You can use the Active Roles Web Interface to delete a user for logon to Azure.
Prerequisites
Only Global Admins can delete Azure users with any roles assigned to them.
|
|
CAUTION: Hazard of data loss! Deleting a user is an irreversible operation. A new user with the same name as a deleted user does not automatically assume the permissions and memberships of the deleted account. For this reason, it is advisable to disable rather than delete accounts. |
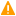
To delete an Azure AD user with the Web Interface
- On the Active Roles Web Interface navigation bar, click Directory Management.
-
On the Views tab in the Browse pane, click Active Directory.
The list of Active Directory domains is displayed.
-
Click the specific domain, container or the Organizational Unit, and then the specific user that you want to delete.
-
In the Command pane, click Delete.
The account is deleted.
Note: In a hybrid environment, the user must be deleted in the on-premises AD first and then the changes must be synchronized with Azure AD. In case, the user is deleted in Azure AD first, the Active Roles Web Interface still displays the Azure properties link for the deleted user but with no information. Further modification of the Azure properties for the deleted user will not be valid.