Compliance checking requests
To retain an overview of potential rule violations, you can run a simplified compliance check. Use the CR approval procedure to test requests for possible rule violations before finally approving them.
The following data of a recipient's request is taken into account by the compliance check:
-
All pending requests
-
All company resources already assigned to the recipient
-
All the recipient's user accounts
-
All entitlement in the target system (for example, Active Directory groups or SAP roles) the recipient has obtained through these user accounts
Auxiliary tables for object assignments are regularly evaluated for the compliance check. Auxiliary tables are calculated on a scheduled basis. Furthermore, the approval procedure only takes into account compliance rules that are created using the simplified definition.
Rule checking does not completely check the requests with this. It is possible that under the following conditions, rule checking does not identify a rule violation:
-
Customer permissions change after the auxiliary table have been calculated.
-
If memberships are requested in business role or organization, a rule is violated by an object that is inherited through the business role or organization. Inheritance is calculated after request approval and can therefore not be identified until after the auxiliary table is calculated again.
-
The customer does not belong to the identities affected by a rule until the request is made.
-
The rule condition was created in expert node or as an SQL query.
TIP: A complete check of assignments is achieved with cyclical testing of compliance rule using schedules. This finds all the rule violations that result from the request.
It is possible that under the following conditions, rule checking identifies a rule violation where one does not exist:
-
Two products violate one rule when they are assigned at the same time. The product requests are, however, for a limited period. The validity periods does not overlap. Still a potential rule violation is identified.
TIP: These requests can be approved after checking by exception approver as permitted by the definition of the violation rule.
The compliance check is not only useful for specifying which rule is violated by a request, but it can also find out which product in the request caused the rule violation. This makes a detailed analysis possible of the rule violation. The request can still be approved by exception approval, the definition of compliance rules permitting. Additional approval steps are added in approval workflows to deal with exception approval.
Conditions for compliance checking requests
-
You can add only one approval step per approval policy with the CR approval procedure.
-
The rule conditions were created in the simple definition.
-
IT Shop properties that are specified for each rule are taken into account in the rule testing. Identification of a rule violation depends on the setting on Rule violation identified.
-
The compliance check should be added as the last approval level in the approval workflow. The subsequent approval levels only get one approval step to determine the exception approver if approval is denied.
Compliance check sequence
-
If an approval step for compliance checking using the CR approval procedure is found in the request’s approval procedure, all products in pending requests are assigned to the customer. It is assumed that all pending requests will be approved and therefore the customer will obtain all the products. The current request is then analyzed with respect to potential violations against the defined rules.
-
If no rule violations are found, the approval step is automatically granted approval and the request is passed on to the approver at the next approval level above.
-
If a rule violation is detected, the request is automatically not granted approval. The request can still be approved by exception approval, the definition of rule violations permitting.
For more information about compliance checking, see the One Identity Manager Compliance Rules Administration Guide.
Identifying rule violations
If the QER | ComplianceCheck | EnableITSettingsForRule configuration parameter is set, properties can be added to compliance rules that are taken into account when rule checking requests.
Specify which violation should be logged for the rule by using the Rule violation identified IT Shop property.
Table 38: Permitted values
|
New rule violation due to a request |
Only rule violations that are added through approval of the current request are logged. |
|
Unapproved exception |
Rule violations that are added through approval of the current request are logged. Already known rule violations that have not yet been granted an exception are also logged. |
|
Any compliance violation |
All rule violations are logged, independent of whether an exception approval has already been granted or not.
This value is automatically set when the Explicit exception approval option is set. |
If the QER | ComplianceCheck | EnableITSettingsForRule configuration parameter is not set, new rule violations are logged through the current request.
For more information about this, see the One Identity Manager Compliance Rules Administration Guide.
Determining exception approvers
Requests that may cause a rule violation can still be approved by exception approval.
To allow exception approval for request with rule violations
-
Enable the Exception approval allowed option for the compliance rule and assign an exception approver.
For more information, see theOne Identity Manager Compliance Rules Administration Guide.
-
Enter an approval step in the approval workflow with the OC or OH procedure. Connect this approval level with the compliance checking approval level at the connection point for denying this approval decision.
