Introduction
This guide describes how to deploy Single Sign-On (SSO) for native IOS applications using the OpenID Connect protocol.
Topics:
Overview
Using the OpenID Connect protocol, the IOS application authenticates the user against Cloud Access Manager and retrieves a set of three security tokens, as shown in Figure 1. The security tokens are known as the ID Token, Refresh Token and Access Token.
Figure 1: Single Sign-On (SSO) procedure for native IOS applications
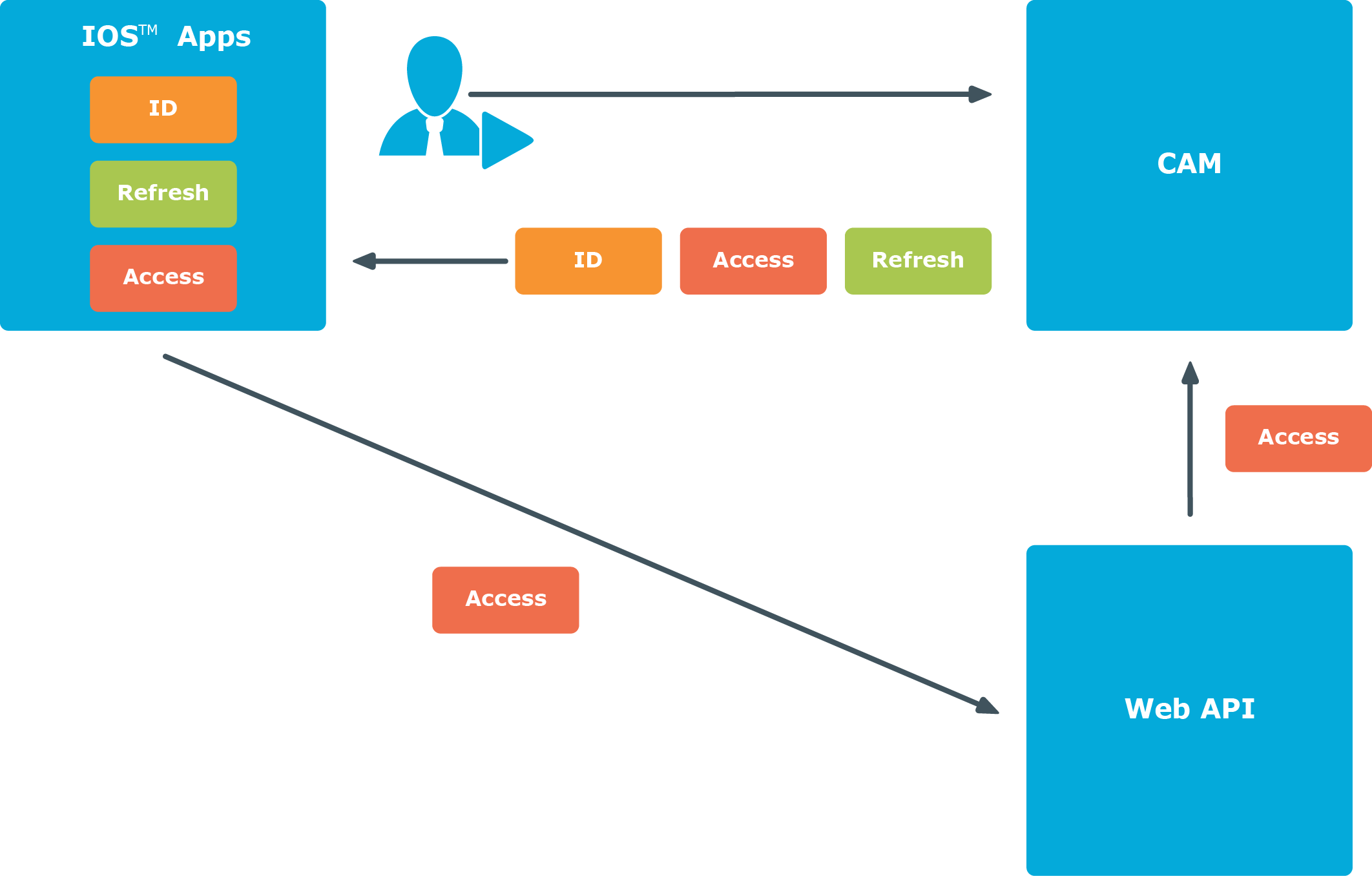
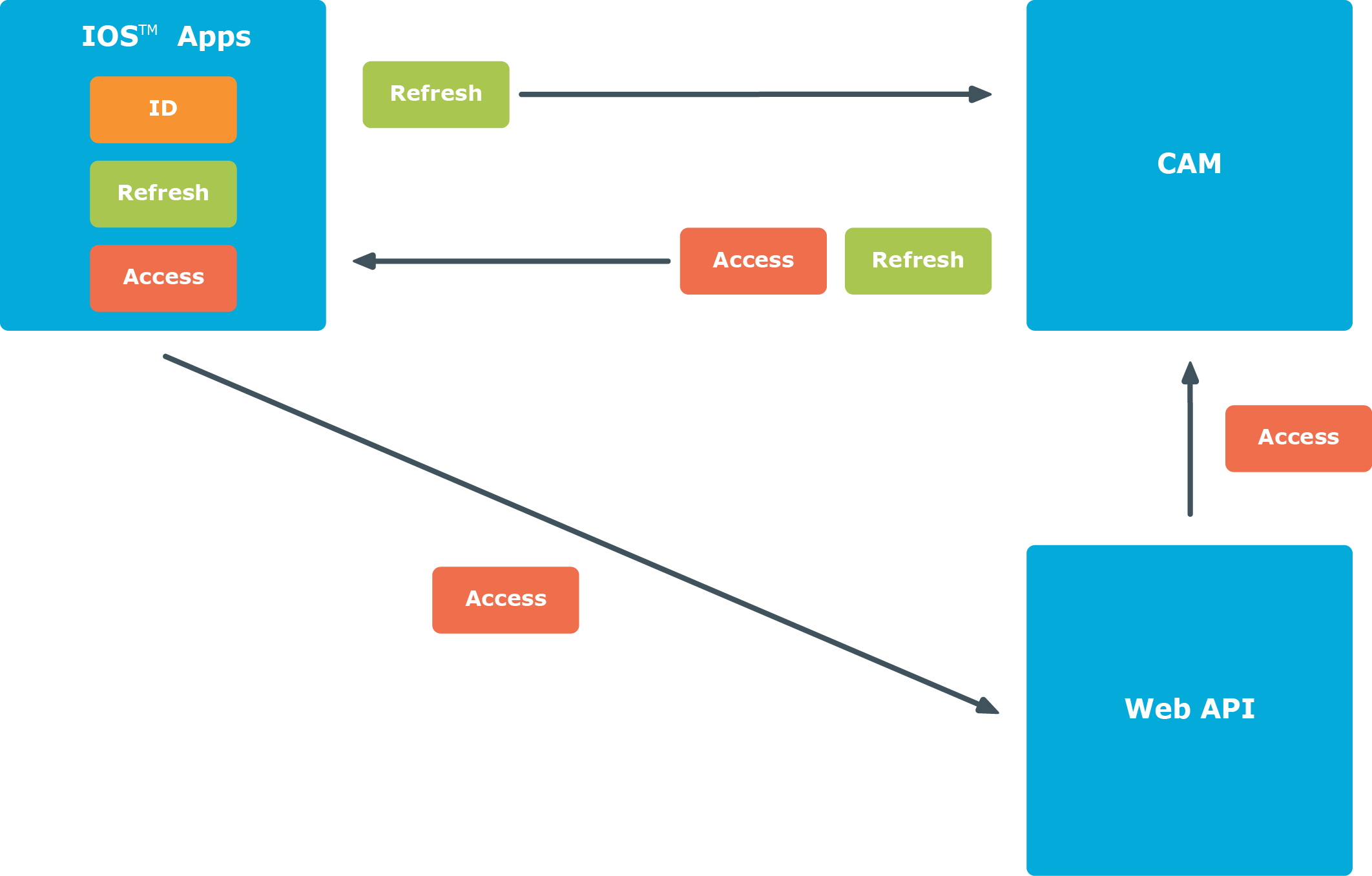
The ID Token contains a collection of identity claims about the user that can be used by the IOS application to identify the user. The Access Token allows the IOS application to securely access OAuth2 protected Web APIs on behalf of the user. When the Access Token expires, the Refresh Token is used by the IOS application to obtain a new Access Token, without the need for the user to re-authenticate as shown in Figure 2.
The Web API validates the Access Token by using it to obtain a set of claims about the user from Cloud Access Manager. The claims are then used by the Web API to identify the user and control the user’s access.
