The following tables contain all the encryption algorithms you can configure One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) to recognize. If you use a configuration that is only partially supported, SPS might ignore the connection without warning.
NOTE: Do not use the CBC block cipher mode, or any sha1-based KEX, MAC, or host key algorithm, which are considered weak.
Key exchange algorithms
The default SPS configuration for both the client and the server is the following:
ecdh-sha2-nistp256,ecdh-sha2-nistp384,ecdh-sha2-nistp521,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256,diffie-hellman-group16-sha512,diffie-hellman-group18-sha512,diffie-hellman-group14-sha256
The following key exchange (KEX) algorithms are recognized:
Figure 247: Key exchange (KEX) algorithms
| ecdh-sha2-nistp256 |
✔ |
|
| ecdh-sha2-nistp384 |
✔ |
|
| ecdh-sha2-nistp521 |
✔ |
|
| diffie-hellman-group1-sha1 |
- |
Not recommended |
| diffie-hellman-group14-sha1 |
- |
Not recommended |
| diffie-hellman-group14-sha256 |
✔ |
|
| diffie-hellman-group15-sha512 |
- |
|
| diffie-hellman-group16-sha512 |
✔ |
|
| diffie-hellman-group17-sha512 |
- |
|
| diffie-hellman-group18-sha512 |
✔ |
|
| diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256 |
✔ |
|
| diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha1 |
- |
Not recommended |
During an SSH session, SPS performs a key re-exchange after each gigabyte of transmitted data or after each hour of connection time, whichever comes sooner.
Cipher algorithms
The default SPS configuration for both the client and the server is the following:
aes128-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes256-ctr
The following cipher algorithms are recognized:
Figure 248: Cipher algorithms
| 3des-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| blowfish-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| twofish256-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| twofish-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| twofish192-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| twofish128-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| aes256-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| aes192-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| aes128-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| aes256-ctr |
✔ |
|
| aes192-ctr |
✔ |
|
| aes128-ctr |
✔ |
|
| serpent256-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| serpent192-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| serpent128-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| arcfour |
– |
Not recommended |
| idea-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| cast128-cbc |
– |
Not recommended |
| none |
– |
Means no cipher algorithm; not recommended |
Message authentication code (MAC) algorithms
The default SPS configuration for both the client and the server is the following:
hmac-sha2-256,hmac-sha2-512
The following MAC algorithms are recognized:
Figure 249: Message Authentication Code (MAC) algorithms
| hmac-sha1 |
– |
Not recommended |
| hmac-sha1-96 |
– |
Not recommended |
| hmac-md5 |
– |
Not recommended |
| hmac-md5-96 |
– |
Not recommended |
| hmac-sha2-256 |
✔ |
|
| hmac-sha2-512 |
✔ |
|
SSH compression algorithms
The default SPS configuration for both the client and the server is the following:
none
The following SSH compression algorithms are recognized:
Figure 250: SSH compression algorithms
| zlib |
– |
Not recommended |
| none |
✔ |
Means no compression |
Host key algorithms
The default SPS configuration for both the client and the server is the following:
ecdsa-sha2-nistp256,ssh-ed25519,rsa-sha2-512,rsa-sha2-256,ssh-rsa
The following host key algorithms are recognized:
Figure 251: Host key algorithms
| ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 |
✔ |
|
| ssh-ed25519 |
✔ |
|
| rsa-sha2-512 |
✔ |
|
| rsa-sha2-256 |
✔ |
|
| ssh-rsa |
✔ |
Not recommended
NOTE: The ssh-rsa public key signature algorithm that depends on SHA-1 is not recommended and will be disabled in a future release. |
With the SPS and Sudo integration, you can collect and analyze Sudo session recordings, called iologs in Sudo terminology, in SPS.
By using SPS to collect and analyze Sudo session recordings, your Sudo recordings are stored and indexed by SPS, and you can use the Search interface, for example, to view the recordings, list commands executed during a Sudo session, and so on.
To be able to use Sudo with SPS, perform the following settings:
-
In SPS, create a new Sudo connection as described in Setting up Sudo connections in SPS.
-
On the client side, configure Sudo as described in Configuring Sudo.
To enable the SPS and Sudo integration, perform the following steps in SPS.
