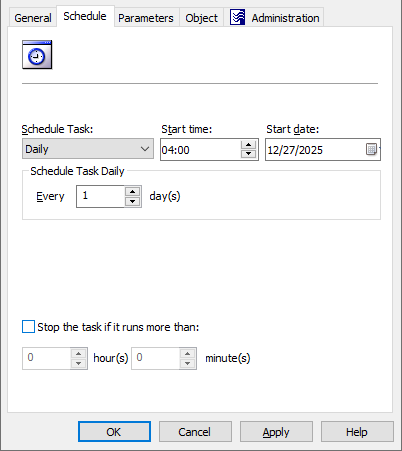
To remove members from an Microsoft 365 (M365) Group, you can use the Remove-QADO365GroupMember cmdlet on the Active Roles Management Shell interface.
For more information on removing a member from an M365 Group using the Management Shell interface, see the Active Roles PowerShell Reference Guide.