Installation
Topics:
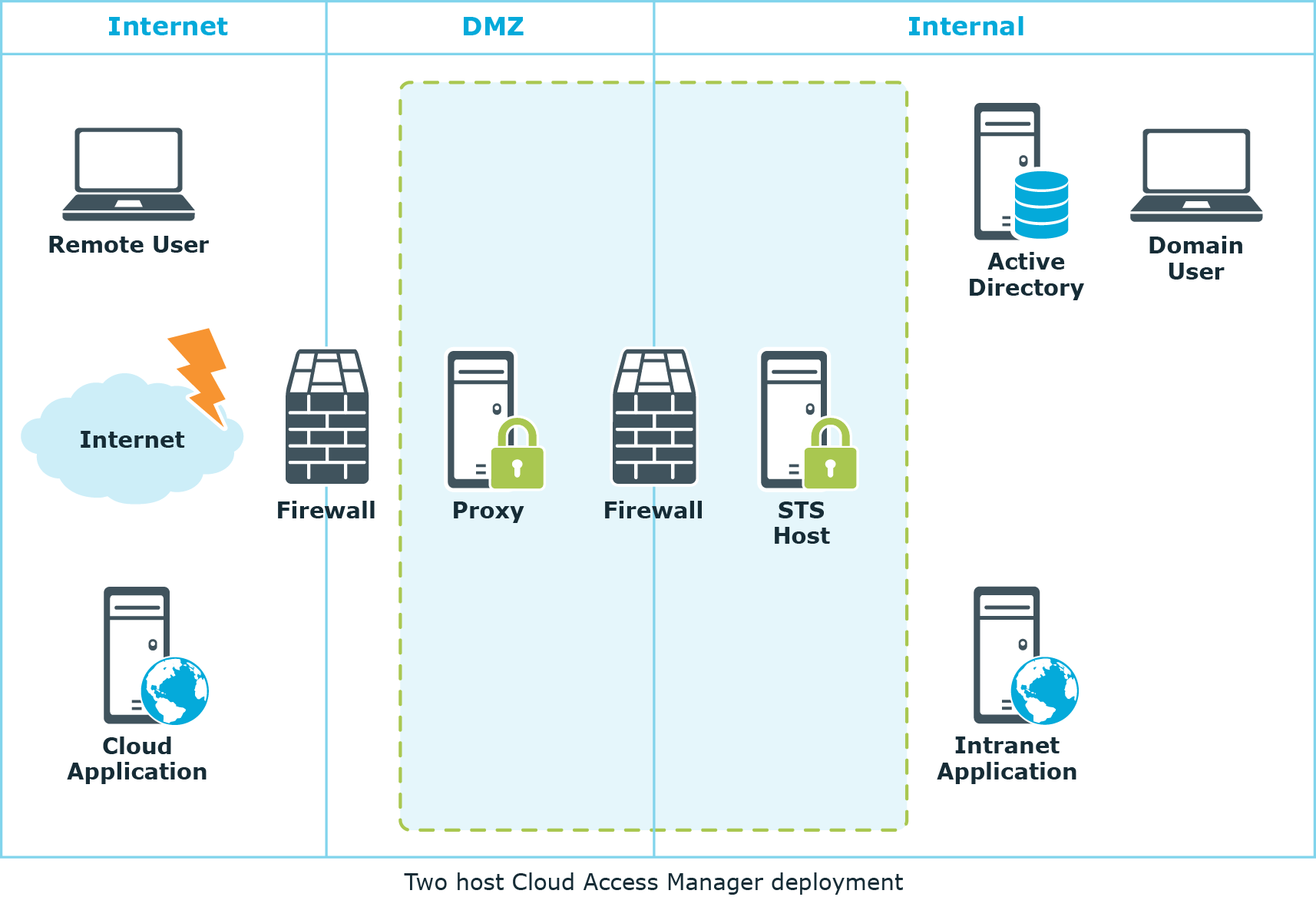
This guide will take you through the steps required to deploy a typical two host production installation of Cloud Access Manager. Once completed, Cloud Access Manager will allow employees to securely Single Sign-On (SSO) to internal and external web-based applications from within the company network and remotely, without the need for a virtual private network (VPN). This example uses two separate hosts, one for the Proxy and the other for the Secure Token Service (STS). The diagram below represents a typical Cloud Access Manager deployment, and shows the proxy host deployed within the DMZ area of the network and the STS host on the internal network.
Figure 1: Two host Cloud Access Manager deployment
Prerequisites
Make sure the following prerequisites are met before you attempt to install Cloud Access Manager, please refer to Proxy host and STS host for component specific requirements.
|
|
NOTE: Please be aware that domain controllers are not valid Cloud Access Manager hosts. |
Browser
| Platform | Browser |
|---|---|
|
Windows |
|
|
Mac |
|
|
iOS |
|
|
Android |
|
1 Supported for Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA).
Proxy host
Ensure the following prerequisites are met before installation:
Deployment location
To support the scenario illustrated in Two host Cloud Access Manager deployment where you need to expose internal applications to external users, the host should be deployed within the DMZ network.