Figure 2: Using the Refresh Token to obtain a new Access Token
Application walkthrough
This sample application consists of two components:
- IOS OpenID Connect application
- .NET OAuth2 protected Web Application Programming Interface (API)
The sample IOS application contains a package called openidconnect which can be used in a standard IOS project to authenticate users using the OpenID Connect Code Flow. The sample Web API contains a .NET Open Web Interface (OWIN) middleware called CAMBearerTokenAuthentication. This can be used in a standard .NET Web API project to authenticate the IOS application using the Access Tokens obtained from Cloud Access Manager.
The function of the sample application components
-
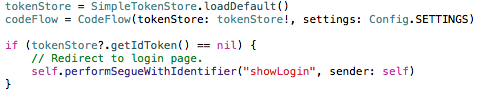
When the application starts it checks for an existing ID Token stored from a previous authentication. If an ID Token does not exist the application sends an authentication request using the system browser to start the OpenID Connect Authorization Code Flow. However if an ID Token does exist, the application skips to Step 4.
-
The user is then prompted to authenticate to Cloud Access Manager using the system browser. After a successful authentication to Cloud Access Manager, the user is redirected back to the application with an authorization code using a custom URI scheme unique to that application.
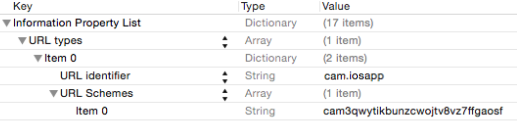
The application’s custom URI scheme is registered in the application’s property list file (Info.plist). The scheme is used by IOS to determine which application to use to open the URI, so the chosen scheme must be unique. In this example the custom URI scheme is the application’s OpenID Connect ClientId in lowercase, prefixed with the name of the SSO provider, Cloud Access Manager (CAM).
-
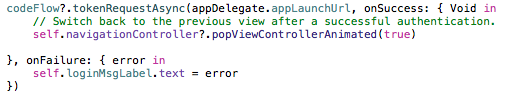
The application uses the authorization code within the redirect URI to obtain an ID Token, Refresh Token and Access Token from Cloud Access Manager. The tokens are stored on the device in an app private area. The Access Token is scoped for use with Cloud Access Manager and the sample Web API. The scope of the Access Token is specified in the authentication request described in Step 1.
-
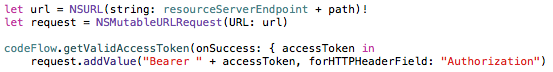
The application can now access the Web API using the Access Token as authorization. The Access Token is included in the authorization header of each request.
-
The Web API validates the Access Token by using it to call the Cloud Access Manager User Info Endpoint. The validation is performed using the provided OWIN middleware which will cache the User Info responses. The OWIN middleware will also verify that the Access Token was scoped for itself by checking that the User Info response contains at least one of its scopes. The claims returned from the User Info Endpoint are used by the Web API to identify the user and control their access.
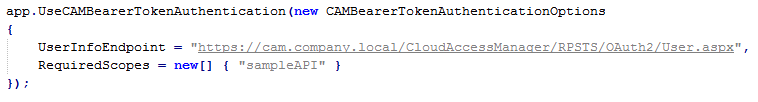
The OWIN authentication middleware is registered and configured using:
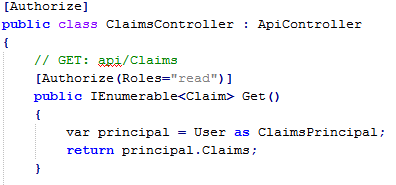
The standard Authorize attribute can be used on the Web APIs to restrict access. The Authorize attribute supports restrictions based on role and user claims which, by default map to the claim names role and preferred_username.
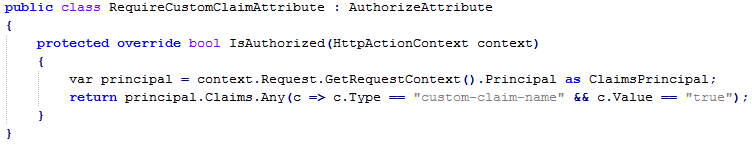
To utilize other claims, a custom AuthorizeAttribute can be created. For example:
- The application uses the Refresh Token to pre-emptively obtain a new Refresh Token and Access Token from Cloud Access Manager when the stored Access Token has expired.
