SonicWALL Single Sign-On
A key component of the malware detection information that enables Cloud Access Manager and Security Analytics Engine risk score evaluations to associate users with malware detections is user identification by firewall. Without this feature, only IP address matches would function, which would limit the malware association capabilities of Security Analytics Engine and prevent external Cloud Access Manager users being associated with malware detection records.
Many user authentication options are available with SonicWALL firewalls, but enabling integrated Single Sign-On (SSO) capabilities that do not prompt the user for authentication credentials include a combination of the following SonicWALL user authentication options:
- Browser-based NTLM authentication using RADIUS to authenticate the users.
- Single Sign-On agent deployments provided by installing and configuring the SonicWALL Directory Services Connector.
|
|
NOTE: We recommend you review the configuration options outlined in the SonicOS Administrator Guide as each option should be evaluated for compatibility requirements and potential limitations. |
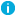
The following example includes a combination of NTLM and SSO Agent configurations, where NTLM is preferred but SSO Agent fallback is used to seamlessly authenticate user access to web sites. The process of authenticating the user is illustrated in Figure 2 and described as follows:
- An internal corporate network user, User1 in the MyCorp domain for example, accesses the internet and is authenticated using the firewall SSO feature.
- Based on the Next Generation Firewall (NGFW) SSO configuration, one or more of the following SSO authentication steps is performed to identify the user as MyCorp\User1:
- NTLM negotiation is attempted with User1’s browser. The browser supplied credentials are forwarded to a configured RADIUS server for authentication and authorization policy evaluations.
- Alternatively, the NGFW may query an installed and configured SonicWALL SSO Agent (Directory Services Connector) for information related to the authenticated user on the source computer IP address. The SSO Agent can be configured with various options for determining the authenticated user, this includes:
- Parsing Domain Controller logs.
- Querying the computer in question using NetAPI or WMI protocols.
Figure 2: SonicWALL Single Sign-On
The Security Analytics Engine SonicWALLProcessor service
