Certain properties of the SSL certificates on Basic Settings > Management > SSL certificate can be monitored in a table format.
| SNMP object: |
SSB-SNMP-MIB::ssbServerCertificateTable |
| Type: |
This is a grouping node |
|
Community (v2c) /
Context (v3) |
Data |
| Short description: |
Detailed information about syslog-ng Store Box(SSB) server certificates |
Certificate table index
| SNMP object: |
SSB-SNMP-MIB::ssbCertificateIndex |
| Type: |
index |
| Short description: |
The index of the certificate or certificate chain in this table. |
Certificate Title field
| SNMP object: |
SSB-SNMP-MIB::ssbCertificateTitle |
| Type: |
string |
|
Community (v2c) /
Context (v3) |
Data |
| Short description: |
The purpose SSB uses the certificate or certificate chain for. |
Certificate "Subject" field
| SNMP object: |
SSB-SNMP-MIB::ssbCertificateSubject |
| Type: |
string |
|
Community (v2c) /
Context (v3) |
Data |
| Short description: |
The 'Subject' field of the certificate. In case of certificate chains, the 'Subject' field of the end-entity certificate (also called the server certificate). |
Certificate "Not before" field
| SNMP object: |
SSB-SNMP-MIB::ssbCertificateNotBefore |
| Type: |
date-time string |
|
Community (v2c) /
Context (v3) |
Data |
| Short description: |
The 'Not before' field of the certificate in generalized ASN.1 format (YYYYMMDDhhmmssZ or YYYYMMDDhhmmss+hhmm or YYYYMMDDhhmmss-hhmm). In case of certificate chains, this is the latest 'Not before' date of the certificates in the chain. |
Certificate "Not after" field
| SNMP object: |
SSB-SNMP-MIB::ssbCertificateNotAfter |
| Type: |
date-time string |
|
Community (v2c) /
Context (v3) |
Data |
| Short description: |
The 'Not after' field of the certificate in generalized ASN.1 format (YYYYMMDDhhmmssZ or YYYYMMDDhhmmss+hhmm or YYYYMMDDhhmmss-hhmm). In case of certificate chains, this is the earliest 'Not after' date of the certificates in the chain. |
This section describes the tools to detect networking problems, and also how to collect core files and view the system logs of syslog-ng Store Box (SSB).
Topics:
SSB T4 and SSB T10
To find syslog-ng Store Box (SSB) appliance T4 and SSB T10 in the server room, you can use IPMI to control the front panel and back panel identify lights.
-
On SSB T4 and SSB T10, navigate to Basic Settings > System > Hardware information > Blink system identification lights.
-
To blink the blue LEDs on the front and back of the SSB appliance, click On.
NOTE: SSB T1 does not support identify lights.
Alternatively, use the command line as follows:
-
To start the blinking of the blue LEDs on the front and back of the SSB appliance, enter:
ipmitool chassis identify force
-
To stop the blinking of the blue LEDs on the front and back of the SSB appliance, enter:
ipmitool chassis identify 0
syslog-ng Store Box Appliance 3000 and syslog-ng Store Box Appliance 3500
To locate syslog-ng Store Box Appliance 3000 and syslog-ng Store Box Appliance 3500, look for an appliance that has a white front panel with a light blue One Identity logo on it.
The Troubleshooting menu provides a number of diagnostic commands to resolve networking issues. Logfiles of syslog-ng Store Box(SSB) can also be displayed here — for details, see Viewing logs on SSB.
Figure 242: Basic Settings > Troubleshooting > System debug — Network troubleshooting with SSB
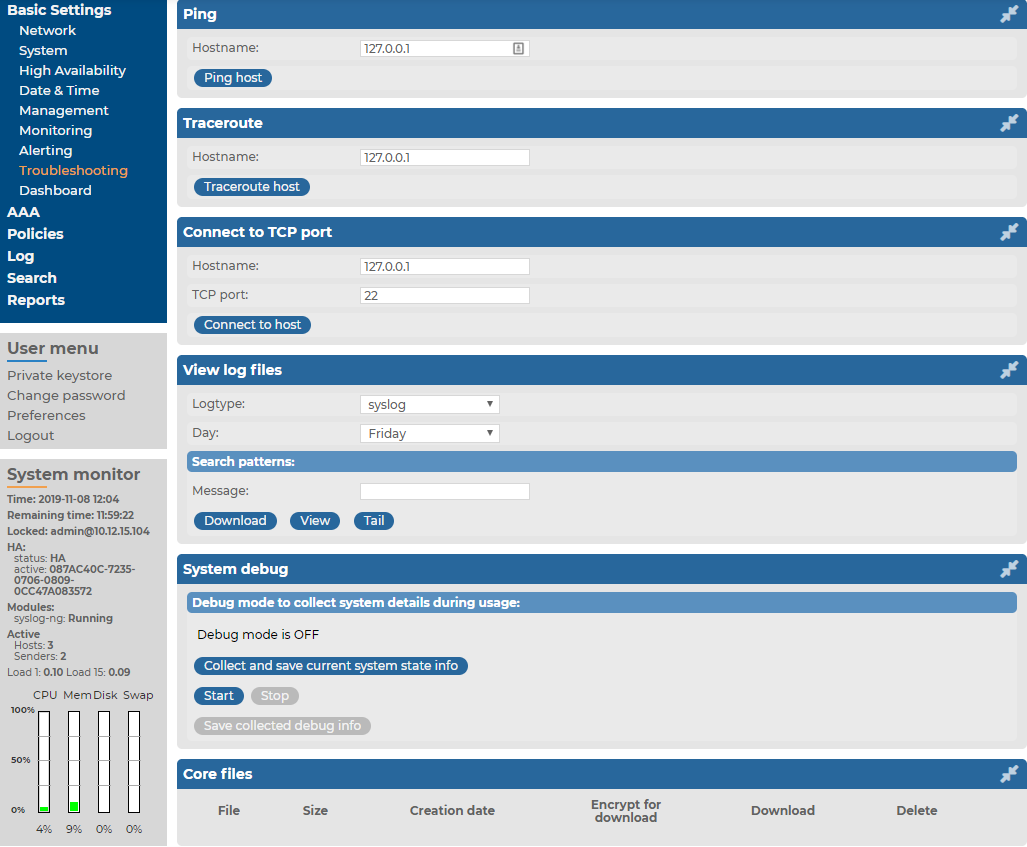
The following commands are available:
-
ping: Sends a simple message to the specified host to test network connectivity.
-
traceroute: Sends a simple message from SSB to the specified host and displays all hosts on the path of the message. It is used to trace the path the message travels between the hosts.
-
connect: Attempts to connect the specified host using the specified port. It is used to test the availability or status of an application on the target host.
To run one of the commands above
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Troubleshooting.
-
Enter the IP address or the hostname of the target host into the Hostname field of the respective command. For the Connect command, enter the target port into the Port field.
-
Click the respective action button to execute the command.
-
Check the results in the popup window. Log files are displayed in a separate browser window.

