The One Identity Safeguard for Privileged Sessions (SPS) web interface can authenticate users to an external LDAP database to simplify the integration of SPS to your existing infrastructure. You can also specify multiple LDAP servers, so that if the first server becomes unavailable, SPS can try to connect to another server.
NOTE: Consider the following:
-
Local users, including the admin user, are available by default.
-
The admin user has every privilege and cannot be deleted.
-
SPS accepts both pre-Windows 2000 style and Windows 2003 style User Principal Names (UPNs). UPNs consist of a username, the at (@) character, and a domain name, for example administrator@example.com.
-
For SSH usernames, SPS supports only valid UTF-8 strings.
-
The following characters cannot be used in:
- user names: /\[]:;|=+*?<>"
-
group names: /\[]:;|=+*?<>"@,
-
When using RADIUS authentication with LDAP users, the users are authenticated to the RADIUS server; however, their group memberships are managed in LDAP. For details, see "Authenticating users to a RADIUS server" in the Administration Guide.
- If the matching rule for an attribute is case insensitive in the LDAP database, SPS treats user names and group names in a case insensitive manner.
Prerequisites
Make sure that the response timeout of the LDAP/Active Directory server is set to a minimum of 120 seconds.
To configure an LDAP server
-
Navigate to Users & Access Control > Login options > Manage AD/LDAP Servers.
-
Select the LDAP server from the list. Alternatively, if no LDAP server exists yet, click Add new server and select the server type you want to create:
-
Active directory
For more information, see Adding a new Active Directory server.
-
POSIX LDAP
For more information, see Adding a new POSIX LDAP server.
-

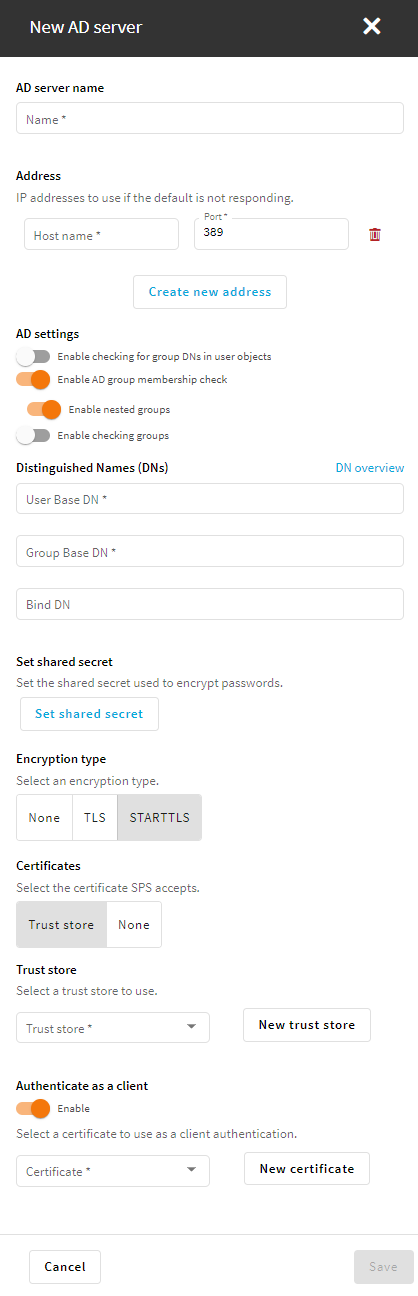
 and enter the address of the next server. If a server is unreachable, SPS will try to connect to the next server in the list in failover mode.
and enter the address of the next server. If a server is unreachable, SPS will try to connect to the next server in the list in failover mode.