Hardware
Ensure that the following hardware requirements are met:
| Hardware | Requirement |
|---|---|
| CPU | Min. 2 multi-core processors |
| Memory | Min. 4 GB |
| Disk Space | Min. 25 GB |
Operating system
Ensure that the following operating system requirements are met with the latest Microsoft Hotfixes applied.
| Hardware |
|---|
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Server Core or |
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Server Core or |
|
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Server Core |
Name resolution
You must configure the host to use the internal Domain Name System (DNS) server(s) so that it can resolve the hostnames of the internal web applications that will be configured. In addition to the internal DNS, Cloud Access Managerrequires a public DNS record for the proxy host and an additional public DNS record for each internal application.
Each of these DNS records must be resolvable to the proxy’s public IP address from outside of your corporate network. To avoid the need to create a new DNS record each time a new application is added to Cloud Access Manager, we recommend that you create a new wildcard DNS subdomain for Cloud Access Manager to resolve any name within the new subdomain to the public IP address of the proxy.
IP addressing
The host must be assigned a private IP address which is accessible from the internal network. For external access a public IP address is required. This is typically assigned to an internet facing router where destination network address translation (DNAT) or port forwarding is performed to route traffic destined for ports 80 and 443 on a public IP address to the private IP address of the proxy host.
Wildcard DNS subdomain
Domain hosting companies typically allow the creation of a wildcard subdomain by adding a new DNS A (Host) record for your domain in the format *.subdomain, where subdomain is the name of the new subdomain you want to create for the Cloud Access Manager Proxy. Point the new DNS record to the public IP address used by the Cloud Access Manager Proxy so that any hostname in the new subdomain resolves to the proxy’s public IP address.
For example, adding a new A record *.webapps to a domain called company.com would allow the Cloud Access Manager Proxy to use hostnames such as:
- portal.webapps.company.com
- webmail.webapps.company.com
- sharepoint.webapps.company.com
Essentially <anything>.webapps.company.com, this allows each internal application to have its own internet resolvable hostname.
To create a wildcard subdomain within the Microsoft DNS server you must first add a new subdomain (zone) and then add a single A (Host) record within the subdomain with the name *. As with the previous instructions, the new DNS record should be pointed to the public IP address used by the Cloud Access Manager Proxy so that any hostname in the new subdomain resolves to the proxy’s public IP address.
Wildcard SSL certificate
A signed wildcard Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate is required to cover the wildcard DNS subdomain used by the Cloud Access Manager Proxy. The wildcard SSL certificate must be obtained using the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) generated by Cloud Access Manager during configuration. For example, if you created a wildcard DNS subdomain called webapps within your domain company.com, then you would need to obtain a signed wildcard SSL certificate for *.webapps.company.com for full instructions, please refer to Managing your SSL Certificate in the One Identity Cloud Access Manager Configuration Guide.
Firewall configuration
Access to TCP ports 80 and 443 on the host should be permitted from both the internal and external network. The host should also be permitted to access the internal web applications through the ports they use, typically TCP port 80 and 443.
Port 8553
Port 8553 is the admin port used to configure the Cloud Access Manager Proxy. The proxy host downloads its configuration and then locally uses port 8553 to load the configuration. Ensure that port 8553 is not already being used by another application. If port 8553 is already in use, enter an alternative port number in the Cloud Access Manager proxy Installation Wizard. This port does not need to be open on the proxy host for Cloud Access Manager to function.
Smart card authentication
If you enable smart card authentication you will need to open the configured port. The default is port 8443.
STS host
Deployment location
The host should be deployed within the internal network.
Hardware
Ensure that the following hardware requirements are met:
| Hardware | Requirements |
|---|---|
| CPU | Min. 8 multi-core processors |
| Memory | Min. 8 GB |
| Disk Space | Min. 50 GB |
| Operating System |
Any of the following:
|
Domain membership
If Active Directory will be used to source users for SSO, the Security Token Service (STS) host must be a member of the Active Directory domain containing these users. Cloud Access Manager can also use federated identities from third party domains using SAML 2.0 or WS-Federation.
Name resolution
You must configure the host to use the internal Domain Name System (DNS) server(s) so that it can resolve the hostnames of the internal web applications that will be configured.
Database
Ensure that the following database requirements are met:
| Database | |
|---|---|
| Database Server | Microsoft SQL Server 2008-2017 |
| Disk space (guideline, assuming typical usage) | 200MB + 2K per user + 2K per user per day (audit) |
Cloud Access Manager requires an instance of Microsoft SQL Server 2008-2017, to store its configuration, audit and session data. Microsoft SQL Server Express can also be used for small deployments, for example, where high availability of the database is not required.
Cloud Access Manager can either create its database within a new dedicated instance of Microsoft SQL Server installed directly on the Security Token Service (STS) host, or in an existing remote instance of Microsoft SQL Server deployed within your internal network.
|
|
NOTE: If you choose to use a dedicated instance of Microsoft SQL Server on the STS host, ensure that it is installed before you run the Cloud Access Manager installer. |
- Herramientas de autoservicio
- Base de conocimientos
- Notificaciones y alertas
- Soporte de productos
- Descargas de software
- Documentación técnica
- Foros de usuarios
- Tutoriales en video
- Aviso de actualizaciones de páginas web (RSS)
- Comuníquese con nosotros
- Obtenga asistencia con las licencias
- Soporte Técnico
- Ver todos

