Wizard for entering filters
At certain points you can define filter conditions. The filter conditions are formulated like a condition (WHERE clause) for a database query.
You can enter database queries directly or put them together with a wizard. Use the  and
and  buttons to switch to the relevant view.
buttons to switch to the relevant view.
-
The comparison operators =, <>, <, >, <=, >=, and like are supported for defining conditions.
-
To link condition you can use the logical operators AND, OR, and NOT.
-
You can use variables in your condition definitions. Variable must be masked.
Syntax: '$<variable>$'
NOTE: If the condition contains a dollar sign, which is not labeling a variable, it must be masked with $.
Example: '300 $$' compared to the value '300 $'
TIP: If you enter a condition directly, you can access predefined variables with the  button.
button.
Each condition is displayed in a special control in the wizard. The controls contain connection points to logically join single conditions or delete single conditions. The connection points are set if you mouse over the edge of the respective control.
Figure 2: Wizard for entering filters
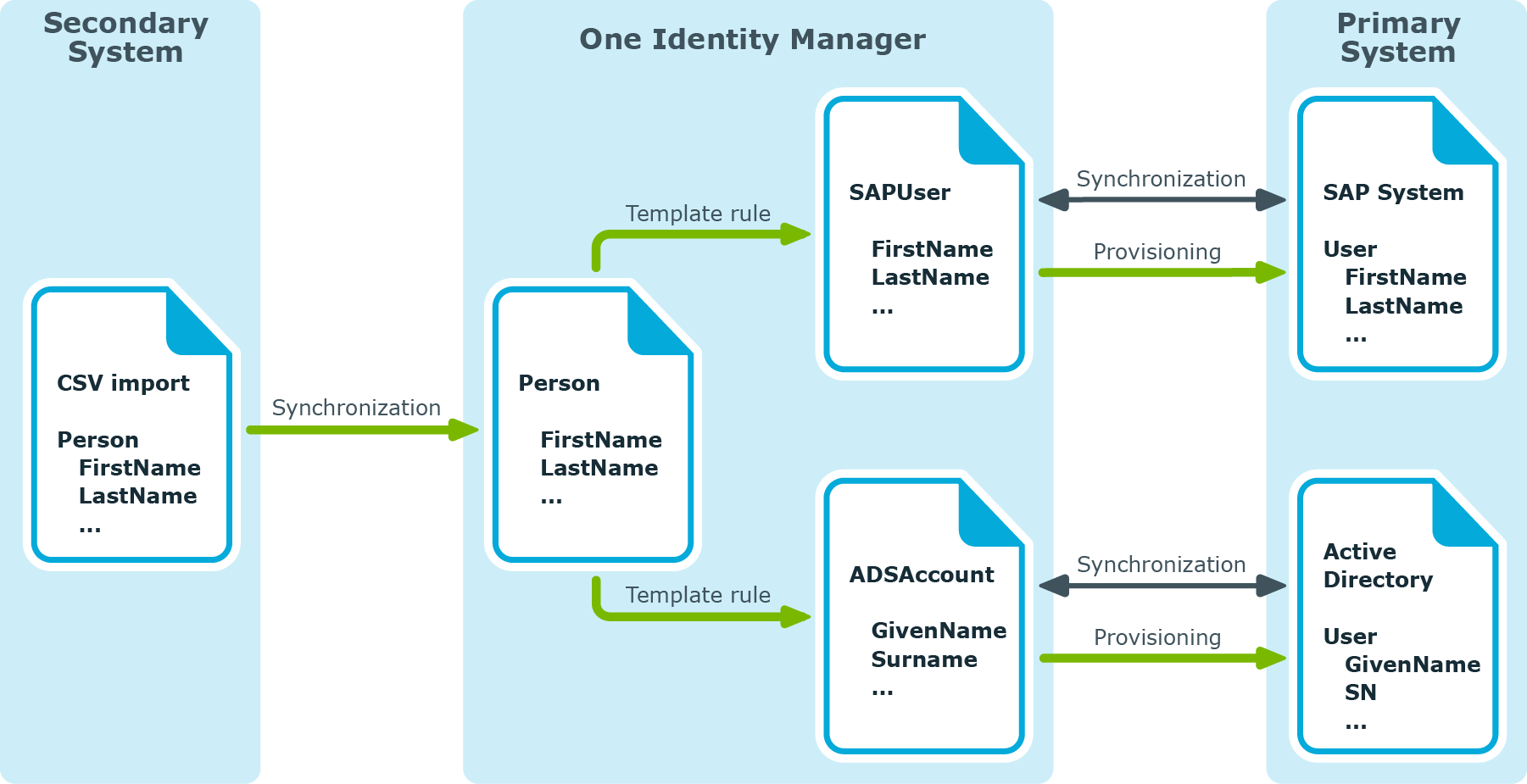
To create a filter with a wizard
-
Click Create condition.
This inserts a control for the first condition.
-
Enter the condition.
-
Click the left-hand part of the condition and select the property to filter by.
The properties for filtering are listed in the drop-down. You can also define other properties and use variables.
-
Specify the comparison operator. Click the comparison operator to change it.
The comparison operators =, <>, <, >, <=, >=, and like are supported for defining conditions.
-
Specify the comparison value on the right-hand side of the condition.
You can enter a string for a comparison value or select a property from the list. You can also use variables.
NOTE: To switch back to the input field again, select Input field from the drop-down.
-
To link condition you can use the logical operators AND, OR, and NOT.
-
Mouse over the edge of the control to which you wish to create a link.
The connection points appear.
-
Mouse over a connection point and select the connection.
This adds a new control for the next condition.
NOTE: To remove a control, select the Delete connection point.
Support for scripting
You can apply scripts at various points in the ; for example, when defining the schema properties, in the object filter, or when you define data operations for system connections through the .You can enter scripts in C# or Visual Basic .NET depending on script's language, which was specified for the synchronization project. You write scripts in a special editing dialog. It has an advanced edit mode which provides additional actions.
To switch to advanced mode
Figure 3: Directly entering a database query
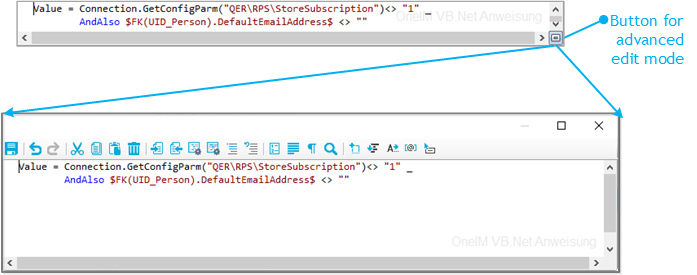
Table 14: Meaning of icon in advanced edit mode
|

