You can view sessions in a card, table or flow view. Click 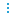
Figure 257: Audit > Sessions — Table view
You can view sessions in a card, table or flow view. Click 
Figure 257: Audit > Sessions — Table view

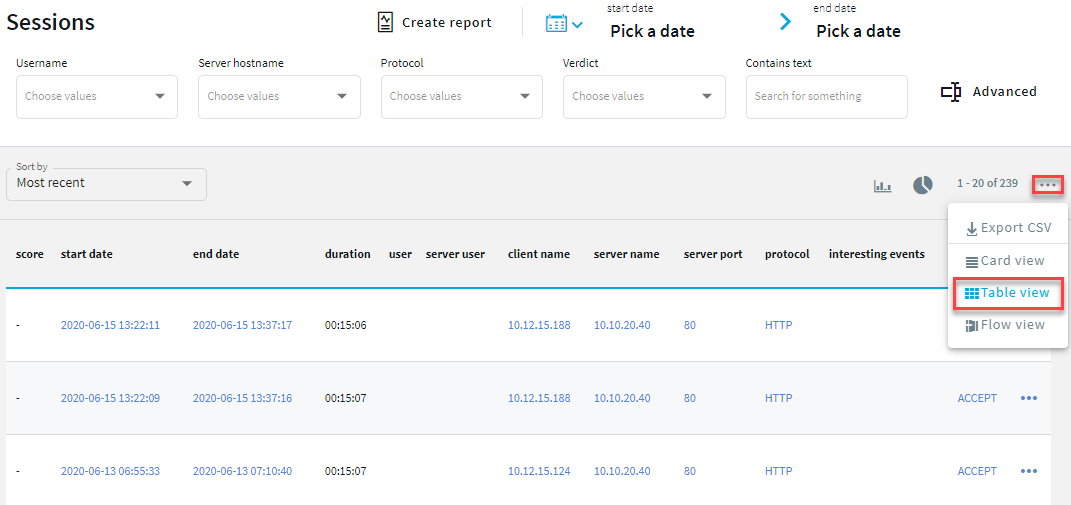
You can view sessions in a card, table or flow view. Click 
Figure 258: Audit > Sessions — Flow view
The flow view allows you to:
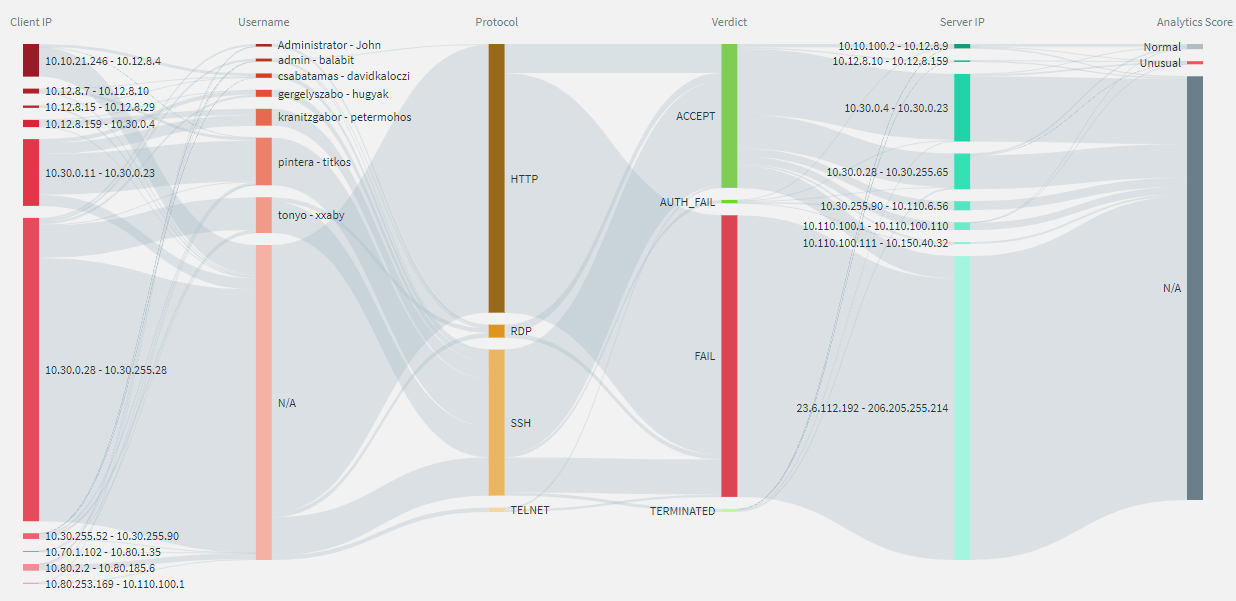
Quickly visualize the distribution of the sessions based on their various metadata, such as, client address, username, protocol, verdict, server address, and One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Analytics (SPA) score.
