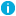
Collecting logs from chroot
Purpose:
To collect logs from a chroot using a syslog-ng client running on the host, complete the following steps:
Figure 21: Collecting logs from chroot
Steps:
-
Create a /dev directory within the chroot. The applications running in the chroot send their log messages here.
-
Create a local source in the configuration file of the syslog-ng application running outside the chroot. This source should point to the /dev/log file within the chroot (for example to the /chroot/dev/log directory).
-
Include the source in a log statement.
NOTE: You need to set up timezone information within your chroot as well. This usually means creating a symlink to /etc/localtime.
Configuring log rotation
The syslog-ng OSE application does not rotate logs by itself. To use syslog-ng OSE for log rotation, consider the following approaches:
Use logrotate together with syslog-ng OSE:
-
Ideal for workstations or when processing fewer logs.
-
It is included in most distributions by default.
-
Less scripting is required, only logrotate has to be configured correctly.
-
Requires frequent restart (syslog-ng OSE must be reloaded/restarted when the files are rotated). After rotating the log files, reload syslog-ng OSE using the syslog-ng-ctl reload command, or use another method to send a SIGHUP to syslog-ng OSE.
-
The statistics collected by syslog-ng OSE, and the correlation information gathered with Pattern Database is lost with each restart.
Separate incoming logs based on time, host or other information:
-
Ideal for central log servers, where regular restart of syslog-ng OSE is unfavorable.
-
Requires shell scripts or cron jobs to remove old logs.
-
It can be done by using macros in the destination name (in the filename, directory name, or the database table name). (For details on using macros, see Templates and macros.)
Example: File destination for log rotation
This sample file destination configuration stores incoming logs in files that are named based on the current year, month and day, and places these files in directories that are named based on the hostname:
destination d_sorted {
file(
"/var/log/remote/${HOST}/${YEAR}_${MONTH}_${DAY}.log"
create-dirs(yes)
);
};This sample logstore destination configuration stores incoming logs in logstores that are named based on the current year, month and day, and places these logstores in directories that are named based on the hostname:
destination d_logstore {
logstore(
"/var/log/remote/${HOST}/${YEAR}_${MONTH}_${DAY}.lgs"
compress(9)
create-dirs(yes)
);
};Example: Command for cron for log rotation
This sample command for cron removes files older than two weeks from the /var/log/remote directory:
find /var/log/remote/ -daystart -mtime +14 -type f -exec rm {} \;The syslog-ng manual pages
This chapter collects the manual pages of syslog-ng OSE and other related applications that are usually distributed and packaged together with the syslog-ng Open Source Edition application.
Manual pages
This chapter collects the manual pages of syslog-ng OSE and other related applications that are usually distributed and packaged together with the syslog-ng Open Source Edition application.