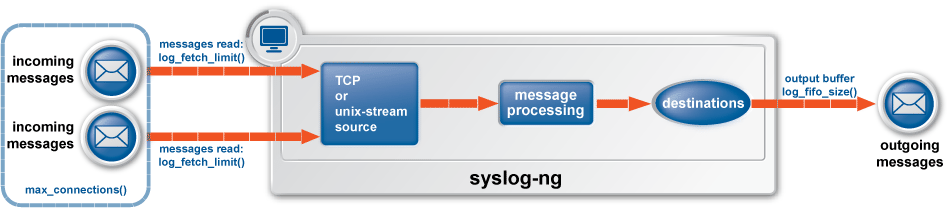
The syslog-ng Premium Edition application can store messages on the local hard disk if the destination (for example, the central log server) or the network connection to the destination becomes unavailable. The syslog-ng PE application automatically sends the stored messages to the destination when the connection is reestablished. The disk buffer is used as a queue: when the connection to the destination is reestablished, syslog-ng PE sends the messages to the destination in the order they were received.
The following destination drivers can use disk-based buffering: elasticsearch(), elasticsearch2(), hdfs(), kafka(), mongodb(), program(), smtp(), snmp(), sql(), unix-dgram(), and unix-stream(). The network(), syslog(), tcp(), and tcp6() destination drivers can also use disk-based buffering, except when using the udp transport method. (The other destinations or protocols do not provide the necessary feedback mechanisms required for disk-based buffering.)
Every such destination uses a separate disk buffer (similarly to the output buffers controlled by log-fifo-size()). The hard disk space is not pre-allocated, so ensure that there is always enough free space to store the disk buffers even when the disk buffers are full.
If syslog-ng PE is restarted (using the /etc/init.d/syslog-ng restart command, or another appropriate command on your platform), it automatically saves any unsent messages from the disk buffer and the output queue. After the restart, syslog-ng PE sends the saved messages to the destination. In other words, the disk buffer is persistent. The disk buffer is also resistant to syslog-ng PE crashes.
The syslog-ng PE application supports two types of disk buffering: reliable and normal. For details, see the section called “Enabling reliable disk-based buffering” and the section called “Enabling normal disk-based buffering”, respectively.
