (RFC 3164) on port 514.
NOTE: All default sources have name resolution enabled.
In addition to the default message sources in the previous list, you can also create your own, customized message sources. For the details of the various settings, see Creating new message sources in SSB and its subsections.
Creating new message sources in SSB
The syslog-ng Store Box (SSB) appliance receives log messages from remote hosts via sources. A number of sources are available by default, but you can also create your own, customized message sources, based on the Syslog or SQL protocol.
For details on using the default message sources of SSB, see Default message sources in SSB.
Creating your own, customized message source
If you do not want to use the default message sources available in SSB, you can create your own, customized message source.
To create your own, customized message source
-
Navigate to Log > Sources and click 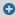 .
.
Figure 122: Log > Sources — Creating new message sources

-
Enter a name for the source into the top field. Use descriptive names (for example, sql_source, or syslog_source ) that help you to identify the source easily.
NOTE: In these sections and subsections, some figures show a custom message source named your-new-source, but you can use any descriptive name to identify your message source.
-
In your new source, select your preferred Source type.
NOTE: When configuring new message sources in SSB, you can configure two source types: Syslog, or SQL.
Figure 123: Two available source types under Log > Sources > <your-new-source>

For further details about each source type, see the following subsections:
Topics:
Configuring your own, customized Syslog type message source
When configuring your own, customized message sources, you can configure two source types: Syslog, or SQL.
For more information about configuring an SQL source type in your own, customized message source, see Configuring your own, customized SQL type message source.
Figure 124: Log > Sources > <your-new-source> — Syslog source type in your own, customized message source
Prerequisites for configuring your own, customized Syslog type message source
Limitations to configuring your own, customized Syslog type message source
Configuration options for your own, customized Syslog type message source
While configuring your own, customized Syslog type message source, you can customize the following:
-
The Listening address and Listening port of your Syslog source type.
-
Transport protocol options, including Incoming log protocol and message format options, and the number of maximum connections under Other source options.
-
Hostname and timestamp-related settings.
-
Monitoring options.
-
Setting the Syslog source type's Encoding under Other options.
For further details on the configuration options, see the following subsections:
Topics:
Configuring the Listening address and Listening port for your Syslog type message source
Under Log > Sources > <your-new-source> > Syslog, you can first customize the Listening address and Listening port for your Syslog type message source.
To configure the Listening address and Listening port of your Syslog type message source
-
Navigate to Log > Sources > <your-new-source> > Source type and select Syslog.
Figure 125: Log > Sources > <your-new-source> > Syslog — Customizing the Listening address and the Listening port for your Syslog type message source
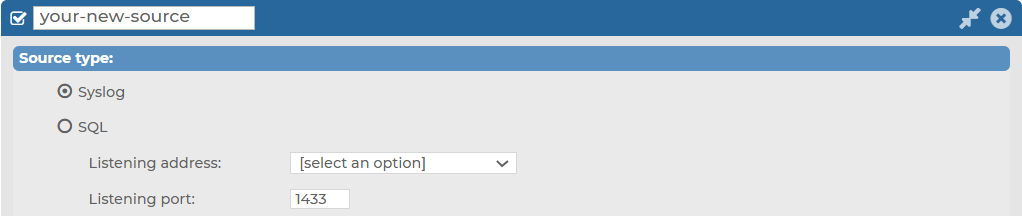
-
Select the Listening address of your choice.
NOTE: Although from version 6.4, syslog-ng Store Box (SSB) supports IPv6 addresses on the external interface and the management interface, you can only select IPv4 addresses for your Syslog sources in the Listening address field.
- Enter the Listening port on which you want your log source to listen.


 .
.

