One Identity Manager offers simplified user account administration for Unix. One Identity Manager concentrates on setting up and editing user accounts and providing the required permissions. To equip users with the required permissions, groups are mapped in One Identity Manager. This makes it possible to use Identity and Access Governance processes such as attesting, Identity Audit, user account management and system entitlements, IT Shop, or report subscriptions for Unix based target systems.
One Identity Manager provides company employees with the user accounts required to allow you to use different mechanisms for connecting employees to their user accounts. You can also manage user accounts independently of employees and therefore set up administrator user accounts.
Additional information about the Unix core directory is loaded into the One Identity Manager database by data synchronization. There are only limited options for customizing this information in One Identity Manager due to the complex dependencies and far-reaching effects of any changes.
One Identity Manager supports most Unix and Linux derivatives. For more information, see the specifications for One Identity Safeguard Authentication Services.
NOTE: The Unix Based Target Systems Module must be installed as a prerequisite for managing Unix-based target systems in One Identity Manager. For more information about installing, see the One Identity Manager Installation Guide.
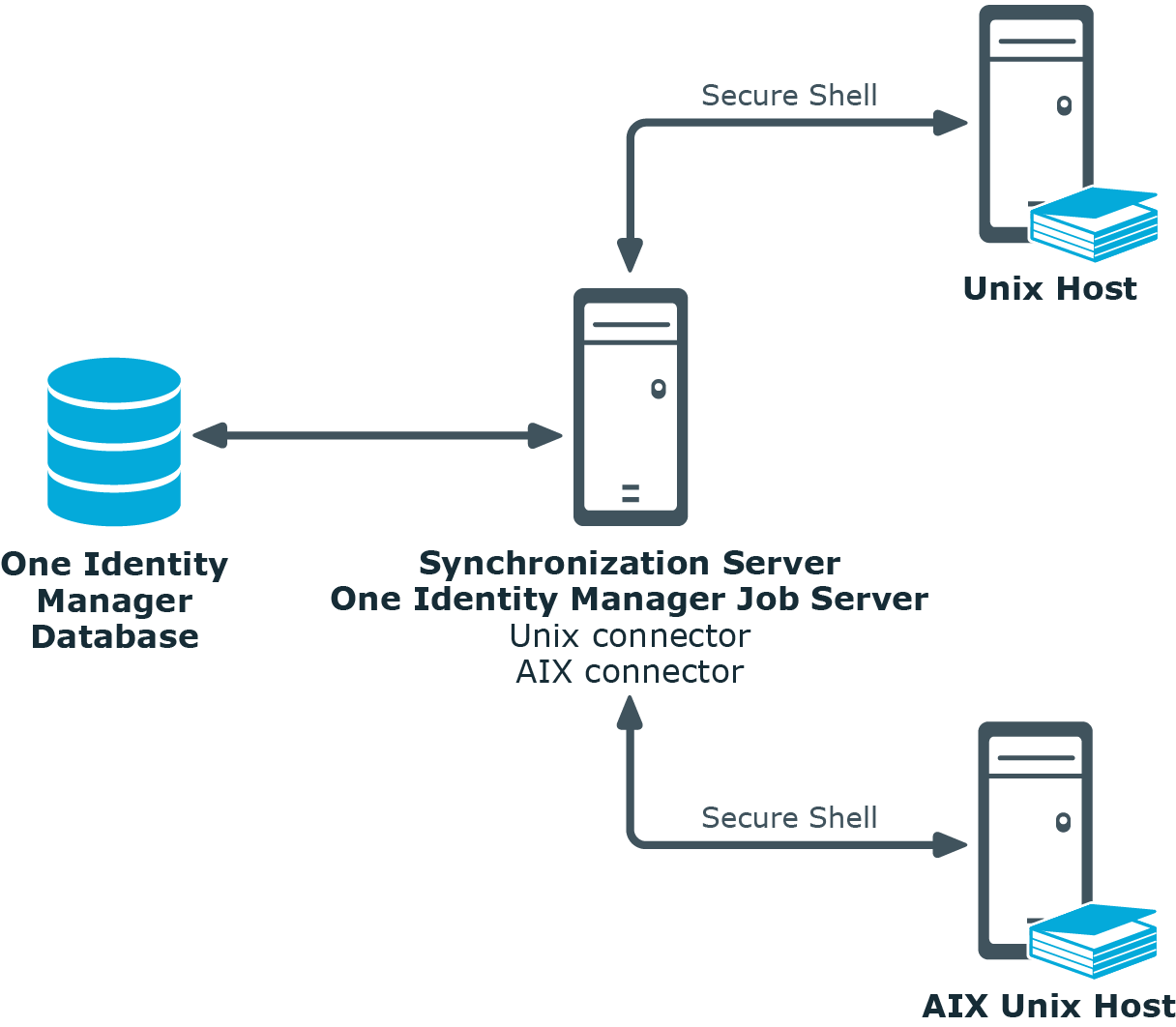
In One Identity Manager, the following servers play a role in managing Unix:
-
Unix host
Unix host where the directory is kept. This host is a selected live host with a good network connection to the synchronization server. The synchronization server connects to this host in order to access the Unix objects.