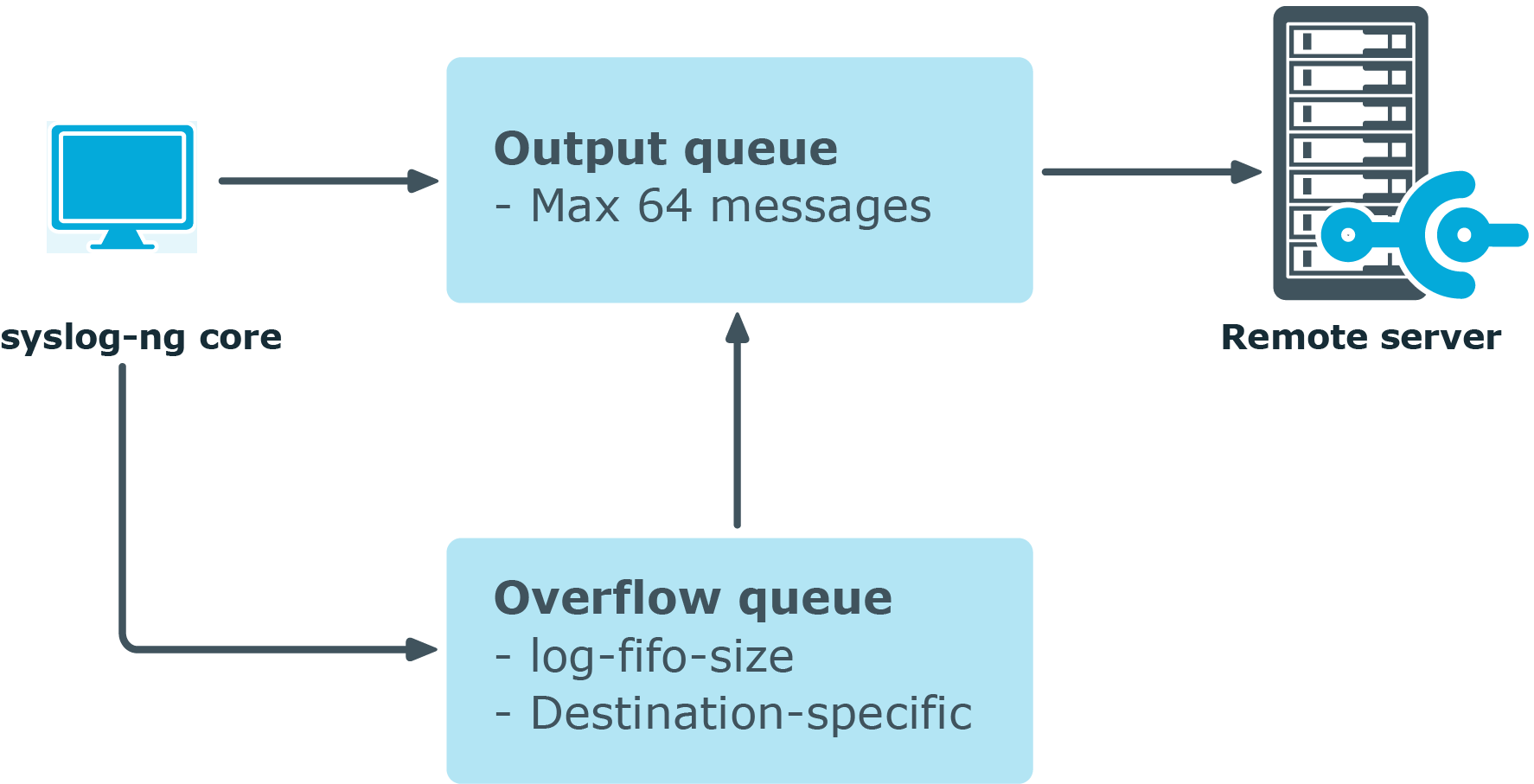
Message handling and normal disk-based buffering. When you use disk-based buffering, and the reliable() option is set to no, syslog-ng PE handles outgoing messages the following way:
-
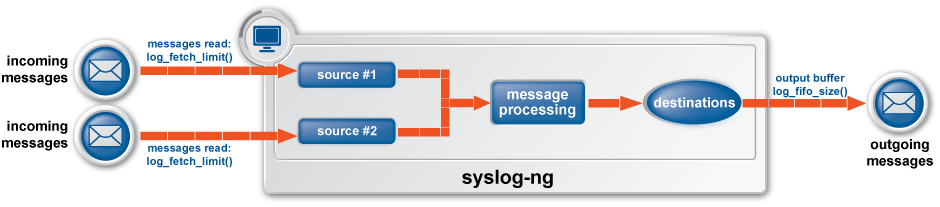
Output queue: Messages from the output queue are sent to the destination (for example, your central log server). The syslog-ng PE application puts the outgoing messages directly into the output queue, unless the output queue is full. By default, the output queue can hold 64 messages (you can adjust it using the quot-size() option).
-
Disk buffer: If the output queue is full, disk-buffering is enabled, and reliable() is set to no, syslog-ng PE puts the outgoing messages into the disk buffer of the destination. (The disk buffer is enabled if the log-disk-fifo-size() parameter of the destination is larger than 0. This option specifies the size of the disk buffer in bytes.)
-
Overflow queue: If the output queue is full and the disk buffer is disabled or full, syslog-ng PE puts the outgoing messages into the overflow queue of the destination. (The overflow queue is identical to the output buffer used by other destinations.) The log-fifo-size() parameter specifies the number of messages stored in the overflow queue. For details on sizing the log-fifo-size() parameter, see also the section called “Managing incoming and outgoing messages with flow-control”.
|
|
NOTE:
Using disk buffer can significantly decrease performance. |
Message handling and reliable disk-based buffering. When you use disk-based buffering, and the reliable() option is set to yes, syslog-ng PE handles outgoing messages the following way.
