Using the Users with Local Admin Rights screen
Available only in Safeguard Privilege Manager for Windows Professional Edition and Professional Evaluation Edition.
Under the Discovery & Remediation tab on the Console, select the Users with Local Admin Rights screen to discover which domain users have been assigned to the local Administrators group on client computers and remove them.
Before you begin, check the following on each target computer
-
The computer is turned on and accessible from the network; and
-
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM), File and Printer Sharing, and Remote Administration are allowed through the firewall.
To remove domain users from the local Administrators group on computers on your domain
-
Within the Select Computers section, click Add and Remove to add and remove computers.
-
You cannot select a domain controller computer.
-
If the File and Printer Sharing exception is not enabled for a computer, it will not display in the list.
-
If the Windows Management Instrumentation exception is not enabled, the Class and OS columns will display the Unavailable value.
-
Click Clear all entries to remove all computers from the list.
-
Click Discover Accounts in local Administrator groups to discover users and domain groups with local administrator rights. By default, the search results will only include domain users and domain groups. However, you can optionally opt to include local and built-in (for informational purposes only) users.
-
In the window that opens, specify whether to search for local Administrator groups, users, or both.
-
Check the Only display domain accounts discovered in the results list option to restrict the search to Domain accounts only. Clear the option to include local accounts from the Administrators group on client machines.
A window displays your progress as the list builds.
-
Complete the following steps.
-
If an error occurs, it will display in the Errors section with a description. The Unable to open log file... notification signifies that no users in the local Administrators group have been detected.
-
Click Open report file to view data on detected users. The button will not be activated if no users have been found in the local Administrators group.
-
When the discovery operation is completed, click Close.
The list of discovered users will display in the User Accounts Discovered in Local Administrators Groups section.
-
Revise the list to only include users you are potentially going to revoke rights from then make your final selection from the remaining list.
-
Click the Exclude selected entries from list link to remove users from this list.
-
Select users from the remaining list, for which you want to revoke their local administrator rights.
-
Click Remove all selected users from local Administrators groups.
-
In the window that opens, click Yes to confirm that you want to remove the users or groups. A window displays your progress as the users are removed.
-
Complete the following steps:
-
If an error occurs, it will display in the Errors section with a description.
-
Click Open report file to view the operation log.
-
When the operation is complete, the users no longer have local administrator rights.
Reporting
Reporting is available only in Safeguard Privilege Manager for Windows Professional Edition or an active Professional Evaluation Edition. Once your trial evaluation license expires, reporting no longer collects data, and no longer generates reports.
Topics:
You can build five types of reports on activities from client computers:
-
Blacklist Activity Report: Lists how frequently a rule is used.
-
Rule Deployment Report: Lists rules deployed on the client computer.
-
Instant Elevation Report: Lists processes that are elevated using Instant Elevation.
-
Rule Details Report: Lists rules that are configured.
-
Advanced Policy Settings Report: Lists Advanced Policy Settings, except those set to the Not Configured option.
In addition to these out of the box reports, you can create custom reports using third-party tools to query the SQL-based Safeguard Privilege Manager for Windows reporting database. Use this database schema to create your own custom reports or data analysis:
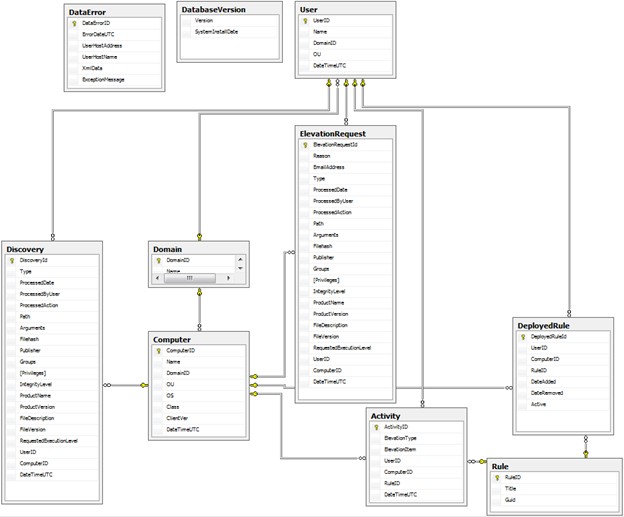
A PAReporting database is created when you set up the server and is configured to work with the ScriptLogic PA Reporting Service, the data collection web service running on a Console host.
Before you generate reports, ensure the following components are set up
-
The Server is configured and you can successfully join the data collection web service running on it.
-
Client data collection settings are configured for the GPOs you will report on. You can generate reports on GPOs for which you have read/write access in Windows.
To learn how to create this type of report and manage the data, see Generating and using reports.
Elevation Activity Report
This report allows you to track which rules were used to elevate processes during a period of time on managed client computers. With this report, you can see when users have run privileged processes and on which computers.
Each privilege Elevation event reported contains these details:
-
Rule Name: The privilege Elevation rule name.
-
Rule GUID: The privilege Elevation rule globally unique identifier (GUID).
-
User (Domain\Name\OU): The user, domain name, and OU.
-
Computer (Domain\Name\OU\Class\OS): The computer, domain name, OU, class, and OS.
-
Elevation Time: The time of the privilege Elevation on the client computer.
To learn how to create this type of report and manage the data, see Generating and using reports.
Blacklist Activity Report
This report allows you to track which rules were used to Blacklist processes during a period of time on managed client computers. With this report, you can see when users have attempted to run blacklisted processes and on which computers.
Each Blacklist event reported contains these details:
-
Type: The privilege Elevation rule type.
-
Blacklisted Item: The path to the blacklisted application or command with the argument (if any).
-
Rule Name: The privilege Elevation rule name.
-
Rule GUID: The privilege Elevation rule globally unique identifier (GUID).
-
User (Domain\Name\OU): The user, domain name, and OU.
-
Computer (Domain\Name\OU\Class\OS): The computer, domain name, OU, class, and OS.
-
Blacklisted Time: The time of the blacklisted event on the client computer.
To learn how to create this type of report and manage the data, see Generating and using reports.