|
Quits advanced edit mode. |
|

|
Undoes last change. |
|

|
Redoes last change. |
|

|
Cuts selected code. |
|
|
Copies selected code into clipboard. |
|

|
Inserts code from clipboard. |
|

|
Deletes selected code. |
|

|
Decreases insert. |
|

|
Increases insert. |
|

|
Automatic text formatting. |
|

|
Formats text selection automatically. |
|

|
Shows/hides line numbers. |
|

|
Inserts comments. |
|

|
Removes comments. |
|
|
Inserts or removes line numbers. |
|
|
Inserts or removes automatic line breaks. |
|
|
Enable or disable automatic completion of words when they are entered. |
|
|
Hides or shows tab and space characters. |
|

|
Searches within code. |
|
|
Inserts code snippet. |
|
|
Shows list of . |
|
|
Shows auto completion list. |
|

|
Shows list with parameter information. |
|

|
Shows additional information. |
Table 15: Shortcut for editing scripts
|
Ctrl + C |
Copy to clipboard. |
|
Ctl + Ins |
Copy to clipboard. |
|
Ctrl + X |
Cut and copy to clipboard. |
|
Shift + Del |
Cut and copy to clipboard. |
|
Ctrl + L |
Cut row and copy to clipboard. |
|
Ctrl + V |
Paste from clipboard. |
|
Shift + Ins |
Paste from clipboard. |
|
Ctrl + Y |
Redo action. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + Z |
Redo action. |
|
Ctrl + Z |
Undo action. |
|
Backspace |
Remove character behind cursor. |
|
Shift + Backspace |
Remove character behind cursor. |
|
Ctrl + Backspace |
Remove word behind cursor. |
|
Del |
Delete character in front of cursor. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + L |
Delete row. |
|
Ctrl + Del |
Delete to end of next word. |
|
Data |
Insert line break. |
|
Shift + Return. |
Insert soft line break. |
|
Ctrl + Return |
Insert row above. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + Return |
Insert row below. |
|
Ctrl + Space |
Auto-complete. |
|
Ctrl + Space + Space |
Show list with parameter information. |
|
Tab |
Insert indent/tab. |
|
Shift + Tab |
Remove indent/tab. |
|
Ctrl + U |
Change marked characters to lowercase. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + U |
Change marked characters to uppercase. |
|
Ins |
Toggle insert mode. |
|
Ctrl + T |
Swap characters in front and behind cursor. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + T |
Swap words in front and behind cursor. |
|
Shift + Alt + T |
Swap row with previous row. |
|
Alt + PgUp |
Move row up. |
|
Alt + PgDn |
Move row down. |
|
PgUp |
Move up |
|
PgDn |
Move down. |
|
Left arrow |
Move left. |
|
Right arrow |
Move right. |
|
Ctrl + Left arrow |
Move to previous word. |
|
Ctrl + Right arrow |
Move to next word. |
|
Home |
Move to start of line. |
|
End |
Move to end of line. |
|
Ctrl + Home |
Move to start of script. |
|
Ctrl + End |
Move to end of script. |
|
PgDn |
Move up a page. |
|
PgUp |
Move down a page. |
|
Ctrl + PgUp |
Move to visible start. |
|
Ctrl + PgDn |
Move to visible end. |
|
Ctrl + ] |
Move to next bracket. (not possible on German keyboard) |
|
Ctrl + Down arrow |
Scroll down. |
|
Ctrl + Up arrow |
Scroll up |
|
Ctrl + F |
Open search dialog. |
|
F3 |
Search next. |
|
Ctrl + F3 |
Search forward. |
|
Shift + F3 |
Search backward. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + F3 |
Find previous. |
|
Ctrl + H |
Replace. |
|
Ctrl + I |
Search forward incrementally. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + I |
Search backward incrementally. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + Num- |
Reduce code block selection. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + Num+ |
Extend code block selection. |
|
Esc |
Remove selection. |
|
Shift + Down arrow |
Extend selection down. |
|
Shift + Up arrow |
Extend selection up. |
|
Shift + Left arrow |
Extend selection left. |
|
Shift + Right arrow |
Extend selection right. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + Left arrow |
Extend selection to previous word. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + Right arrow |
Extend selection to next word. |
|
Shift + Home |
Extend selection to start of line. |
|
Shift + End |
Extend selection to end of line. |
|
Shift + Alt + Home |
Extend selection to start of script. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + End |
Extend selection to end of script. |
|
Shift + PgUp |
Extend selection by one page up. |
|
Shift + PgDn |
Extend selection by one page down. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + PgUp |
Extend selection to visible start. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + PgDn |
Extend selection to visible end. |
|
Ctrl + A |
Select all. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + W |