The mem-buf-size() option determines when flow-control is triggered. All messages arriving to the log path that includes the destination using the disk-buffer are written into the disk-buffer, until the size of the disk-buffer reaches (disk-buf-size() minus mem-buf-size()). Above that size, messages are written into both the disk-buffer and the memory-buffer, indicating that flow-control needs to slow down the message source. These messages are not taken out from the control window (governed by log-iw-size()), causing the control window to fill up. If the control window is full, the flow-control completely stops reading incoming messages from the source. (As a result, mem-buf-size() must be at least as large as log-iw-size().)
Enabling reliable disk-based buffering
The following destination drivers can use disk-based buffering: elasticsearch(), elasticsearch2(), hdfs(), kafka(), mongodb(), program(), smtp(), snmp(), sql(), unix-dgram(), and unix-stream(). The network(), syslog(), tcp(), and tcp6() destination drivers can also use disk-based buffering, except when using the udp transport method. (The other destinations or protocols do not provide the necessary feedback mechanisms required for disk-based buffering.)
To enable reliable disk-based buffering, use the disk-buffer(reliable(yes)) parameter in the destination. Use reliable disk-based buffering if you do not want to lose logs in case of reload/restart, unreachable destination or syslog-ng PE crash. This solution provides a slower, but reliable disk-buffer option. It is created and initialized at startup and gradually grows as new messages arrive. The filename of the reliable disk buffer file is the following: <syslog-ng path>/var/syslog-ng-00000.rqf.
Example 8.7. Example for using reliable disk-based buffering
destination d_BSD {
network(
"127.0.0.1"
port(3333)
disk-buffer(
mem-buf-size(10000)
disk-buf-size(2000000)
reliable(yes)
)
);
};
Enabling normal disk-based buffering
The following destination drivers can use disk-based buffering: elasticsearch(), elasticsearch2(), hdfs(), kafka(), mongodb(), program(), smtp(), snmp(), sql(), unix-dgram(), and unix-stream(). The network(), syslog(), tcp(), and tcp6() destination drivers can also use disk-based buffering, except when using the udp transport method. (The other destinations or protocols do not provide the necessary feedback mechanisms required for disk-based buffering.)
To enable normal disk-based buffering, use the disk-buffer(reliable(no)) parameter in the destination. Use normal disk-based buffering if you want a solution that is faster than the reliable disk-based buffering. In this case, disk buffering will be less reliable and it is possible to lose logs in case of syslog-ng PE crash. The filename of the normal disk buffer file is the following: <syslog-ng path>/var/syslog-ng-00000.qf.
It is possible to use this option without using the disk-buffer plugin. In this case, use the log-disk-fifo-size() parameter in the destination.
Example 8.8. Example for using normal disk-based buffering
When using the disk-buffer plugin
destination d_BSD {
network(
"127.0.0.1"
port(3333)
disk-buffer(
mem-buf-length(10000)
disk-buf-size(2000000)
reliable(no)
)
);
};
Without disk-buffer plugin
destination d_BSD {
network(
"127.0.0.1"
port(3333)
log-disk-fifo-size(2000000)
log-fifo-size(10000)
);
};
Enabling memory buffering
To enable memory buffering, use the log-fifo-size() parameter in the destination. All destination drivers can use memory buffering. Use memory buffering if you want to send logs to destinations where disk-based buffering is not available. Or if you want the fastest solution, and if syslog-ng PE crash or network downtime is never expected. In these cases, losing logs is possible. This solution does not use disk-based buffering, logs are stored only in the memory.
Example 8.9. Example for using memory buffering
destination d_BSD {
network(
"127.0.0.1"
port(3333)
log-fifo-size(10000)
);
};