-
Synchronization server
The synchronization server for synchronizing the One Identity Manager database with the Unix-based target system. The One Identity Manager Service with the Unix machine role is installed on the synchronization server. The Unix machine role contains the Unix connector and the AIX connector. The Unix connector is used for synchronization and provisioning Unix-based objects. The AIX connector is implemented for synchronizing and provisioning IBM AIX systems objects. The connectors communicate directly with the Unix host.
Figure 1: Architecture for synchronization
The following users are used for setting up and managing Unix-based target systems.
Table 1: Users
| Target system administrators |
Target system administrators must be assigned to the Target systems | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Administer application roles for individual target system types.
-
Specify the target system manager.
-
Set up other application roles for target system managers if required.
-
Specify which application roles for target system managers are mutually exclusive.
-
Authorize other employees to be target system administrators.
-
Do not assume any administrative tasks within the target system. |
| Target system managers |
Target system managers must be assigned to the Target systems | Unix application role or a child application role.
Users with this application role:
-
Assume administrative tasks for the target system.
-
Create, change, or delete target system objects.
-
Edit password policies for the target system.
-
Prepare groups to add to the IT Shop.
-
Can add employees who have another identity than the Primary identity.
-
Configure synchronization in the Synchronization Editor and define the mapping for comparing target systems and One Identity Manager.
-
Edit the synchronization's target system types and outstanding objects.
-
Authorize other employees within their area of responsibility as target system managers and create child application roles if required. |
| One Identity Manager administrators |
administrator and administrative system users Administrative system users are not added to application roles.
administrators:
-
Create customized permissions groups for application roles for role-based login to administration tools in the Designer as required.
-
Create system users and permissions groups for non role-based login to administration tools in the Designer as required.
-
Enable or disable additional configuration parameters in the Designer as required.
-
Create custom processes in the Designer as required.
-
Create and configure schedules as required.
-
Create and configure password policies as required. |
| Administrators for the IT Shop |
Administrators must be assigned to the Request & Fulfillment | IT Shop | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
|
|
Product owner for the IT Shop |
Product owners must be assigned to the Request & Fulfillment | IT Shop | Product owners application role or a child application role.
Users with this application role:
|
| Administrators for organizations |
Administrators must be assigned to the Identity Management | Organizations | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
|
| Business roles administrators |
Administrators must be assigned to the Identity Management | Business roles | Administrators application role.
Users with this application role:
|
Use configuration parameters to configure the behavior of the system's basic settings. One Identity Manager provides default settings for different configuration parameters. Check the configuration parameters and modify them as necessary to suit your requirements.
Configuration parameters are defined in the One Identity Manager modules. Each One Identity Manager module can also install configuration parameters. In the Designer, you can find an overview of all configuration parameters in the Base data > General > Configuration parameters category.
For more information, see Configuration parameters for managing Unix-based target systems.

