When processing a request to deprovision a user, Active Roles uses this policy to determine the home folder deprovisioning options, and then updates the configuration of the user’s home folder accordingly.
The available home folder deprovisioning options are summarized in the following table. For each option, the table outlines the policy effect on the user’s home folder.
Table 27: Policy effect on the user’s home folder
|
Remove the user’s permissions on the home folder |
Modifies the home folder security so that the deprovisioned user cannot access his or her home folder. |
|
Grant the user’s manager read access to the home folder |
Makes it possible for the person designated as the deprovisioned user’s manager to view and retrieve data from the home folder of that user. The manager is determined based on the Manager attribute of the deprovisioned user account in Active Directory. |
|
Grant selected users or groups read access to the home folder |
Makes it possible for the specified users or groups to view and retrieve data from the deprovisioned user’s home folder. |
|
Make the selected user or group the owner of the home folder |
Designates the specified user or group as the owner of the deprovisioned user’s home folder. The owner is authorized to control how permissions are set on the folder, and can grant permissions to others. |
|
Delete the home folder when the user account is deleted |
Upon the deletion of a user account, analyzes whether the user’s home folder is empty, and then deletes or retains the home folder, depending on the policy configuration. A policy can be configured to only delete empty folders. Another option is to delete both empty and non-empty folders. |
To configure a Home Folder Deprovisioning policy, select Home Folder Deprovisioning on the Policy to Configure page in the New Deprovisioning Policy Object Wizard or in the Add Deprovisioning Policy Wizard. Then, click Next to display the Options to Deprovision Home Folder page.
Figure 93: Options to Deprovision Home Folder
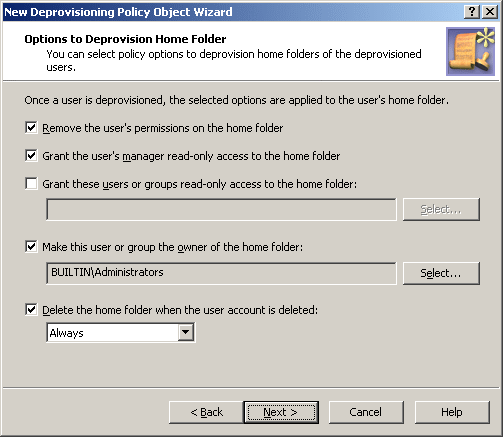
On this page, you can select the home folder deprovisioning options you want Active Roles to apply when deprovisioning a user.
The names of the first four options are self-explanatory. These refer to the policy options summarized in the table above:
-
Remove the user’s permissions on the home folder.
-
Grant the user’s manager read-only access to the home folder.
-
Grant these users or groups read-only access to the home folder.
-
Make this user or group the owner of the home folder.
Select check boxes next to the options you want to be applied.
The third option requires that you click Select to choose users or groups. The users or groups you select will be authorized to view and retrieve data from the home folders of the deprovisioned users.
The fourth option requires that you click Select to choose one user or group. The user or group you select will be authorized to control permissions on the home folders of the deprovisioned users.
You can also configure the policy to delete home folders. If you select the Delete the home folder when the user account is deleted check box, the policy causes Active Roles to delete the home folder once the user account associated with that folder is deleted. You can refine this behavior by selecting one of these options from the list beneath the check box:
-
If home folder is empty: Prevents Active Roles from deleting not empty home folders. If a given home folder contains any data, the policy does not delete that folder.
-
Always: Allows Active Roles to delete both empty and not empty home folders. Regardless of whether a given home folder contains any data, the policy deletes that folder upon user account deletion.
When you are done, click Next and follow the instructions in the wizard to create the Policy Object.
To configure a Home Folder Deprovisioning policy
-
On the Policy to Configure page, select Home Folder Deprovisioning, and then click Next.
-
On the Options to Deprovision Home Folder page, select the options you want the policy to apply when deprovisioning a user account. You can select any combination of these options to deprovision the home folder for the deprovisioned user account:
-
Remove the user’s permissions on the home folder
-
Grant the user’s manager read-only access to the home folder
-
Grant these users or groups read-only access to the home folder
-
Make this user or group the owner of the home folder
-
Delete the home folder when the user account is deleted
-
If you selected the Grant these users or groups read-only access to the home folder check box, click Select and use the Select Objects dialog to specify the users or groups you want.
-
If you selected the Make this user or group the owner of the home folder check box, click Select and use the Select Objects dialog to specify the user or group you want.
-
If you selected the Delete the home folder when the user account is deleted check box, select one of these options:
-
Always to have the policy delete the home folder regardless of whether the folder contains any files or sub-folders.
-
If home folder is empty to prevent the home folder from being deleted if it contains any files or sub-folders.
-
Click Next.
-
On the Enforce Policy page, you can specify objects to which this Policy Object is to be applied:
-
Click Next, and then click Finish.
The policy described in this scenario performs the following functions during the user deprovisioning process:
To implement this scenario, you must perform the following actions:
-
Create and configure the Policy Object that defines the appropriate policy.
-
Apply the Policy Object to a domain, OU, or Managed Unit.
As a result, when deprovisioning a user account in the container you selected in Step 2, Active Roles modifies the security on the user’s home folder as prescribed by this policy.
The following two sections elaborate on the steps to implement this scenario.