Cloud Access Manager configuration
Perform the following configuration steps within Cloud Access Manager to enable single sign-on to native IOS applications.
To configure Cloud Access Manager for single sign-on to native IOS applications
-
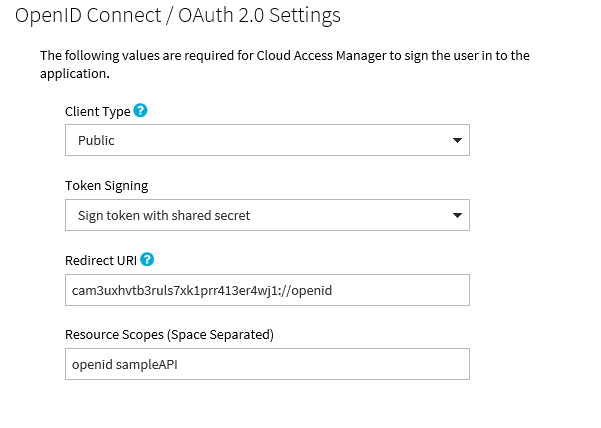
Make sure that the settings on the OpenID Connect / OAuth 2.0 Settings page are as follows:
-
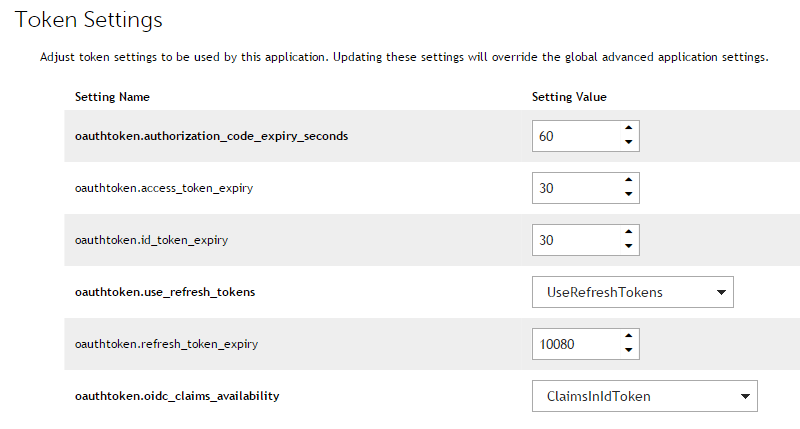
Make sure that the settings on the Token Settings page are as follows:
-
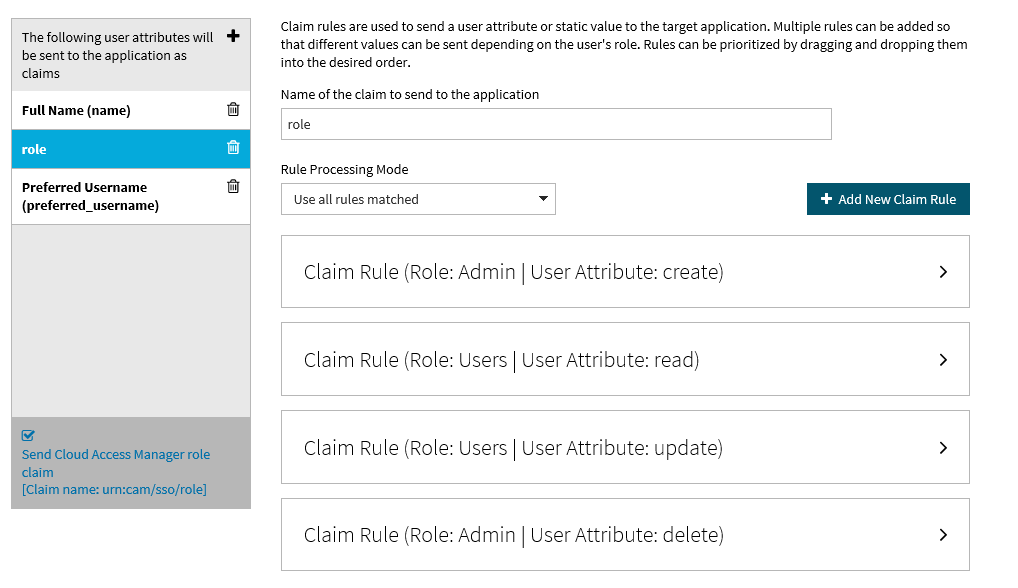
Make sure that the settings on the Claim Mapping page are as follows: