Indexing audit trails allows you to search in the content of the audit trails, for example, to search for specific texts that the user has seen or typed in the session. The following describes how to configure SPS to index the audit trails. For details, see Configuring the internal indexer.
To configure SPS to index the audit trails
-
Navigate to Basic Settings > Local Services > Indexer service, and select Indexer service.
-
Define the Maximum parallel audit trails to index on box. The default value is set to the number of detected CPU cores.
-
(Optional) If you have encrypted audit trails and you want to index them, upload the necessary RSA keys (in PEM-encoded X.509 certificates).
-
Click
.
-
Navigate to Policies > Indexer Policies.
-
To create a new Indexer Policy, click
.
-
To configure what languages to detect, select Manual language selection. Select the language(s) to detect.
-
Navigate to the Control page of the traffic type (for example Traffic Controls > SSH), and select the connection policy to index.
-
Select Enable indexing.
-
To determine the priority level of indexing this connection, select the appropriate Priority level.
-
Select the Indexing Policy to be used.
-
Click
.
-
Check which channel policy is used in the connection, and navigate to the Connection policies page.
-
Select the channel policy used in the connection to index, and verify that the Record audit trail option is selected for the channels you want to index (for example, the Session shell channel in SSH, or the Drawing channel in RDP).
-
Click
.
-
Test the new configuration: try to initiate a connection from the client (your computer) to the server.
-
After successfully connecting to the server, do something in the connection, for example, execute a simple command in SSH (for example, ls /tmp), or launch an application in RDP (for example, the Windows Explorer), then disconnect from the server.
-
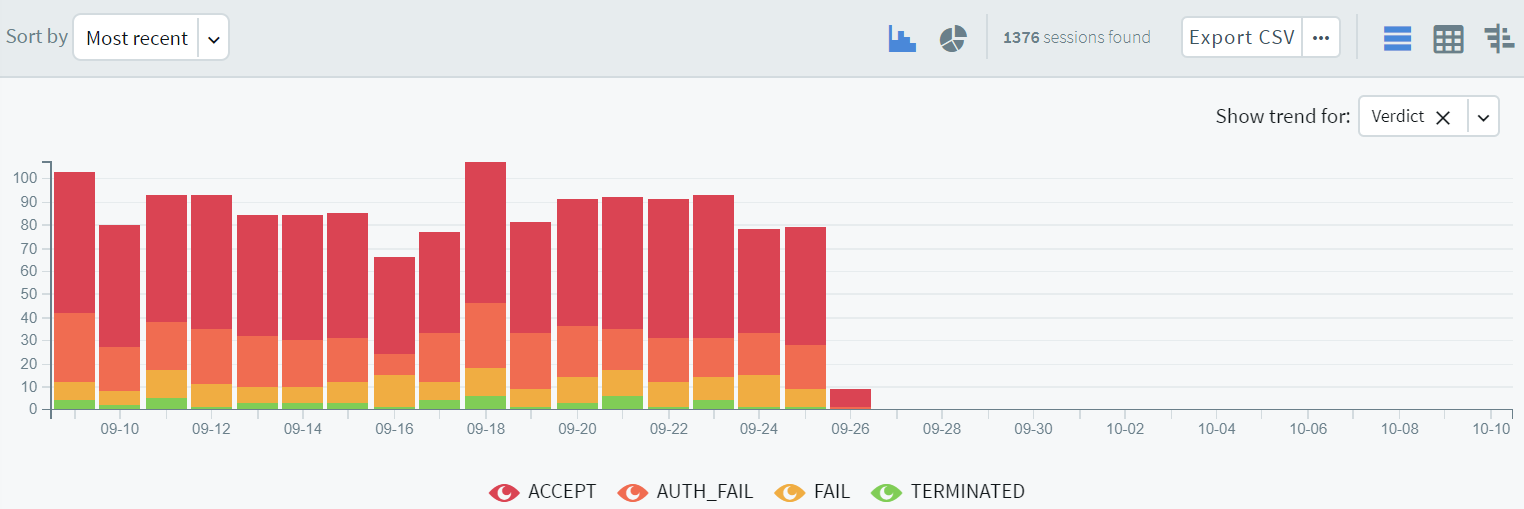
Navigate to Sessions on the SPS web interface. Your sessions are displayed in the list of connections. Note that for the transparent connection, the client addresses the target server, while the non-transparent connection addresses SPS.
-
Click the
icon. A summary will be displayed about the connection. Enter a text that was displayed in the connection into the search box, for example, the command you executed in SSH, or a menu item or other text you have seen in RDP (for example, Start). SPS will automatically generate a screenshot showing when the text was displayed in the connection.