The metadata of the sessions are presented as vertical bars and each bar represents the proportional value of the data.
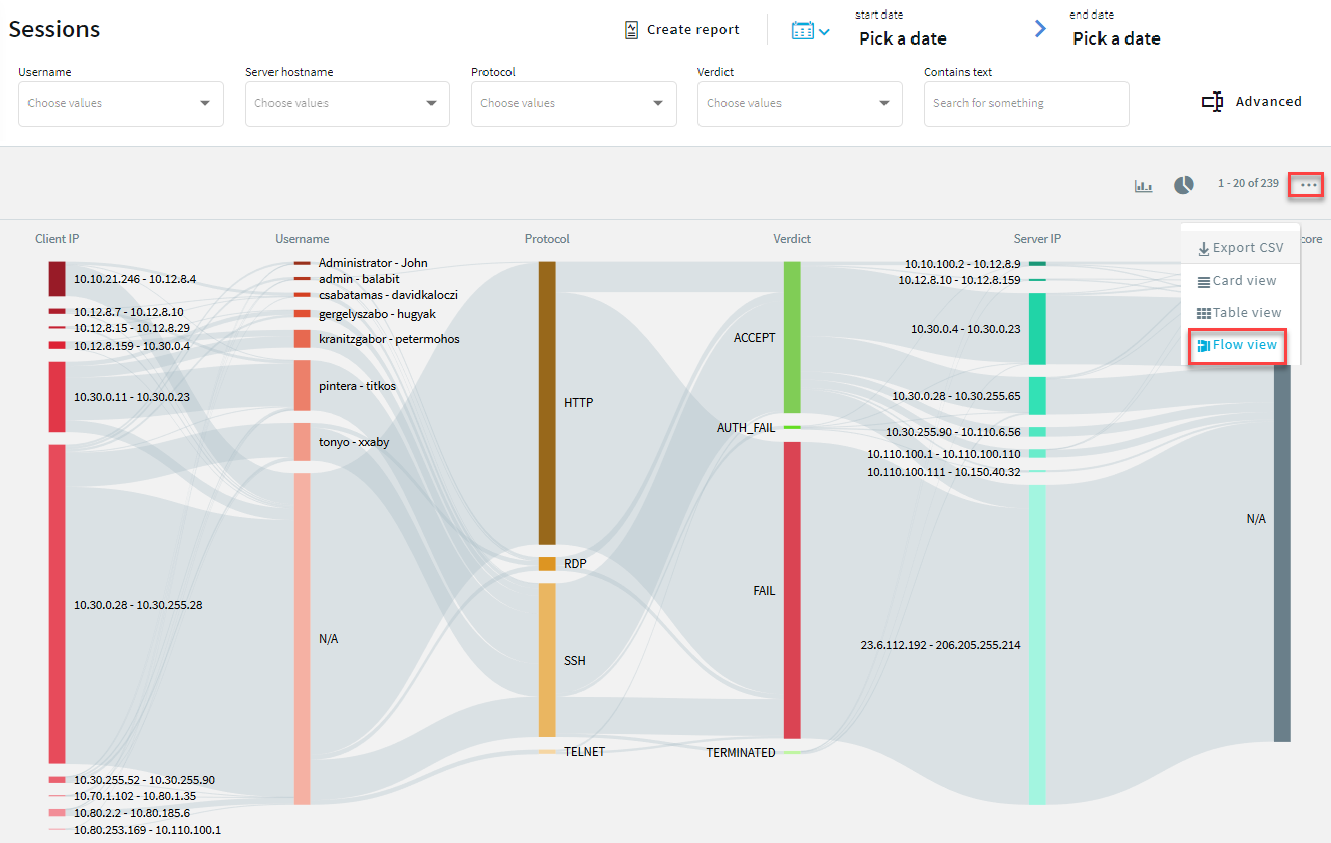
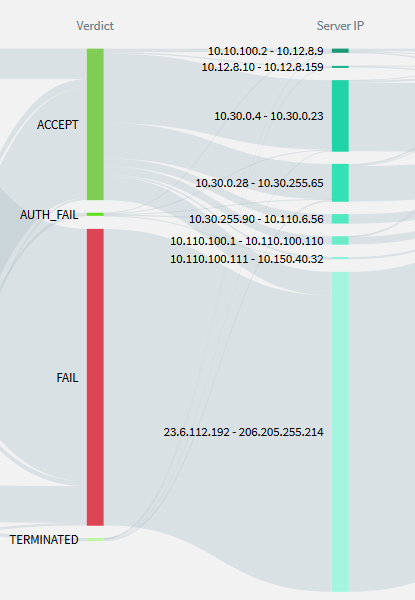
The Verdict column shows that most of the sessions failed, a large number were accepted, and the rest of the sessions fall into the category of AUTH_FAIL, and TERMINATED.
Figure 259: Audit > Sessions > Flow view — proportional data representation
See at a glance the relationship between various metadata and identify patterns in user behavior.
You want to have an overview of activities where access was denied.
A quick look at the Verdict column shows that there were several accesses where the authentication failed (AUTH_FAIL) and the lines from the AUTH_FAIL field point to several server addresses.
Figure 260: Audit > Sessions > Flow view — relationship between metadata
Use it interactively to drill down further on information.
To drill down on information, click on an item, then click Search.
TIP: To exclude an item, press Ctrl while clicking the item.
You want to investigate if there were any unusual activities. To take a closer look, in the Analytics Score column, click Unusual, then click Search.
The flow view now only displays the unusual session activities. You can further narrow your search as required.