Select word. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + ] |
Select up to the next bracket. (not possible on German keyboard) |
|
Shift + Alt + Down arrow |
Extend selected block down. |
|
Shift + Alt + Up arrow |
Extend selected block up. |
|
Shift + Alt + Left arrow |
Extend selected block left. |
|
Shift + Alt + Right arrow |
Extend selected block right. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + Alt + Left arrow |
Extend selected block by one word to the left. |
|
Ctrl + Shift + Alt + Right arrow |
Extend selected block by one word to the right. |
|
Ctrl + mouse wheel |
Adjust text size. |
There is additional help provided for creating script code.
Syntax highlighting
The input fields support syntax highlighting depending on the syntax type.
Auto-completion
You can use auto-completion when you write script code. You can enable automatic completion in the input fields with the  button in advanced edit mode. This suggests a word to automatically complete the keyword as it is entered. If a keyword is expected at a certain position in the source code, auto-completion comes up automatically after a few letters. Although, after specific characters, such as period (.) or parenthesis ((), automatic completion is always offered. Alternatively, you can use the Ctrl + space shortcut in the relevant positions within the input fields to call up autocomplete.
button in advanced edit mode. This suggests a word to automatically complete the keyword as it is entered. If a keyword is expected at a certain position in the source code, auto-completion comes up automatically after a few letters. Although, after specific characters, such as period (.) or parenthesis ((), automatic completion is always offered. Alternatively, you can use the Ctrl + space shortcut in the relevant positions within the input fields to call up autocomplete.
The amount of scripted code to enter is reduced by displaying the names of properties or functions that can be used. The contents of the list is determined by the key words in the code. This way, you can use scripts from the script library.
Entering code snippets
One Manager provides code snippets for you to use as . You can insert code snippets using the following options:
- Using the
 icon
icon
-
Select the  icon.
icon.
-
Select the code snippet.
- Using a shortcut
-
Press F2.
-
Select the code snippet.
NOTE: If you select a code snippet directly using a shortcut or the  icon, a short description and the shortcut name are displayed in a tooltip.
icon, a short description and the shortcut name are displayed in a tooltip.
If the script tests a fixed value that contains at least two dollar characters, the dollar characters must be masked.
Save changes permanently
Different wizards are run to add new objects like , mappings, or workflows with the . The data you enter is temporarily saved. Changes to these objects are also saved only temporarily.
To save changes to the synchronization project permanently
-
In the Synchronization Editor toolbar, click Commit to database.
- OR -
-
To save the synchronization project with change labels, open the Commit to database menu item and click Commit and assign a change label. For more information about working with change labels, see the One Identity Manager Operational Guide.
One Identity Manager compresses the schemas when the synchronization project is saved for the first time. This removes schema data from the synchronization projects that is not required in the synchronization configuration. This can speed up loading the synchronization project.
NOTE: As long as patches are being applied to a synchronization project, no other changes can be permanently saved. Wait until the update is complete before making any changes.
If an update fails, correct the error first and run the update again before saving other changes to the synchronization project.
Establishing remote connections
To configure with a target system, One Manager must load the data from the target system. One Identity Manager communicates directly with the target system to do this. Sometimes direct access from the workstation, on which the is installed, is not possible. For example, because of the firewall configuration or the workstation does not fulfill the necessary hardware and software requirements. If direct access is not possible from the workstation, you can set up a remote connection.
To permit remote access to a target system
-
Provide a server installed with the following software.
-
-
connector
-
Target specific client components as they must be installed on the .
