One Identity Manager can be used to define rules that maintain and monitor regulatory requirements and automatically deal with rule violations. Define compliance rules to test entitlements or combinations of entitlements in the context of identity audit for employees in the company. On the one hand, existing rule violations can be found by checking rules. On the other hand, possible rule violations can be preemptively identified and this prevented.
Figure 1: Identity audit in One Identity Manager
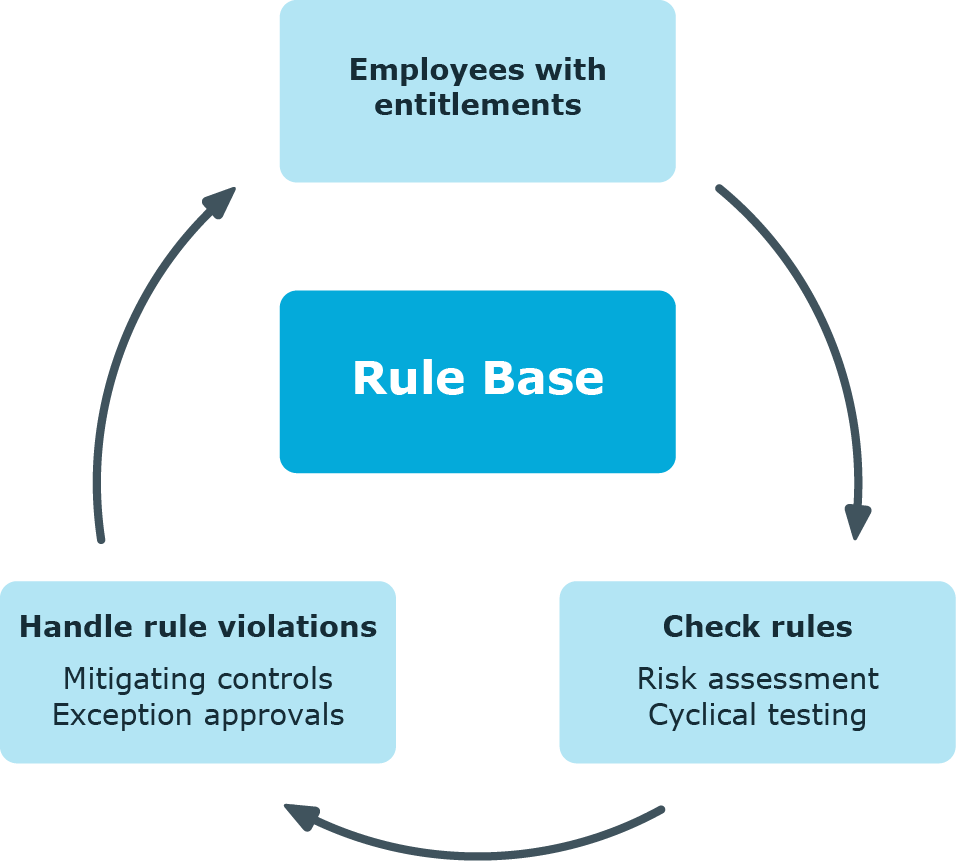
Simple rule examples are:
-
An employee may not obtain two entitlements A and B at the same time.
-
Only employees with a particular department can have a particular entitlement.
-
Every user account has to have a manager assigned to it.
You can use the identity audit function of One Identity Manager to:
-
Define rules for any employee assignments
-
Evaluate the risk of possible rule violations
-
Specify mitigating controls
-
Initiate regular or spontaneous rule checks
-
Detailed testing of edit permissions for employees within an SAP client (using SAP functions)
-
Evaluate rule violations with differing criteria
-
Create reports about rules and rule violations
Based on this information, you can made corrections to data in One Identity Manager and transfer them to the connected target systems. The integrated report function in One Identity Manager can be used to provide information for the appropriate tests.
To use the identity audit function
If you disable the configuration parameter at a later date, model components and scripts that are not longer required, are disabled. SQL procedures and triggers are still carried out. For more information about the behavior of preprocessor relevant configuration parameters and conditional compiling, see the One Identity Manager Configuration Guide.
The following users are included in setting up and administration of the rule base and editing rule violations.
Table 1: Users
|
Administrators for Identity Audit |
Administrators must be assigned to the Identity & Access Governance | Identity Audit | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Enter base data for setting up company policies.
-
Create compliance rules and assign rule supervisors to them.
-
Can start rule checking and view rule violations as required.
-
Create reports about rule violations.
-
Enter mitigating controls.
-
Create and edit risk index functions.
-
Monitor Identity Audit functions.
-
Administer application roles for rule supervisors, exception approvers and attestors.
-
Set up other application roles as required. |
|
Rule supervisors |
Rule supervisors must be assigned to the Identity & Access Governance | Identity Audit | Rule supervisors application role or a child application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Are responsible for compliance rule content, for example, an auditor or a auditing department.
-
Edit the compliance rule working copies, which are assigned to the application role.
-
Enable and disable compliance rules.
-
Can start rule checking and view rule violations as required.
-
Assign mitigating controls. |
|
One Identity Manager administrators |
administrator and administrative system users Administrative system users are not added to application roles.
administrators:
-
Create customized permissions groups for application roles for role-based login to administration tools in the Designer as required.
-
Create system users and permissions groups for non role-based login to administration tools in the Designer as required.
-
Enable or disable additional configuration parameters in the Designer as required.
-
Create custom processes in the Designer as required.
-
Create and configure schedules as required. |
|
Exception approvers |
Administrators must be assigned to the Identity & Access Governance | Identity Audit | Exception approvers application role or a child application role.
Users with this application role:
|
|
Compliance rules attestors |
Attestors must be assigned to the Identity & Access Governance | Identity Audit | Attestors application role.
Users with this application role:
NOTE: This application role is available if the module Attestation Module is installed. |
|
Compliance and security officer |
Compliance and security officers must be assigned to the Identity & Access Governance | Compliance & Security Officer application role.
Users with this application role:
-
View all compliance relevant information and other analysis in the Web Portal. This includes attestation policies, company policies and policy violations, compliance rules, and rule violations and risk index functions.
-
Edit attestation polices. |
|
Auditors |
Auditors are assigned to the Identity & Access Governance | Auditors application role.
Users with this application role:
|
Various basic data is required to create rules, run rule checks and handle rule violation.
Use rule groups to group rules by functionality, for example, to group account policies, or to separate functions ("Segregation of duties").
To create or edit a rule group
-
In the Manager, select the Identity Audit > Basic configuration data > Rule groups category.
-
Select a rule group in the result list. Select the Change main data task.
- OR -
Click  in the result list.
in the result list.
-
Edit the main data of the rule group.
- Save the changes.
Enter the following data for a rule group
Table 2: Rule group properties
|
Group name |
Name of the rule group. |
|
Description |
Text field for additional explanation. |
|
Parent group |
Rule group above this one in a hierarchy.
To organize rule groups hierarchically, select the parent rule group in the menu. |


 in the result list.
in the result list.