For a detailed description on configuring connections, see General connection settings.
Prerequisites
-
You have the SPS license required to integrate SPS and Sudo. For more information, contact our Sales Team.
-
An X.509 certificate and its private key to encrypt the communication between the client and SPS. Use your own PKI system to generate these certificates, as they cannot be created on SPS.
To create a Sudo connection in SPS
-
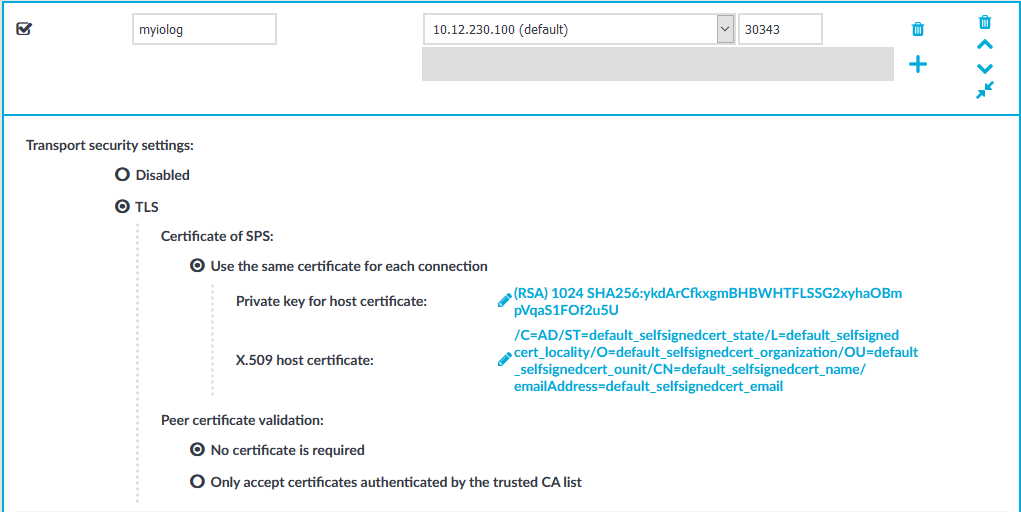
Navigate to Sudo iolog Control > Connections.
Figure 252: Sudo iolog Control > Connections — Creating a Sudo connection in SPS
-
Since SPS can have multiple network interfaces, select an IP address where the Sudo clients can send the iologs. If required, you can change the port number.
-
TLS is disabled by default as you have to configure certificates manually. Make sure that you enable it as iologs carry highly sensitive information.
To require encryption, select TLS. When the connection is encrypted, SPS has to show a certificate to the peer.
-
Select the certificate to show to the peers.
-
Generate and sign a certificate for SPS in your PKI system, and export the certificate and its private key.
-
Select Use the same certificate for each connection.
-
Select Private key for host certificate, click 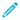 and upload the private key.
and upload the private key.
-
Select X.509 host certificate, click  and upload the certificate.
and upload the certificate.
-
Select how SPS should authenticate the peers.
-
To permit connections from peers without requesting a certificate, select No certificate is required.
-
To permit connections only from peers with a valid certificate that was signed by a specific CA, complete the following steps.
-
Create a list of trusted Certificate Authorities that will be used to validate the certificates of the peers. For details on creating a trusted CA list, see Verifying certificates with Certificate Authorities.
-
Select Only accept certificates authenticated by the trusted CA list.
-
Select the certificate authority list to use in the Trusted CA field.
-
Select Enable indexing.
Figure 253: Sudo iolog Control > Enable indexing — Select indexing policy
-
To determine the priority level of indexing this connection, select the appropriate Priority level. Selecting a high priority level means that the trails of this connection are indexed first. Selecting a low priority level means that the trails of this connection are also indexed, but there might be a delay in indexing if there are a lot of high-priority connections waiting to be indexed. Selecting near real-time means that the indexing of sessions starts when sessions are still ongoing.
-
Select the Indexing policy to be used.
Both built-in indexer policies feature automatic language detection. To specify a particular language detection configuration, select the indexing policy if you have created before. For more information, see Configuring the internal indexer.