In order to process malware detection information forwarded by the SonicWALL Next Generation Firewall (NGFW) in AppFlow details, the optional Security Analytics Engine SonicWALLProcessor Service must be installed and configured to receive AppFlow information and forward malware detection records to the Security Analytics Engine web site. Once received by the Security Analytics Engine web site, the malware detection records are stored for subsequent risk score evaluations when users access Cloud Access Manager applications.
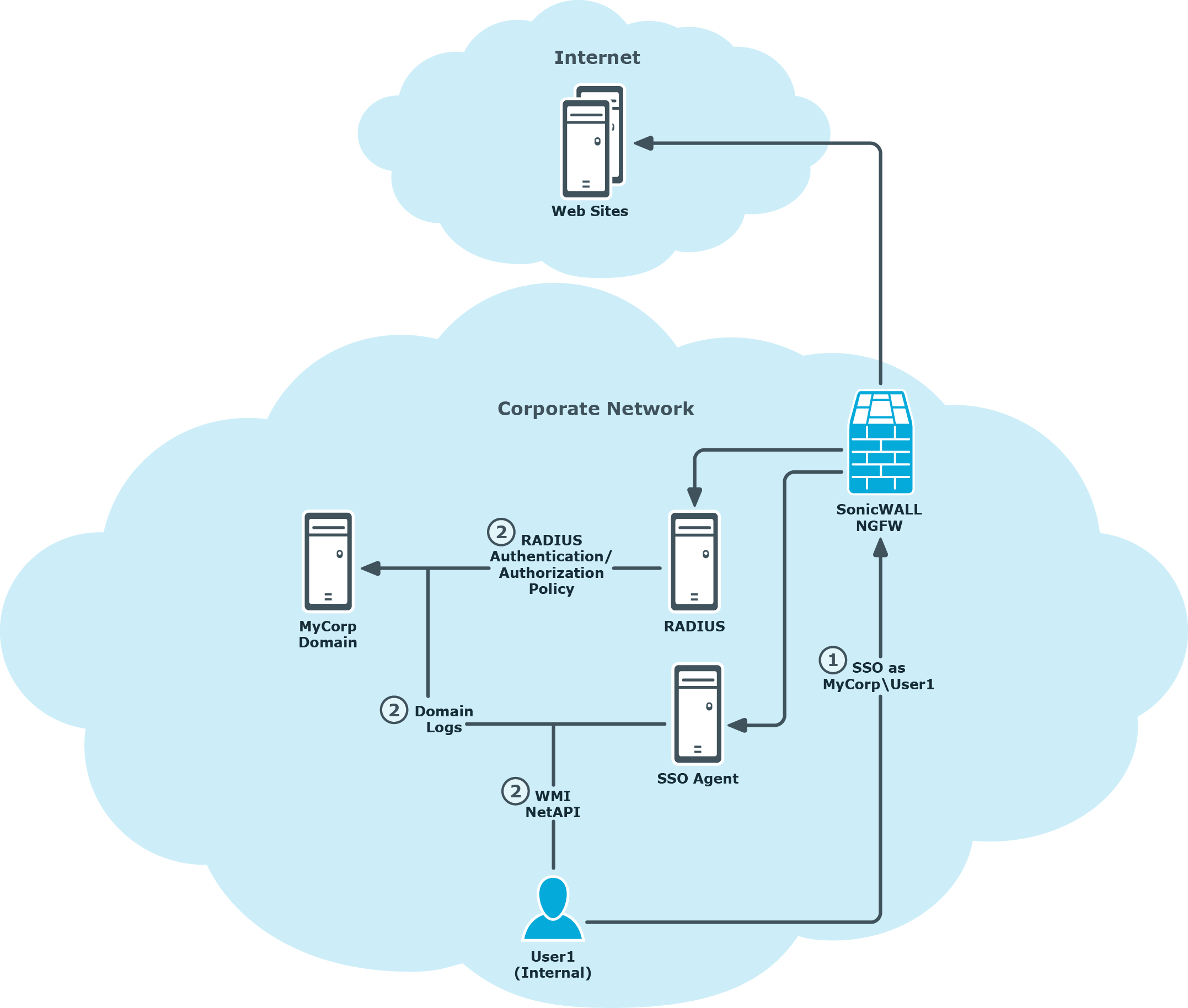
The process of malware detection information flowing from the SonicWALL NGFW through the Security Analytics Engine SonicWALLProcessor Service to the Security Analytics Engine web site is illustrated in Figure 3 and described as follows:
- An internal corporate network user, User1 in the MyCorp domain for example, accesses the internet and the NGFW detects malware during the browsing activity.
-
Based on the AppFlow configuration in the NGFW, the malware detection details, including the IP address and SSO user details, are sent to the Security Analytics Engine SonicWALLProcessor Service as follows:
IP: 10.6.100.102
User: MyCorp\User1
- The Security Analytics Engine SonicWALLProcessor Service receives the malware detection details and forwards malware detection records to the Security Analytics Engine web site.
Figure 3: Security Analytics Engine malware detection
Cloud Access Manager user authentication
Cloud Access Manager user authentication
Cloud Access Manager provides several user authentication options through configured Front-End Authenticators (FEA) that you can use to provide user identification details for Security Analytics Engine to match SonicWALL malware detection records. In the following example, both Active Directory and LDAP authenticator configuration details are provided that will support Security Analytics Engine and the SonicWALL malware record provided domain\user user name format:
- Active Directory Authenticator - User attributes that support the domain\user user name format are retrieved automatically.
- LDAP Authenticator – Utilize LDAP user attributes that will enable user name correlation to SonicWALL malware records by correlating to the user attributes in the directory used for SonicWALL authentication, for example:
- Unique Id – canonicalName (Active Directory) or distinguishedName (OpenLDAP).
- Login Name – sAMAccountName (Active Directory) or Uid (OpenLDAP).
- Mail – mail (Active Directory or OpenLDAP).