Figure 261: Audit > Sessions > Flow view — interactive drill down
The following describes how to assign users to access sessions only for connections for which they are granted permission.
Users need the Search privilege to access the Search interface.
Assigning the Search privilege to a user on the Users & Access Control > Appliance Access page, automatically enables the Access all sessions privilege, and grants the user access to every session. Access is granted even if the user is not a member of the groups listed in the Access Control option of the particular connection policy.
You have created a user for which you want to assign the search privilege. For more information, see Creating local users in One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS).
You have created a usergroup. For more information, see Managing local user groups.
To assign users to access sessions only for connections for which they are granted permission
Navigate to Users & Access Control > Appliance Access.
Figure 262: Users & Access Control > Appliance Access — Configuring search privileges
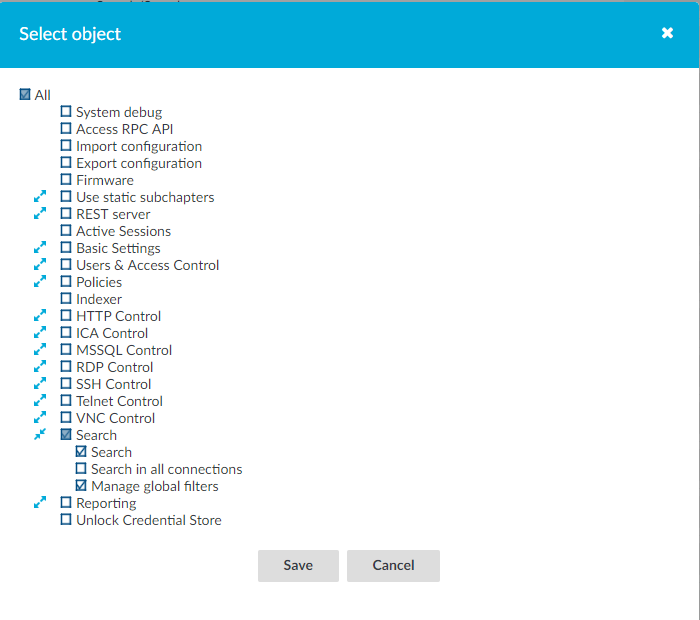
Assign the Search privilege to your usergroup as described in Assigning privileges to user groups for the One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) web interface.