NOTE:
-
Only apply this approval procedure immediately after an approval level with the CR approval procedure.
-
For each approval workflow, only one approval step can be defined using the OC or OH approval procedure.
-
If the QER | ComplianceCheck | EnableITSettingsForRule configuration parameter is set, you can use the rule's IT Shop properties to configure which rule violations are presented to an exception approver. Set or unset Explicit exception approval to do this.
For more information, see Explicit exception approval.
Table 39: Approval procedures for exception approval
|
OC (Exception approvers for violated rules) |
The approval decision is agreed on by the exception approvers of the violated rule. As it may be possible that several rule are broken with one request, the request is presented to all the exception approvers in parallel. If one of the exception approvers rejects the exception, the request is rejected. |
|
OH (exception approver for worst rule violation) |
The approval decision is agreed on by the rule's exception approver which poses the highest threat. In this way, you can accelerate the exception approval procedure for a request that violates several rules.
Ensure the following apply for this approval procedure:
|
Example
Four different compliance rules are violated by a request for Active Directory group membership. The target system manager of the Active Directory domain is entered as exception approver for all the compliance rules.
Using the OC approval procedure, the target system manger must grant approval exceptions for all four compliance rules.
Using the OH approval procedure, the target system manager is presented with the request only for the compliance rule with the highest severity code. The manager's decision is automatically passed on to the other violated rules.
Figure 7: Example of an approval workflow with compliance checking and exception approval
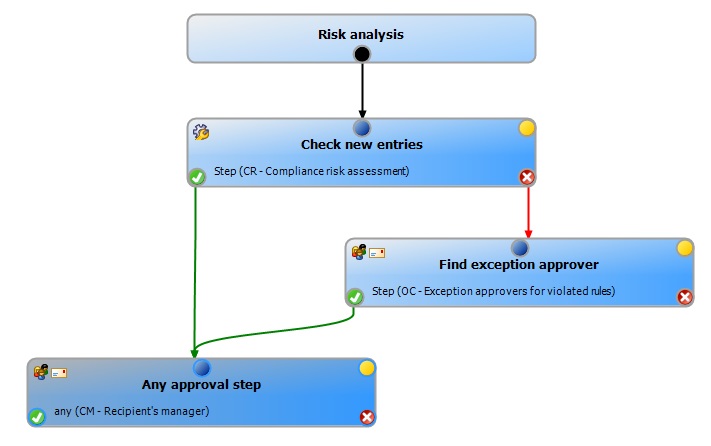
Sequence of compliance checking with exception approval
-
If a rule violation is detected during compliance checking, the request is automatically not granted approval. The request is passed on to the approver of the next approval level for approval.
-
Exception approvers are found according to the given approval procedure.
-
If exception approval is granted, the request is approved and assigned.
-
If exception approval is not granted, the request is denied.
NOTE:
-
As opposed to the manager/deputy principle normally in place, an exception approver’s deputy is NOT permitted to grant exception approval alone.
-
You cannot determine fallback approvers for exception approvers. The request is canceled if no exception approver can be established.
-
The chief approval team cannot grant exception approvals.
Restricting exception approvers
By default, exception approvers can also make approval decisions about requests in which they are themselves requester (UID_PersonInserted) or recipient (UID_PersonOrdered). To prevent this, you can specify the desired behavior in the following configuration parameter and in the approval step:
-
QER | ComplianceCheck | DisableSelfExceptionGranting configuration parameter
-
QER | ITShop | PersonOrderedNoDecideCompliance configuration parameter
-
QER | ITShop | PersonInsertedNoDecideCompliance configuration parameter
-
Approval by affected identity option in the approval step for finding exception approvers
If the requester or approver is not allowed to grant approval exceptions, their main identity and all sub identities are removed from the circle of exception approvers.
Summary of configuration options
Requesters can grant exception approval for their own requests, if:
- PersonInsertedNoDecideCompliance configuration parameter is not set.
Recipients can grant exception approval for their own requests, if:
Requesters cannot grant exception approval, if:
Recipients cannot grant exception approval, if:

