Detailed information about this topic
The goal of this topic is to proactively manage disk capacity as it relates to Safeguard Privilege Manager for Windows. The capacity planning information provided here contains steps to help understand, install, and configure the Safeguard Privilege Manager for Windows database environment.
Eighty percent of database issues deal with disk capacity problems and in many cases, they are caused by failure to adhere to best practices. Failure to adhere to best practices should never happen as these issues are very predictable and could be prevented with a comprehensive database plan.
This section gives you a breakdown of the Safeguard Privilege Manager for Windows database structure to better understand the database environment and walks through capacity planning best practices to minimize the risk of disk over- utilization.
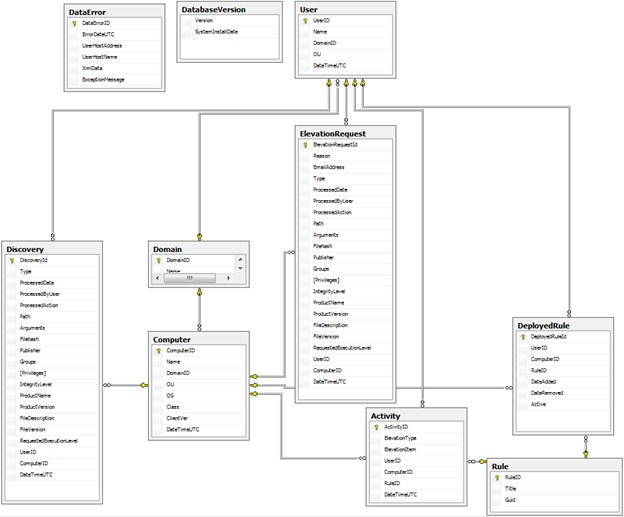
Figure 2: Safeguard Privilege Manager for Windows Database Diagram
|
1 |
4.7 MB |
9.4 MB |
|
10 |
10.5 MB |
21.0 MB |
|
100 |
73.0 MB |
146.0 MB |
|
1,000 |
692.6 MB |
1385.2 MB |
|
2,000 |
1,378.6 MB |
2,757.2 MB |
|
5,000 |
3,439.9 MB |
6,879.8 MB |
|
10,000 |
6,876.4 MB |
13,752.8 MB |
|
15,000 |
10,313.0 MB |
21,626.0 MB |
|
20,000 |
13,749.5 MB |
27,498.0 MB |
|
50,000 |
34,368.8 MB |
68,736.0 MB |
|
100,000 |
68,734.2 MB |
137,468.4 MB |
Table 1: Table size estimate for one Safeguard Privilege Manager for Windows user
|
Activity |
1,000 |
4,222.68 |
422,268.00 |
|
Computer |
1 |
84.38 |
84.38 |
|
DatabaseVersion |
1 |
72.09 |
72.09 |
|
DataError |
20 |
8,834.25 |
176,685.00 |
|
DeployedRules |
20 |
49.15 |
983 |
|
Discovery |
30 |
3,8049.23 |
1,141,476.9 |
|
Domain |
1 |
84.38 |
84.38 |
|
ElevationRequest |
20 |
54,540.61 |
1,090,812.2 |
|
Reports_Scheduled |
10 |
4,575.25 |
45,752.50 |
|
Reports_SharedFiles |
10 |
9,436.70 |
94,367.0 |
|
Rule |
20 |
304.99 |
6,099.8 |
|
User |
1 |
4,443.48 |
4,443.48 |
|
Total Size 4,683,128.73 bytes |
As the number of users grow, some tables increase in size more rapidly than others. For this reason, the database size does not grow proportionately.
Database size calculation uses the following rules:
-
The Activity table generates one thousand records per user.
-
The number of Computer records are equal to the number of user records.
-
20 reports represent one user.
-
The DatabaseVersion table should be one record irrespective of the number of user in the environment.
-
The DataError table is estimated to be twenty records to one user.
-
The DeployedRules table should generate twenty records per one user.
-
The Discovery table should generate roughly thirty records per user.
-
The number of Domain table records are set to one per user.
-
Twenty ElevationRequest records are generated per user.
-
There are ten Reports_Scheduled records per user.
-
There are ten Reports_SharedFilters per user.
-
Twenty Rule records are generated per user.
-
One user record exists in the User table per user.
Table 2: Database size for multiple users
|
1 |
4.7 MB |
|
10 |
10.5 MB |
|
100 |
73.0 MB |
|
1,000 |
692.6 MB |
|
2,000 |
1,378.6 MB |
|
5,000 |
3,439.9 MB |
|
10,000 |
6,876.4 MB |
|
15,000 |
10,313.0 MB |
|
20,000 |
13,749.5 MB |
|
50,000 |
34,368.8 MB |
|
100,000 |
68,734.2 MB |

