To delete a sync workflow step
- In the Administration Console, open the Sync Workflows tab.
- Click the name of the sync workflow in which you want to delete a step.
- Click Delete below the step you want to delete.
- When prompted, confirm that you want to delete the step.
When you run a sync workflow, its steps are executed in the order they are displayed in the Administration Console. If necessary, you can change the order of steps in a sync workflow.
To change the order of steps in a sync workflow
- In the Administration Console, open the Sync Workflows tab.
- Click the name of the sync workflow in which you want to change the order of steps.
- Use the Move up and Move down links to arrange the steps as necessary.
When configuring a synchronization step, you can use the Rules to generate unique object name list to specify rules for creating or modifying object names in the target connected system. The Rules to generate unique object name list looks similar to the following:
Figure 9: Add synchronization step
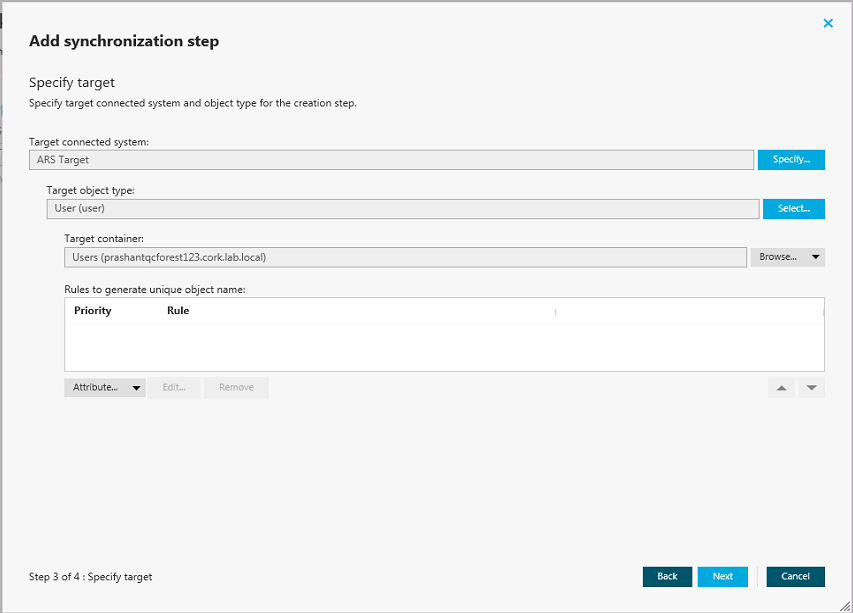
To configure rules for generating object names
- Click the down arrow on the leftmost button provided below the Rules to generate unique object name list.
- Select a list item:
- Attribute. Allows you to select the target object attribute whose value you want to use as the object name.
- Rule. Allows you to configure a rule to generate target object names. For details, see Using value generation rules.
- PowerShell Script. Allows you to type a PowerShell script to generate target object names.
When the Rules to generate unique object name list includes two or more entries, uses the uppermost rule in the list to generate the target object name. If the generated object name is not unique, uses the next rule in the list, and so on.
To copy and paste an existing rule
- In the Rules to generate unique object name list, right-click a rule, and then select Copy from the shortcut menu.
- In the rules list, right-click an entry, and then select Paste from the shortcut menu.
In a sync workflow step you can configure a set of rules to automatically modify attribute values during the step run. By using these rules, you can select or generate an initial value, transform this value if necessary, and then assign the resulting value to the object attribute you want.
To create a rule to modify attribute values
- In the Administration Console, open the Sync Workflows tab.
- Click the name of the appropriate sync workflow, then click the name of the sync workflow step.
- Depending on the workflow step type, complete the corresponding actions:
- Creating step. Click the Creation Rules tab, and then expand the Initial Attribute Population Rules element.
- Updating step. Click the Updating Rules tab, and then expand the Rules to Modify Object Attributes element.
- Deprovisioning step. Click the Deprovisioning Rules tab, and then expand the Rules to Modify Object Attributes element.
- In the element you have expanded, click the down arrow on the leftmost button to select a rule type:
- Forward Sync Rule. Allows you to create a rule that synchronizes attribute values from the source to the target data system. This type of rule is available in creating, updating, and deprovisioning steps. For more information, see Configuring a forward sync rule.
- Reverse Sync Rule. Allows you to create a rule that synchronizes attribute values from the target to the source data system. This type of rule is available in creating, updating, and deprovisioning steps. For more information, see Configuring a reverse sync rule.
- Merge Sync Rule. Allows you to create a rule that merges the values of specified attributes between the source and the target data systems. As a result, the attribute values in the source and the target become identical. This type of rule is only available in updating steps. For more information, see Configuring a merge sync rule.

