Client requirements
The Single Sign-on for SAP solution is used with SAP GUI clients running on Windows systems that are joined to an Active Directory domain. The Single Sign-on for SAP installs and configures the qgsskrb5.dll module, which provides a SAP Secure Network Communications (SNC) compliant Generic Security Services Application Program Interface (GSSAPI) to the Microsoft Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) translation layer. You do not need to install any additional client software.
NOTE: The qgsskrb5.dll maps the GSSAPI interfaces used by SAP GUI to the corresponding SSPI system calls.
Functional description
Once you have joined a UNIX server to the Active Directory domain using Safeguard Authentication Services, you can configure an SAP Server to use the GSSAPI libraries provided by Safeguard Authentication Services. You can then configure SAP GUI clients running on a supported operating system and joined to the same Active Directory domain (or forest) to use the credentials provided by Active Directory log-on to seamlessly authenticate to the SAP Server.
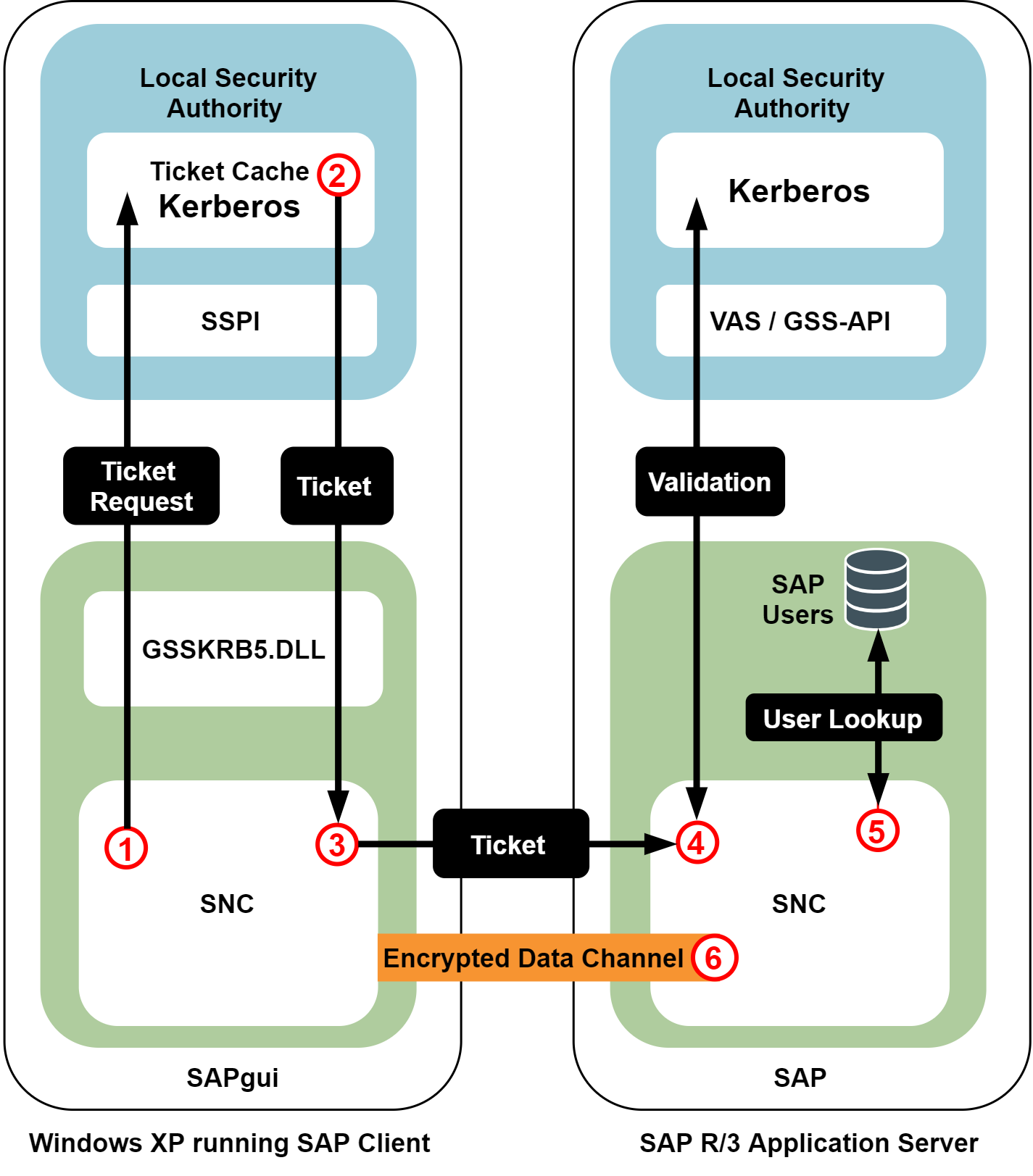
The workflow of the solution's operation:
-
When the user wants to access an SAP application, the SAP GUI requests a Kerberos service ticket with the current user's log-on credentials using the Single Sign-on for SAP SNC module (GSSKRB5.DLL). The configuration stored in the SAP system profile identifies the specific SAP instance (in this case, a SAP system running on a UNIX host, with Safeguard Authentication Services installed).
-
The system responds with a Kerberos service ticket from the local cache or the Active Directory Key Distribution Center (KDC).
-
Next, the SAP GUI client opens a connection to the SAP Application Server and provides the Kerberos service ticket.
-
The SAP Application Server processes the service ticket, validating it using the SNC GSSAPI libraries provided by Safeguard Authentication Services.
-
If the ticket is successfully authenticated and the SAP Application Server can map the Active Directory user name it to the corresponding account in the SAP user database, the user is logged in to the SAP Application Server.
-
Depending on the SAP configuration, all of the network communications can then be encrypted.
Authentication uses the existing Active Directory credentials acquired when the user logged on to their desktop. As a result, the user is never required to enter a user name and password.
Figure 1: SAP Server Configuration
Summary
The Single Sign-on for SAP solution provides increased security, identity integration, centralized auditing, data integrity, data privacy, and user experience. The integration of UNIX and Linux hosts with Active Directory through Safeguard Authentication Services allows SAP clients and servers to use the capabilities of the SAP Secure Network Communications (SNC) interface as a common security and authentication infrastructure. In addition, clients and servers can fully leverage the ability of Active Directory to provide a secure authentication token in the form of a Kerberos ticket, while retaining the benefits of continued deployment of SAP server solutions on UNIX hosts.
Quick start
The topics in this section lead you through the most common configuration of Safeguard Authentication Services Single Sign-on for SAP.