 for more details and select from the list.
for more details and select from the list.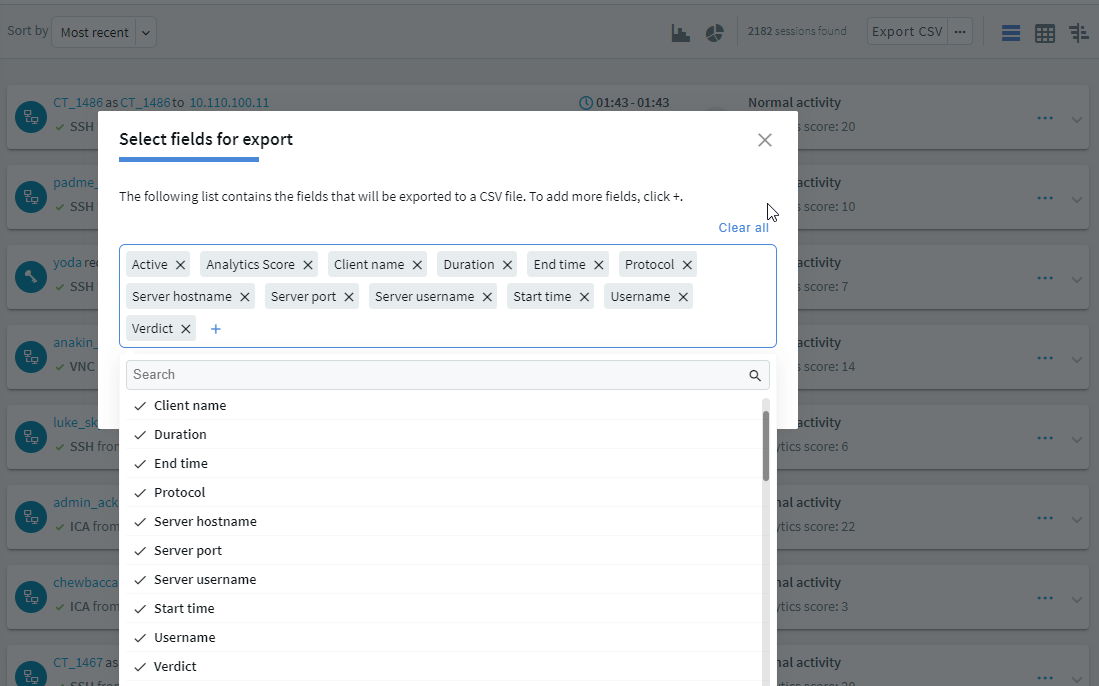
 (shortcuts) button to restrict the search to one of the preset time ranges. For example, to investigate an incident that occurred sometime in the last hour, you can select Today, but a better option is Last 60 minutes.
(shortcuts) button to restrict the search to one of the preset time ranges. For example, to investigate an incident that occurred sometime in the last hour, you can select Today, but a better option is Last 60 minutes.
 icon.
icon.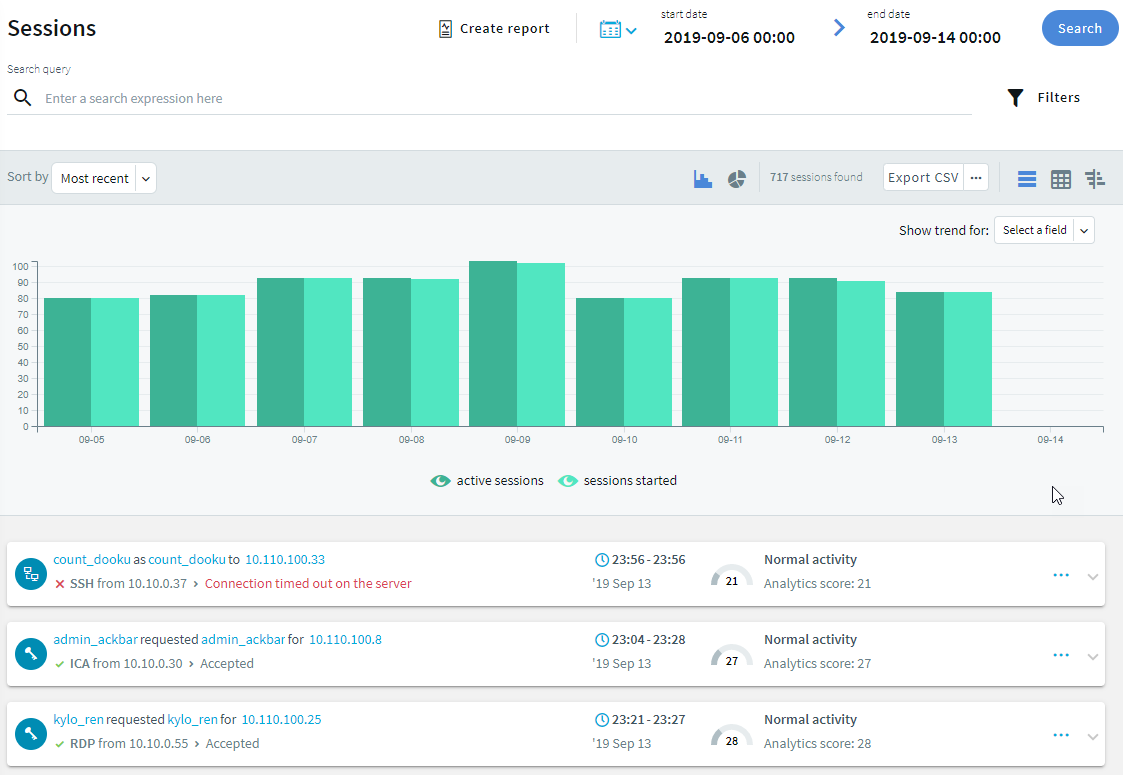
 . To disable the started sessions and view only the active sessions in the timeline, click
. To disable the started sessions and view only the active sessions in the timeline, click  .
