You can define conflicting roles to prevent identities, devices, or workdesks from being assigned to several roles at the same time and from obtaining mutually exclusive company resources through these roles. At the same time, specify which departments, cost centers, and locations are mutually exclusive. This means you may not assign these roles to one and the same identity (device, workdesk).
NOTE: Only roles, which are defined directly as conflicting roles cannot be assigned to the same identity (device, workdesk). Definitions made on parent or child roles do not affect the assignment.
Example:
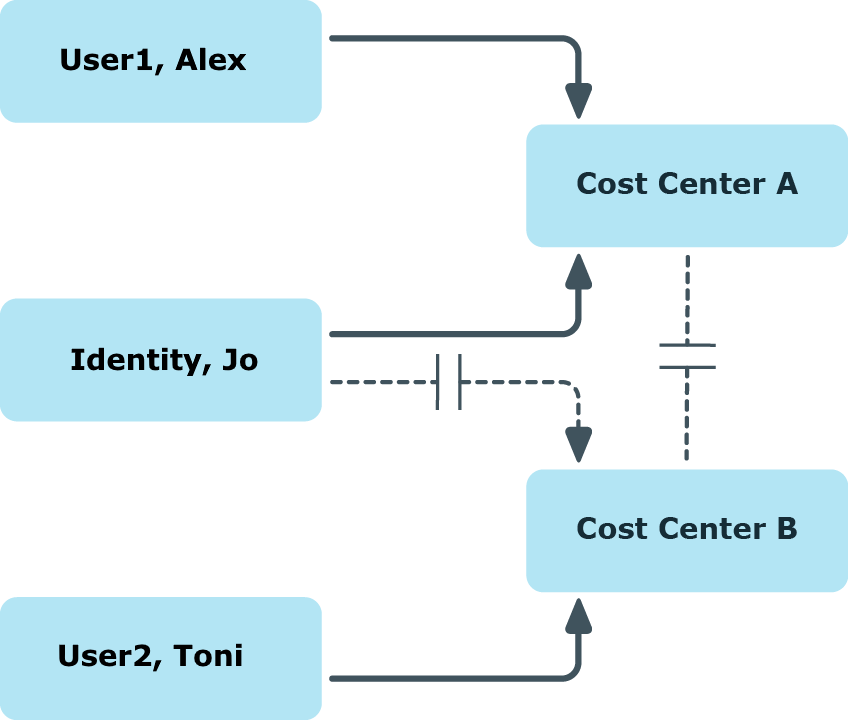
Cost center B is named as conflicting role to cost center A. Alex User1 and Jo Identity are members of cost center A. Toni User2 is a member of cost center B. Jo Identity cannot be assigned to cost center B. Apart from that, One Identity Manager prevents Alex User1 and Toni User2 from being assigned to cost center A.
Figure 12: Members in conflicting roles
To configure inheritance exclusion
Related topics
Dynamic roles are used to dynamically assign memberships to departments, cost centers, location, business roles, application roles, and IT Shop nodes. Identities, devices, and workdesks are not permanently assigned to these roles, just when they fulfill certain conditions. A check is performed regularly to assess which identities (devices or workdesks) fulfill these conditions. This means the role memberships change dynamically. For example, company resources can be assigned dynamically to all identities in a department in this way; if an identity leaves the department they immediately lose the resources assigned to them.
Example: Dynamic role functionality
All external identities are added to a new dynamic role. These identities should be assigned to a company resource ABC. The dynamic role is initially defined with the following data:
| Dynamic role |
External identities |
| Description |
All external identities |
| Object class |
Identity |
| Condition |
IsExternal = 1 |
| Department |
A_1 |
The department A_1 is now assigned the resource ABC. All identities that fulfill the condition at the time the dynamic role was defined are assigned to department A_1 and therefore inherit the resource ABC. Identities that fulfill the condition at a later date, are assigned to department A_1 from that moment. Conversely, identities in department A_1 are removed the moment they are no longer known as external identities by One Identity Manager. The resource ABC is no longer available to those identities assuming they have not been assigned the resource through other channels.
Role memberships through dynamic roles are implemented as indirect, secondary assignments. Therefore secondary assignment of identities, devices, and workdesks to role classes must be permitted. If necessary, further configuration settings need to be made.
Identities can be excluded automatically from dynamic roles on the basis of a denied attestation or a rule violation. An excluded list is maintained to do this. Excluded lists can also be defined for individual identities. In addition, identities can also become members of the role directly or by assignment request or delegation. These memberships are not restricted by the exclusion list.
For more information on automatic exclusion in the event of a denied attestation, see the One Identity Manager Attestation Administration Guide. For more information on automatic exclusion in the event of a rule violation, see the One Identity Manager Web Designer Web Portal User Guide.
Detailed information about this topic
Related topics
You can create dynamic roles for departments, cost centers, locations, business roles, application roles, and IT Shop nodes. This allows you to specify memberships in these roles.
To create a dynamic role
-
In the Manager, select the role for which you want to create a dynamic role.
-
Select the Create dynamic role task.
-
Enter the required main data.
- Save the changes.
To edit a dynamic role
-
In the Manager, select the role for which the dynamic role was created.
-
Open the role's overview form.
-
Select the Dynamic roles form element and click on the dynamic role.
-
Select the Change main data task.
-
Edit the data and then save the changes.
Related topics
IMPORTANT: If the condition includes a large number of objects to assign, calculating memberships can place a heavy load on the DBQueue Processor and consequently on the database server.
A dynamic role condition is defined as a valid Where clause for database queries and must relate to the selected Identity, Hardware, or Workdesk object class.
In the Manager, you have different ways of creating conditions:
-
You can enter it directly as an SQL query.
-
You can use the Where clause wizard to create the conditions.
-
Alternatively, you can enter conditions for identities with the filter designer.
NOTE: If you select the For the account with the target system type or For the entitlement with target system type condition type in the filter designer, only columns that are mapped in Unified Namespace and for which the Display in the filter designer column property is enabled can be selected.
Using the @UID_Org variable, you can access the role or organization referenced by the dynamic role.
Example:
The condition for the dynamic role for identities only takes effect if the identity's location (Person.UID_Locality) matches the location of the assigned role or the organization (BaseTree.UID.UID_OrgLocality).
Where clause extension:
...
and uid_locality = (select b.UID_OrgLocality from BaseTree b where b.UID_Org = @UID_Org)
Example:
The condition for the dynamic role for identities is only effective if the assigned role or organization have a certain property.
Where clause extension:
...
and exists (select top 1 1
from BaseTree b
where b.UID_Org = @UID_Org
and b.CustomProperty01 = '123'
)
NOTE: If you add comments to the condition using the comment characters --, // or %, the DBQueue Processor cannot correctly calculate the dynamic role. The calculation quits with an error. Always use the comment characters /* ... */ to enclose comments.
Related topics