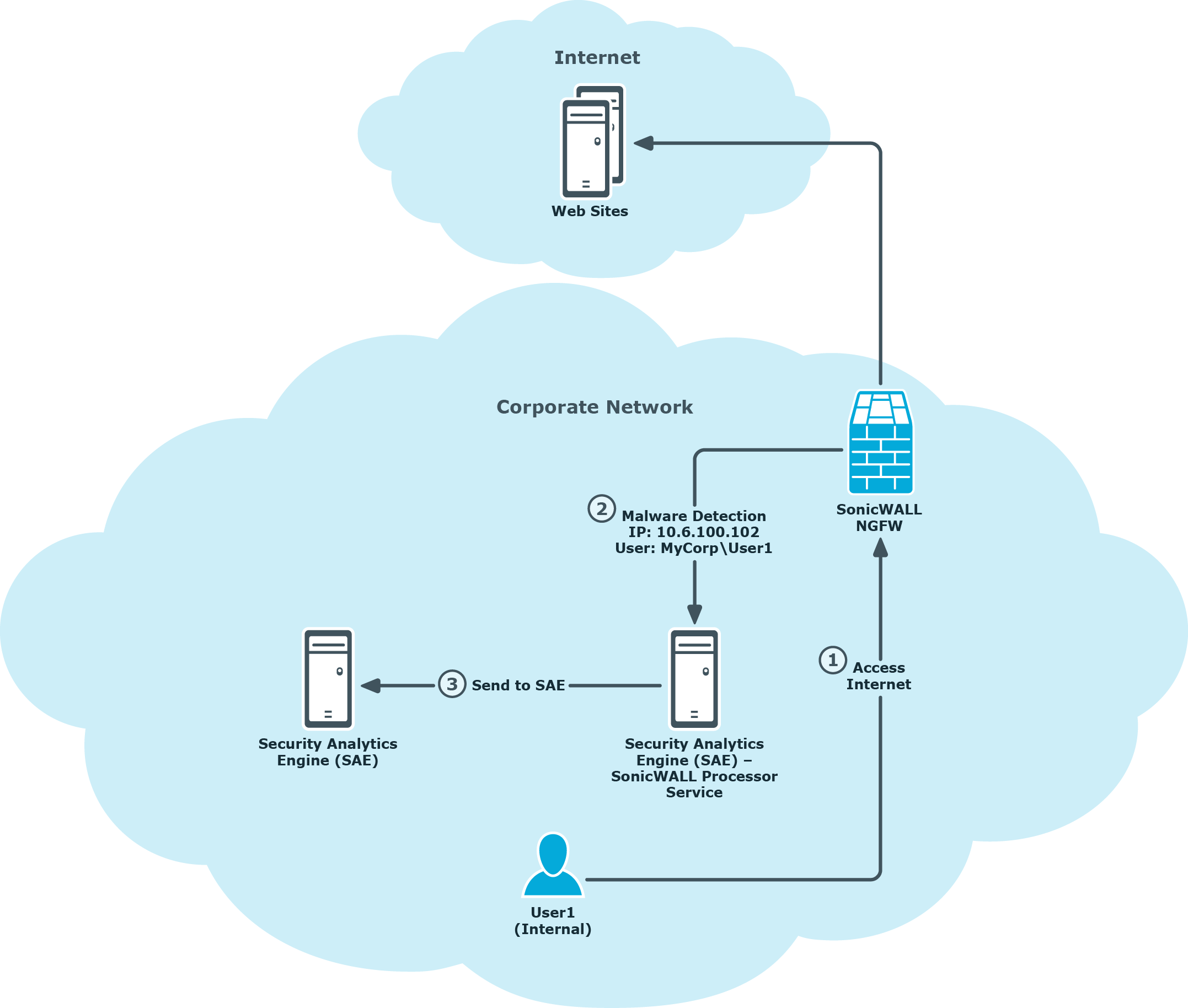
The process of Cloud Access Manager authenticating internal and external users and forwarding IP address and user identification information to Security Analytics Engine for risk policy evaluation, including finding records associated with malware, is depicted in Figure 4 and described below:
-
User1 accesses a Cloud Access Manager application from either inside the corporate network, or optionally from the Internet.
-
Cloud Access Manager performs evaluations to determine whether the user’s access to the application is authorized.
-
When the user is authenticated using either an Active Directory or LDAP FEA, user identification attributes are retrieved that detail the user identity and are used as part of the authorization evaluation, these include:
Active Directory FEA
Upn: MyCorp\User1
UniqueId: 0A2524D3-352D-4025-B6EE-7AC868D7A3D4
Mail: user1@mycorp.com
or
LDAP FEA
Upn: User1
UniqueId: CN=Corp User1,CN=Users,DC=mycorp,DC=com
Mail: user1@mycorp.com
-
While determining authorization, Cloud Access Manager queries Security Analytics Engine to determine the user’s risk score, and forwards the IP address and user attribute information for processing by Security Analytics Engine. During the risk score evaluation, Security Analytics Engine will search for malware records received from the firewall and match on either a user name or IP address.
In the case where an LDAP FEA is used, the Security Analytics Engine evaluation will correlate the LDAP provided attributes to the mycorp\User1 format.
Figure 4: Cloud Access Manager Front-end Authenticators and user identification
Using split DNS to forward internal IP addresses to the Security Analytics Engine
When Cloud Access Manager notifies the Security Analytics Engine of a security event, it includes, as part of the contextual information, the IP address of the end-user’s machine. Since users can access Cloud Access Manager from the internal network, as well as from the Internet, Cloud Access Manager must ensure that the correct IP address (internal or external) is reported. To ensure that the internal address is reported for connections coming from the internal network, split DNS must be configured for the Cloud Access Manager proxy hostname.