.
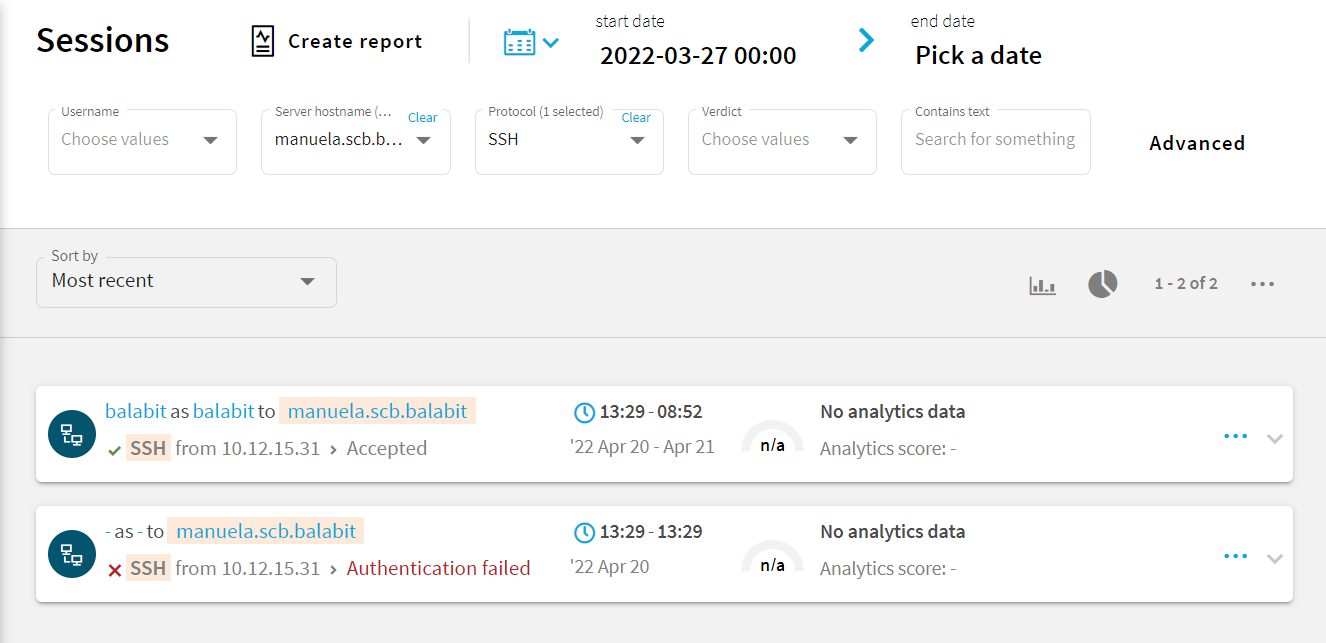
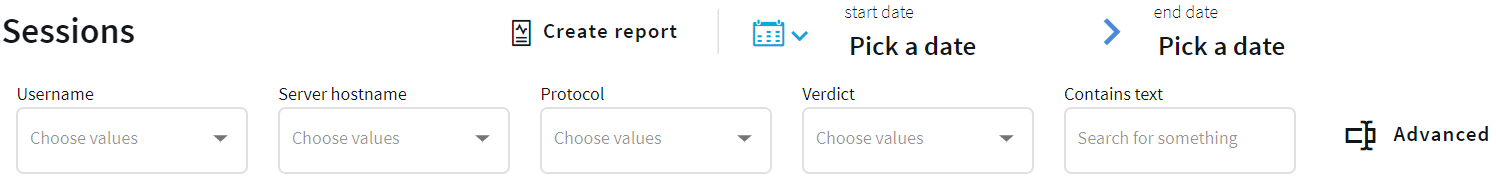
 and set the filters you need from the appropriate columns. For example, to search for a specific username, select it using the drop-down menu of the Username column. For a more generic search, you can enter any text in the Contains text column.
and set the filters you need from the appropriate columns. For example, to search for a specific username, select it using the drop-down menu of the Username column. For a more generic search, you can enter any text in the Contains text column.