Deselect the Access all sessions privilege so that users can access sessions only for connections for which they are granted permission.
To grant permission to a specific connection, navigate to the Connections page of the traffic (for example to Traffic Controls > SSH > Connections), and select the connection policy to modify.
Scroll down to the Access Control section, and click 
Enter the name of the usergroup whose members are permitted to access the Search interface into the Authorizer Group field. This group must exist on the Users & Access Control > Local User Groups page.
|
|
Caution:
Usernames, the names of user lists, and the names of usergroups are case sensitive. |
Set the permissions of the usergroup.
If the usergroup can authorize (that is, enable) and audit (that is, monitor in real-time and download the audit trails) the sessions, select Permission > Follow&Authorize.
If the usergroup can only audit the sessions but cannot authorize, select Permission > Follow.
NOTE: If the Client user is > Member of field is set, the auditor can only monitor the sessions of the specified usergroup. However, if Client user is > Member of field is set, the Auditor cannot access the Sessions page. To avoid this problem, add another Access Control rule for the Authorizer Group without setting the Client user isfield.
The admin user of One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) can audit and authorize every connection.
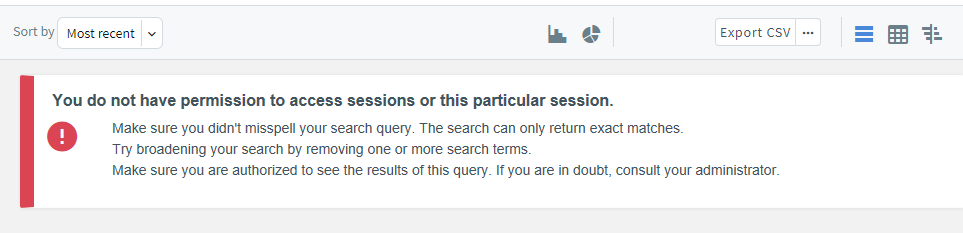
Users with the relevant privileges can now access the sessions for which they are granted permission. If users do not have the required permission to access sessions, a warning message is displayed and no session is visible as shown below:
Figure 263: Audit > Sessions — Permission denied
Specify a time range to restrict, or filter your search criteria by setting boundaries on your searches. You can restrict the search to one of the preset time ranges, or use a custom time range for a more specific search.
When you specify a time range, the search result includes:
Connections started and finished anywhere between the start time and end time you specified.
Connections started anywhere between the start time and end time you specified.
Connections ended anywhere between the start time and end time you specified.
Active connections if they were started anywhere between the start time and the end time you specified.
For example, at 17:00 PM you specify a start date of 10:00 AM and end date of 15:00 PM for your search. The search result includes:
Connections started at 8:00 AM and ended at 14:00 PM.
Connections started at 11:00 AM and ended at 14:00 PM.
Connections started at 11:00 AM and ended at 16:00 PM.
Active connections started at 11:00 AM.
Active connections started at 10:00 AM.
To specify time ranges
To select the start date of your search, click Pick a date.
Alternatively, use the 
Figure 264: Audit > Sessions — Pick a date

From the calendar, select the start date as required.
NOTE: The date refers to the timezone configured on SPS.
For exact time ranges, specify to search by the hour and minute.
