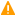
| SNMP object: | HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrStorageTable |
|
Community (v2c) / Context (v3) |
Data and system |
This section describes monitoring syslog-ng Store Box(SSB)'s disk usage. Disk usage is measured per mountpoint (that is, partition).
Data partition
| Mountpoint | /mnt/firmware |
| Partition | data partition |
| Community |
<community-of-extended-node> (Basic Settings > Monitoring > SNMP agent settings > Community) |
| Context | "" (empty string) |
Free disk space that can be acquired by your main production system (for example, logspaces).
To make sure that you have the free disk space you are comfortable with, monitor the free disk space. This partition can fill up with for example the following:
-
received logs
-
generated reports
-
collected statistics
-
core dumps
If you cannot keep your free disk space in your comfortable interval (with scheduled cleanups) you probably need to purchase more SSB appliances. For assistance, contact our Support Team.
NOTE: If you have configured Basic Settings > Management > Disk space fill up prevention, be aware that SSB will stop receiving log after reaching the configured threshold. By default, clients are disconnected when disks are 90 percent full. For details, see Preventing disk space fill up.
| For which systems and configurations is it applicable? | Applicable for all configurations and systems. |
| Value change frequency | The file system's available space is continuously decreasing, depending on logspaces, reports, statistics, and core files. |
| Related issues and issue indicators | The monitored values may indicate that the used storage space has reached the level configured under Basic Settings > Management > Disk space fill up prevention. In this case, archiving starts (if archiving is configured), and incoming logs are rejected. Note that if the disk fill up prevention level is reached too often and too soon, it indicates a serious issue. |
|
|
Caution:
Hazard of data loss If the used storage space of the file system under /mnt/firmware exceeds the allowed rate configured under Basic Settings > Management > Disk space fill up prevention, SSB will stop receiving log messages. To avoid data loss, archive your logs or store them in some other way (for example, forward your log messages to different logstores). Alternatively, reconsider your configuration settings, upgrading the capacity of your SSB appliance, or purchasing more SSB appliances. |
Solution:
-
Consider upgrading the capacity of your SSB appliance or purchasing more SSB appliances (for more information, see Hardware specifications or contact our Sales Team).
- Reconsider your configuration settings.
- Archive your logs from your logspaces to clean up logstores on your SSB appliance.
System partition
| Mountpoint | /initrd/mnt |
| Partition | system partition (if SSB is in HA mode, the system firmware partition of both nodes) |
| Community | <id-of-the-node> |
| Context | <id-of-the-node> |
The space on this mountpoint is required only by the system. Generally, this is independent from how you use SSB. The only important thing here to have some free space on the mountpoint.
Make sure that you have some free space on this mountpoint. As a recommended threshold, set a trigger to 80% in your monitoring system. If there is only about 20% free space left on this mountpoint, contact our Support Team.
NOTE: Monitoring the size of specific logspaces is not possible this way. If you are interested in the size of a specific logspace, you can configure a size limit alert for that logspace on the SSB web interface. For details on configuring a disk size alert for a specific logspace, see Creating logstores.
| For which systems and configurations is it applicable? | Applicable for all configurations and systems. |
| Value change frequency | The available storage space is not supposed to decrease significantly. |
| Related issues and issue indicators | The monitored values may indicate that the system is out of storage space, or that the available storage space is running very low. |
|
|
Caution:
Hazard of data loss If the used storage space of the file system under /mnt/firmware exceeds the allowed rate configured under Basic Settings > Management > Disk space fill up prevention, SSB will stop receiving log messages. To avoid data loss, archive your logs or store them in some other way (for example, forward your log messages to different logstores). Alternatively, reconsider your configuration settings, upgrading the capacity of your SSB appliance, or purchasing more SSB appliances. |
Solution:
If you encounter an issue related to the file system under /initrd/mnt, contact our Support Team.