Synchronization Service performs data synchronization operations and include the Synchronization Service Console that provides a graphical user interface for managing connections to data systems and data synchronization operations.
Synchronization Service
Capture Agent
Synchronization Service Capture Agent allows you to synchronize user passwords between Active Directory domains managed by Synchronization Service and other connected data systems. The following diagram shows how the Password Synchronization feature of Synchronization Service works:
Figure 2: Password synchronization
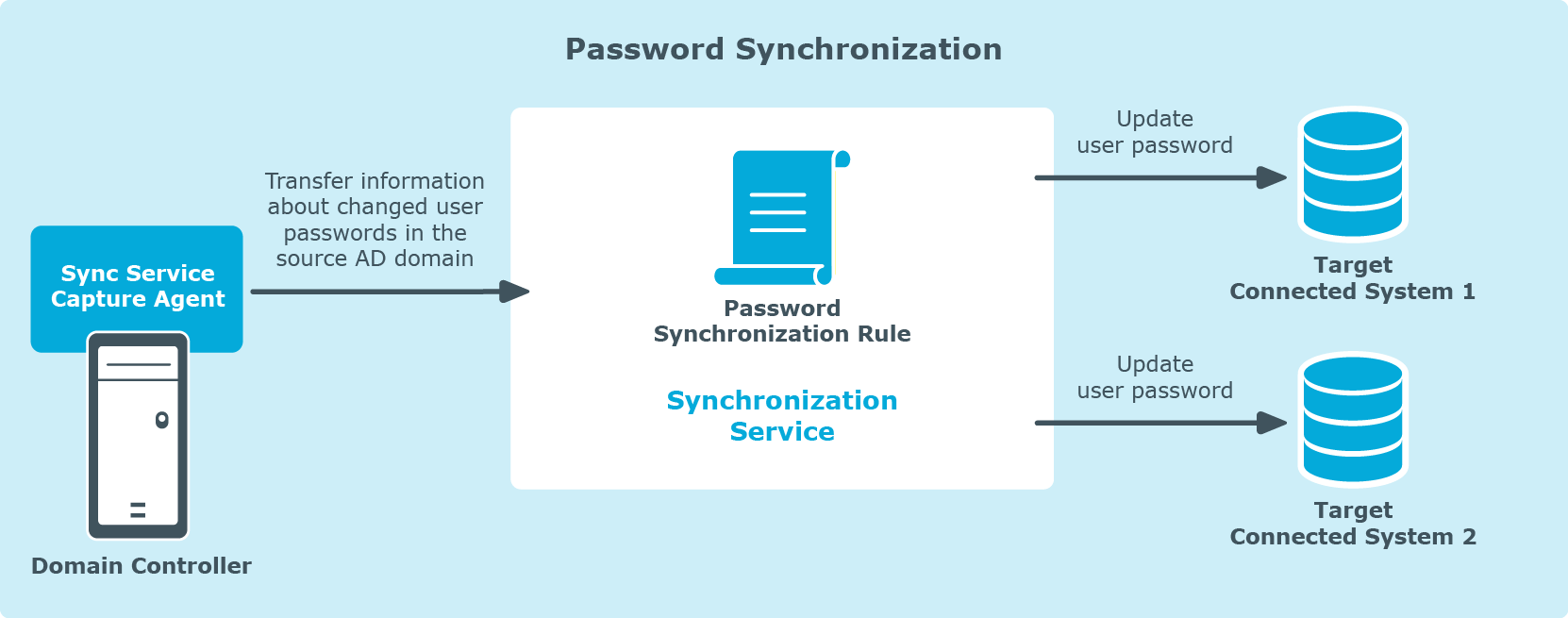
Capture Agent tracks changes to user passwords in the source Active Directory domain and provides that information to Synchronization Service, which in turn synchronizes the changes with target connected data systems by using the password synchronization rules you specified. To synchronize passwords, you need to install Capture Agent on each domain controller in the Active Directory domain you want to use as a source for the password synchronization operations.
Connectors and connected data systems
Synchronization Service lets you synchronize identity information between a wide variety of external data systems. To synchronize identities, you must connect Synchronization Service to your data systems through special connectors. A connector enables Synchronization Service to access a specific data system and read and synchronize identity data in that system.
For the list of supported data systems, see Extensibility.
Sync workflows
A sync workflow is a set of synchronization steps (or synchronization operations) that define how to synchronize objects between two connected data systems. A sync workflow can comprise one or more synchronization steps. You can use the Synchronization Service Console, a component of Synchronization Service, to configure as many sync workflows as needed.
You can configure a synchronization step to perform one of the following operations:
-
Creation: Creates objects in the target connected data systems based on the changes made to specific objects in the source connected system. When creating a new object, Synchronization Service assigns initial values to the object attributes based on the attribute population rules you have configured.
-
Update: Changes the attributes of objects in the target connected data systems based on the changes made to specific objects in the source connected system. To define the objects that will participate in the update operation you can use object mapping rules. For more information, see Mapping objects.
-
Deprovision: Modifies or removes objects in the target connected data systems after their counterparts have been disconnected from the source connected system. Synchronization Service can be configured to remove objects permanently or change them to a specific state.