Figure 265: Audit > Sessions — Specify hour and minute
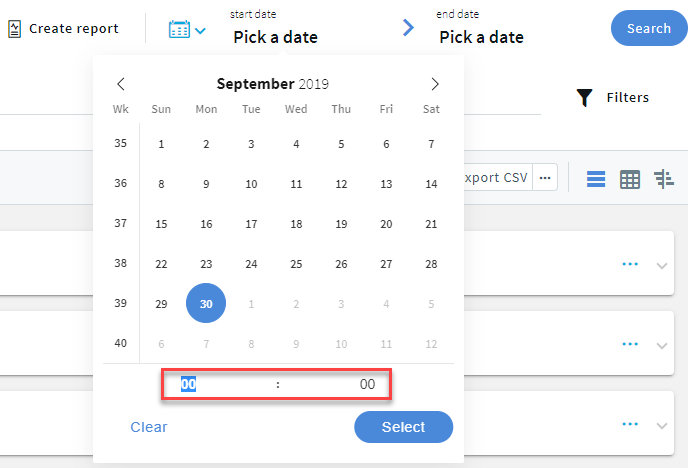
To select the end date of your search, click Pick a date and select a date as required.
If you specify only the start date, the end date is set to the current time.
Optional: To clear the start and end date, click 
Optional: You can use the timeline for a quick time range selection and visual representation of sessions in the selected interval.
Click the 
Figure 266: Audit > Sessions — Using the timeline
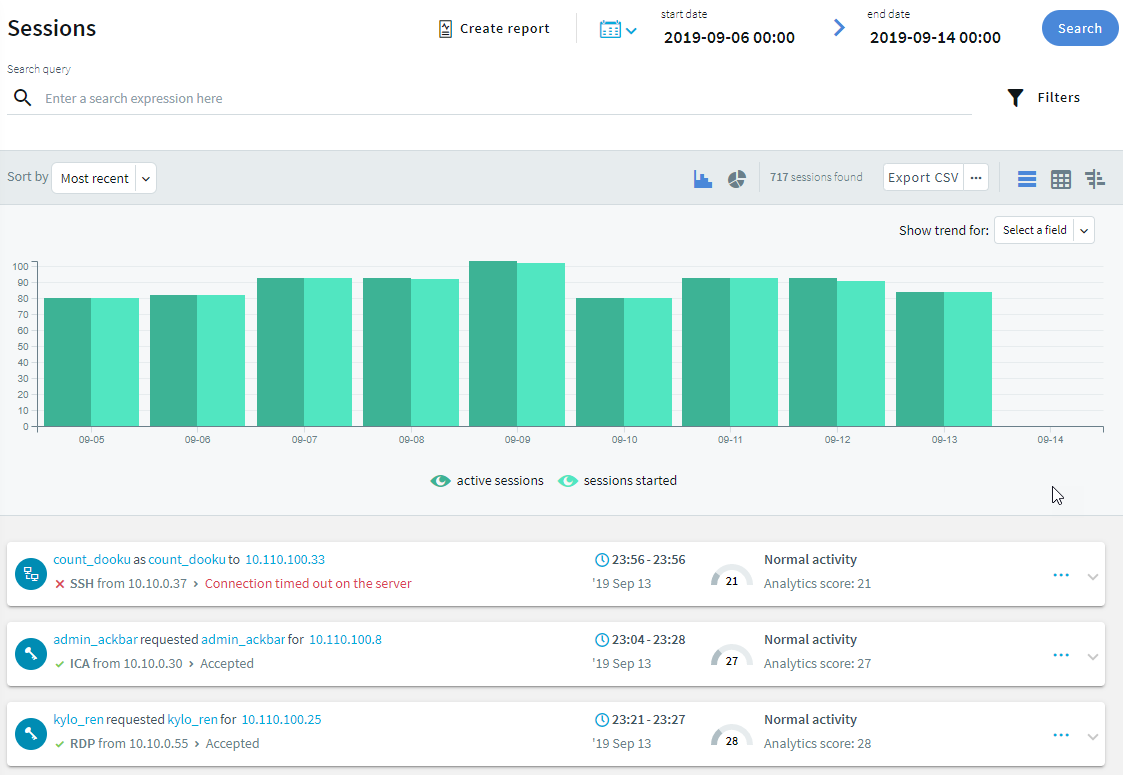
The bars display the number of results in the selected interval.