-
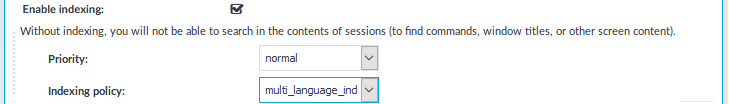
To limit the number of new connection requests accepted from a single client IP address per minute, enter the maximum number of accepted connections into the Connection rate limit field.
Figure 254: Sudo iolog Control > Connections — Additional settings
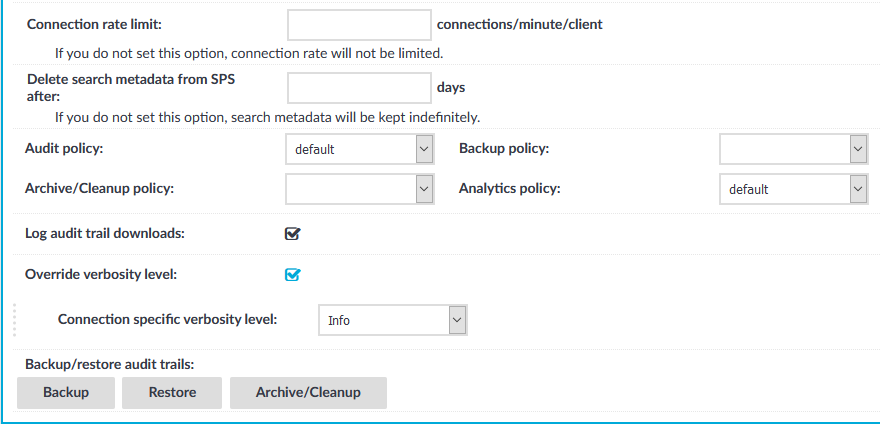
-
Enter how long SPS (in days) should keep the metadata into the Delete search metadata from SPS after field. For example, if you specify 365, SPS deletes the data of connections older than a year. Enter zero (0) to keep the data indefinitely (this is also the default behavior of SPS).
-
If configured, select a policy to control various aspects of the connection. For more information, see Policies.
-
If you want to find out if the audit trail file of a relevant indexed session has already been downloaded, select Log audit trail downloads.
-
Optional: To set a verbosity level for this connection, select Override verbosity level and select the desired log level from the Connection specific verbosity level field.
NOTE: The new verbosity level applies only to new sessions started after committing the change. The verbosity level of active sessions do not change.
-
Click  .
.
Before you can use the SPS and Sudo integration, perform the Sudo-side configuration steps as described in Configuring Sudo.
To enable the SPS and Sudo integration, perform the following steps on the client side.
Prerequisites
-
For Sudo, you need a host with Sudo 1.9 or higher installed.
-
You have the SPS license required to integrate SPS and Sudo. For more information, contact our Sales Team.
-
For SPS, you have configured Sudo iolog connections as described in Setting up Sudo connections in SPS.
To enable the SPS and Sudo integration
-
In Sudo, open the sudoers file using visudo.
-
Add the following lines:
Defaults ignore_iolog_errors
Defaults log_servers = <IP of SPS>:<PORT of SPS>
Defaults log_output
Defaults log_input
Where the options are as follows:
Table 11: Options for the Sudo-side configuration
|
ignore_iolog_errors |
Allow running commands even if sudoers cannot write to the I/O log. |
|
log_servers |
Specify the IP address of your SPS. Additionally, you can specify the port number of SPS. If you use Transport Layer Security (TLS) for encryption, you must also specify it as described below. |
|
log_output |
Enable recording any change, which appears on the screen. |
|
log_input |
Ensure recording of any user input, that is, anything the user types. |
-
To require encryption (recommended), use TLS as follows:
-
Configure the log_servers option in the sudoers file:
Defaults log_servers = <IP of SPS>:<PORT of SPS>(tls)
-
Configure the log_server_cabundle, log_server_peer_cert, or log_server_peer_key settings with the required TLS settings. For more information, see Securing server connections in the Sudoers Manual.
For example, add the path to the certificate authority bundle file in .pem format as shown in the example below:
Defaults log_server_cabundle = <path_to_PEM_file>/<file_name>.pem
Expected result
On the client side, start typing sudo and open any program.
In SPS, you can view the session using the Search interface.


 and upload the private key.
and upload the private key.

 .
.