The basis for role mining is always a cluster analysis when the Analyzer with help of mathematical algorithm tries to find single clusters, meaning identities with similar permissions. In the process, either hierarchical structures are built or predefined structures are applied that can be used for constructing your own role model.
In role mining, you not only try to find single clusters and assign these to business roles, but you also try to develop direct hierarchical role structures that can then be effectively used through standard inheritance mechanisms.
Automatic role mining supports One Identity Manager through two different cluster analysis methods that differ in the way they calculate the distances between individual clusters. The use of existing role structures, for example, organizational structure from ERP systems, is possible. Permissions analysis can then be used to assign permissions to these role structures. Lastly, role structures can be freely defined and assignment of permissions and identities can be manually evaluated based on existing permissions.
Figure 14: Cluster analysis methods in the Analyzer
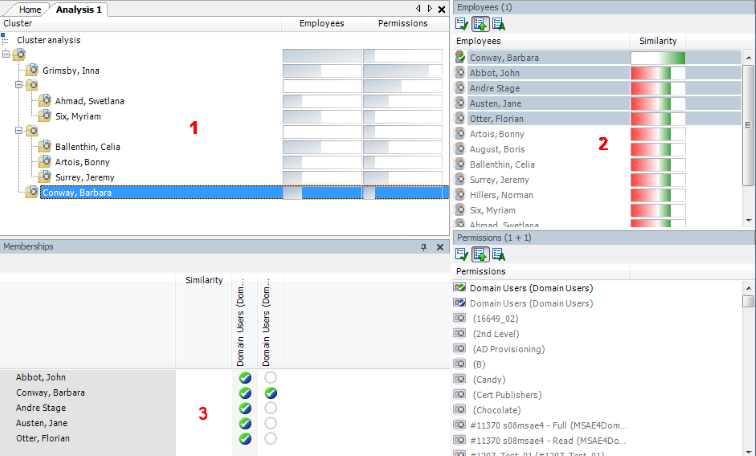
In clustering methods, Analyzer calculates a frequency distribution from user permissions in the different application systems, like Active Directory, HCL Domino, or SAP R/3. Certain permissions may have a higher weighting in comparison to others. The number of a permissions' members can, for example, represent this sort of criteria. This is acknowledged through the Analyzer during calculation and taken into account by weighting the distance between clusters. This allows the hierarchical structures arising from the analysis to be optimized in advance and the smallest possible number of roles to be attained.