The active sessions columns indicate all the sessions, which were active in the selected interval. The sessions started columns indicate all the sessions started during the selected interval. For example, if the selected interval is today between 8:00 AM and 9:00 AM, then a session started at 7:00 AM but lasting after 8:00 AM is displayed in the active sessions column. A session started at 8:30 AM is displayed in the sessions started column. Since the session was active during the selected time interval, the session started at 8:30 AM is also displayed in the active sessions column.
To disable the active sessions and view only the started sessions in the timeline, click 
Hovering the mouse above a bar displays the number of entries and the start and end date of the period that the bar represents.
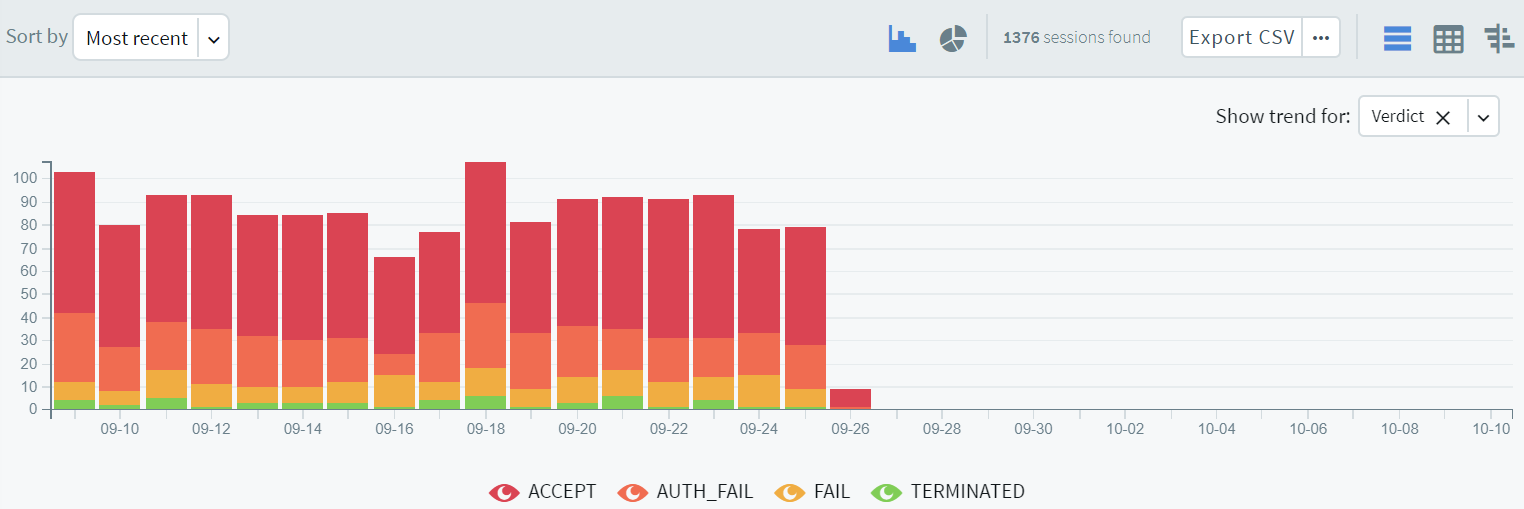
Trend analysis allows you to use the timeline to find changes over time. For example, to find the time range where terminated connections had a significant peak compared to other days, from the Show trend for drop-down menu, select Verdict. Note that you can only view trend analysis for Active, Analytics Score, Client name, Protocol, Server hostname, Server port, Server username, Username and Verdict. All the other selections are grayed out.
The colors of the bars in the timeline allow you to quickly find the time range with a higher number of terminated sessions.
Optional: To clear the trend analysis view, from the Show trend for drop-down menu, select X.
Figure 267: Audit > Sessions — Using the timeline - trend analysis
To select a range, drag the mouse pointer across the timeline or use Shift+Click and select multiple bars.
© 2025 One Identity LLC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Nutzungsbedingungen Datenschutz Cookie Preference Center