For more information, see the administration guides for connecting target systems.
-
Configure the RemoteConnectPlugin.
-
Start the program.
-
In the module list, select Plugins and click Insert.
-
In the Select module type, select the RemoteConnectPlugin and click OK.
-
In the module list, select RemoteConnectPlugin.
-
To edit the plugin properties, select the property and click Edit.
-
Bind address (HttpBindAddress): IP address of the network card to use.
Value: + - Uses all network cards.
-
Port (Port): Server port used to reach the RemoteConnectPlugin.
Value: The RemoteConnectionPlugin uses the 2880 port by default.
NOTE: The firewall must allow incoming TCP connections on this port.
-
Use HTTPS: Defines whether a secure connection (HTTPS) is used.
Value: Enabled - Always use a secure connection in a production environment.
The option must only be disabled if you are using a HTTPS proxy. The One Identity Manager tools (like the Synchronization Editor) always establish a secure connection via HTTPS.
-
In the module list, select AuthMethod.
-
Click Select module and select the authentication method to authenticate incoming queries.
-
ADGroupAuthentication: Authentication through membership in an Active Directory group.
Prerequisites: The remote connection server and the workstation must be in the same Active Directory domain.
-
Authentication type (HttpAuthentication): Authentication type to use.
Permitted values: Ntlm, IntegratedWindowsAuthentication
-
Permitted Active Directory group (PermittedADGroup): Distinguished name or object SID of the Active Directory group whose members are authorized to use a remote connection.
-
SecretAuthentication: Authentication through knowledge of a secret.
-
Secret: Hash value of the secret that a user must enter for authentication.
Calculate the hash value with your preferred external hash value calculator and accept this value. Enter the method used to calculate the hash value at the same time.
Syntax: [#<algorithm>(-<Format>)]<hash value>
Example: [#SHA512]<HexSHA512Hash>
-
Click Ctrl + S to save the changes to the One Identity Manager Service configuration.
-
Declare the remote connection server as Job server in One Identity Manager.
-
Start the One Identity Manager Service.
TIP: The remote connection server requires the same configuration as the synchronization server (with regard to the installed software and entitlements). Use the synchronization server as remote connection server as well by installing the RemoteConnectPlugin.
To edit a Job server
-
In the , select the Base Data > Installation > Job server category.
-
Enter a new Job server using the Job servers > New menu item.
-
Edit the Job server's main data.
-
Select the View > Server functions menu item and specify the server functionality.
Select a minimum of the following server functions:
-
Select the View > Machine menu item and assign roles to the server.
Select at least the following roles:
-
Enter the queue name of the Job server in the configuration file of the One Identity Manager Service.
For more information, see the One Identity Manager Configuration Guide and the administration guides for connecting target systems.
Permissions for the One Identity Manager Service user account.
The RemoteConnectPlugin uses an internal HTTPS server for remote access. The user account's permissions for the One Identity Manager Service must be extended accordingly.
-
Users require permission to open an HTTP server. The administrator must grant URL approval to the user to do this. This can be run with the following command line call:
netsh http add urlacl url=https://+:<port number>/Remoting/ user=<domain>\<user name> listen=yes
-
If the One Identity Manager Service has to run under the Network Service's user account (NT Authority\NetworkService), explicit permissions for the internal web service must be granted. This can be run with the following command line call:
netsh http add urlacl url=https://+:<port number>/Remoting/ user="NT AUTHORITY\NETWORKSERVICE" listen=yes
-
You can check the result with the following command line call:
netsh http show urlacl
The RemoteConnectPlugin port certificate
-
The RemoteConnectPlugin port must be assigned a certificate because the RemoteConnectPlugin uses HTTPS for remote access. This can be run with the following command line call:
netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:<port number> certhash=<certificate thumbprint> appid="{F06D38CA-DF0F-4D72-BC33-D3F6472A8DEE}"
-
You can check the result with the following command line call:
netsh http show sslcert


button.


























